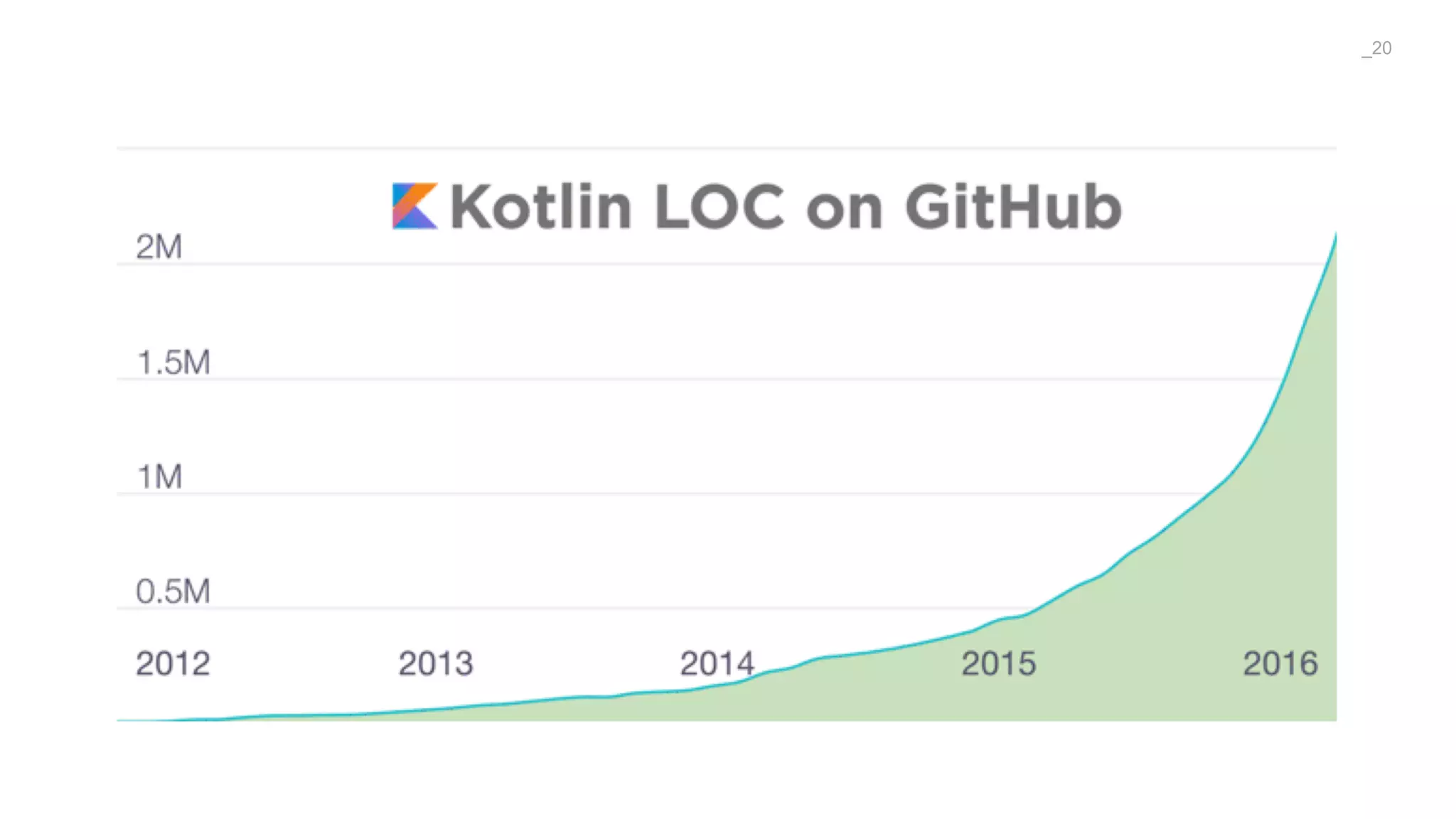
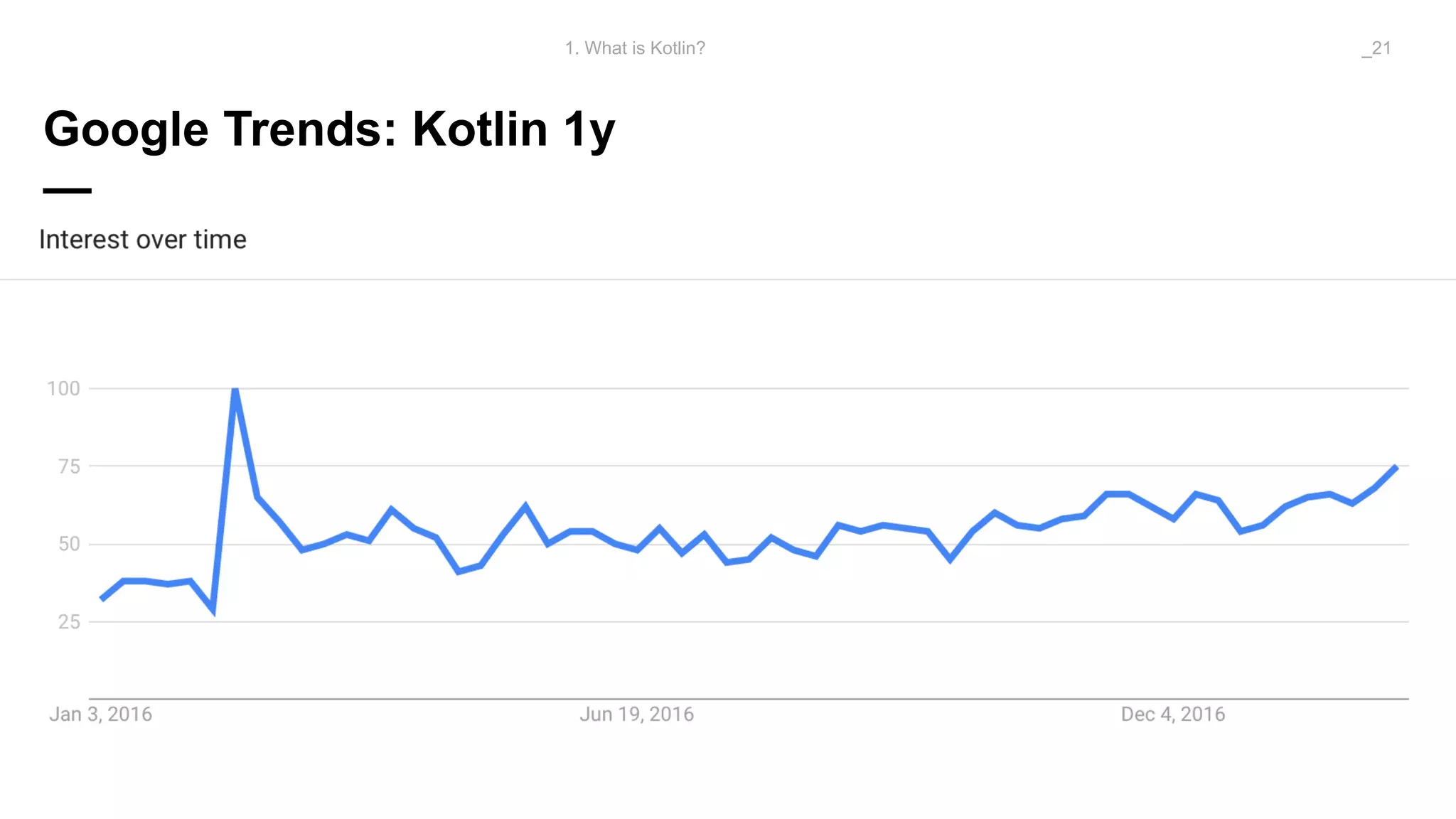
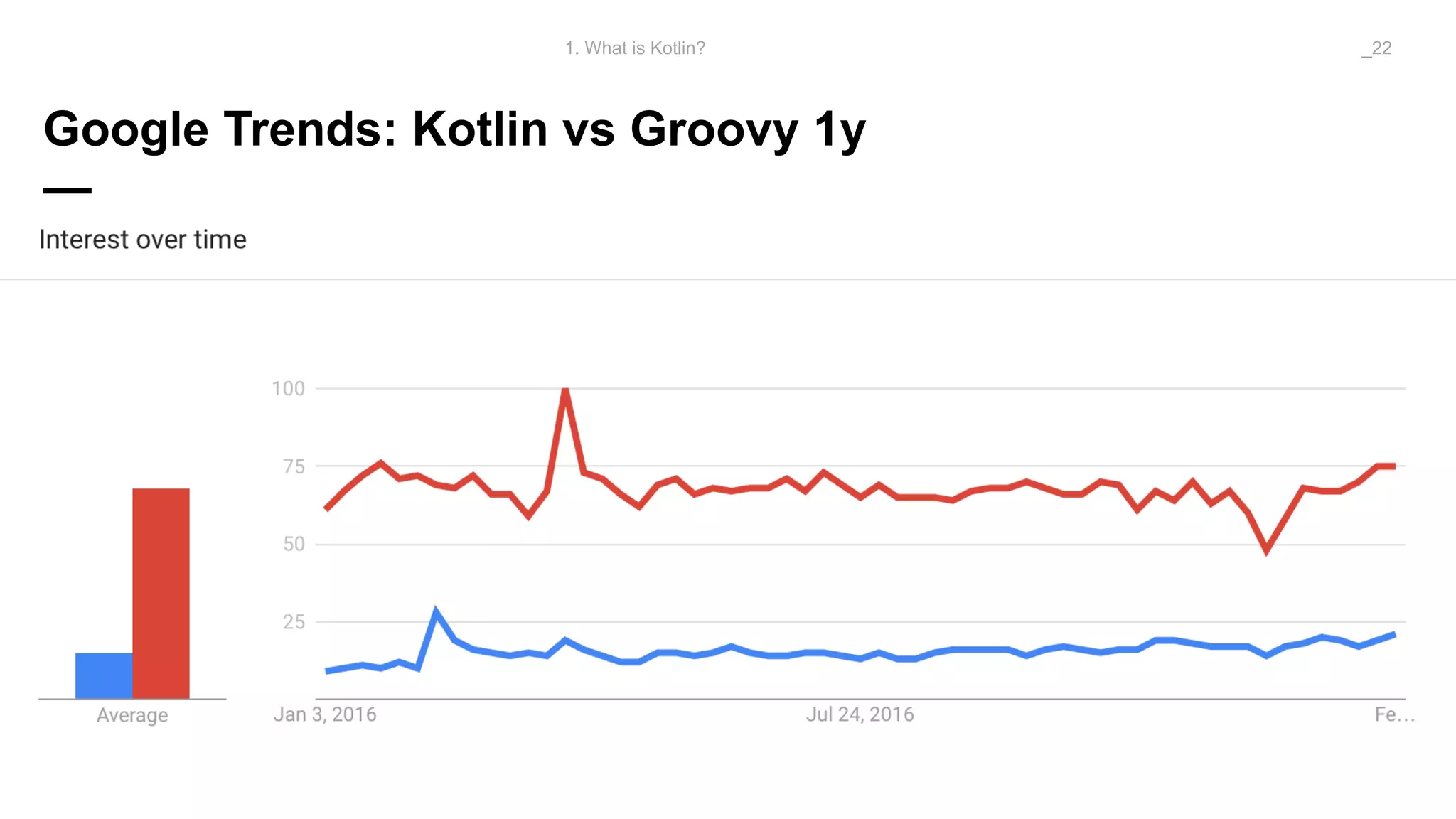
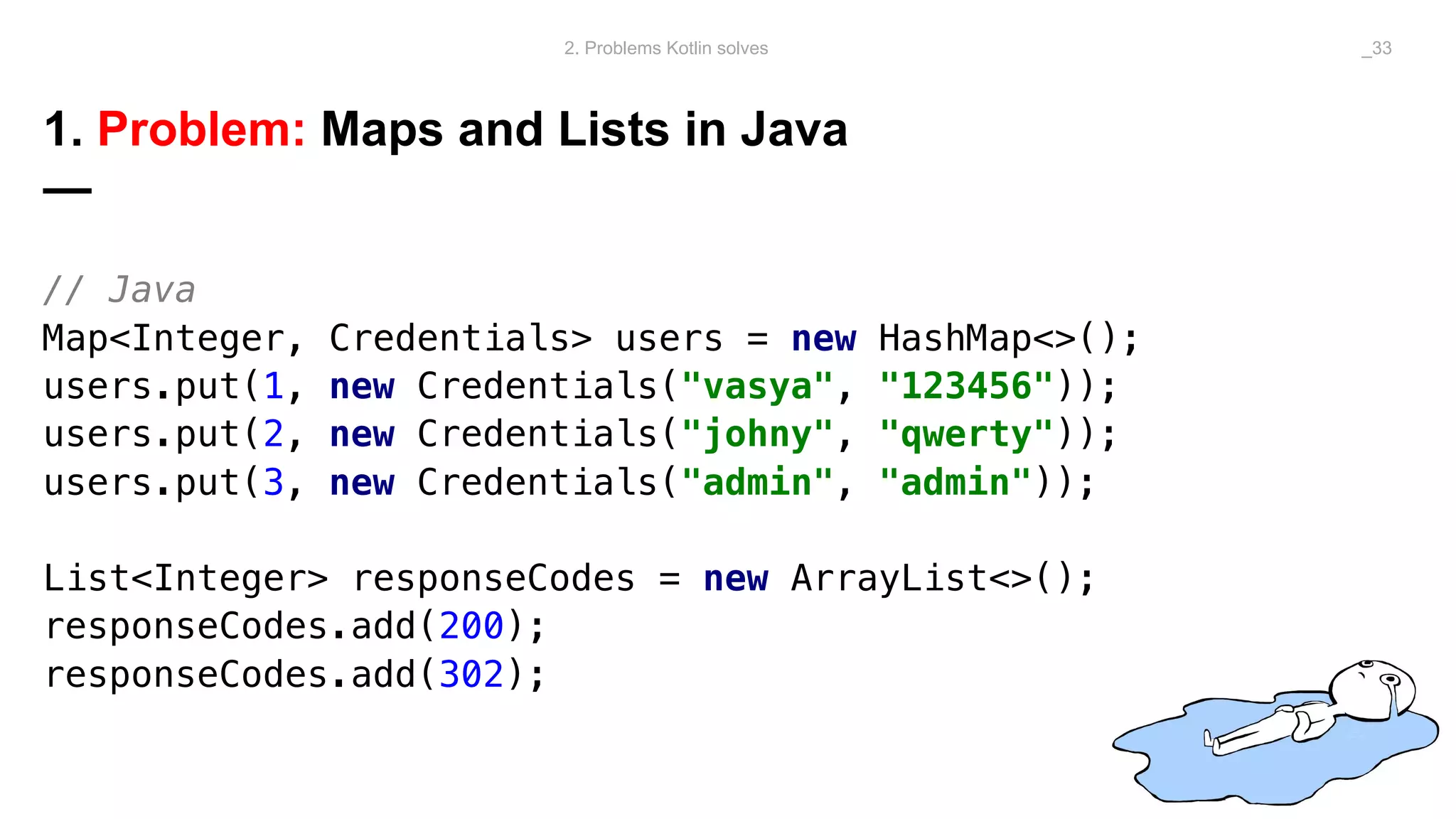
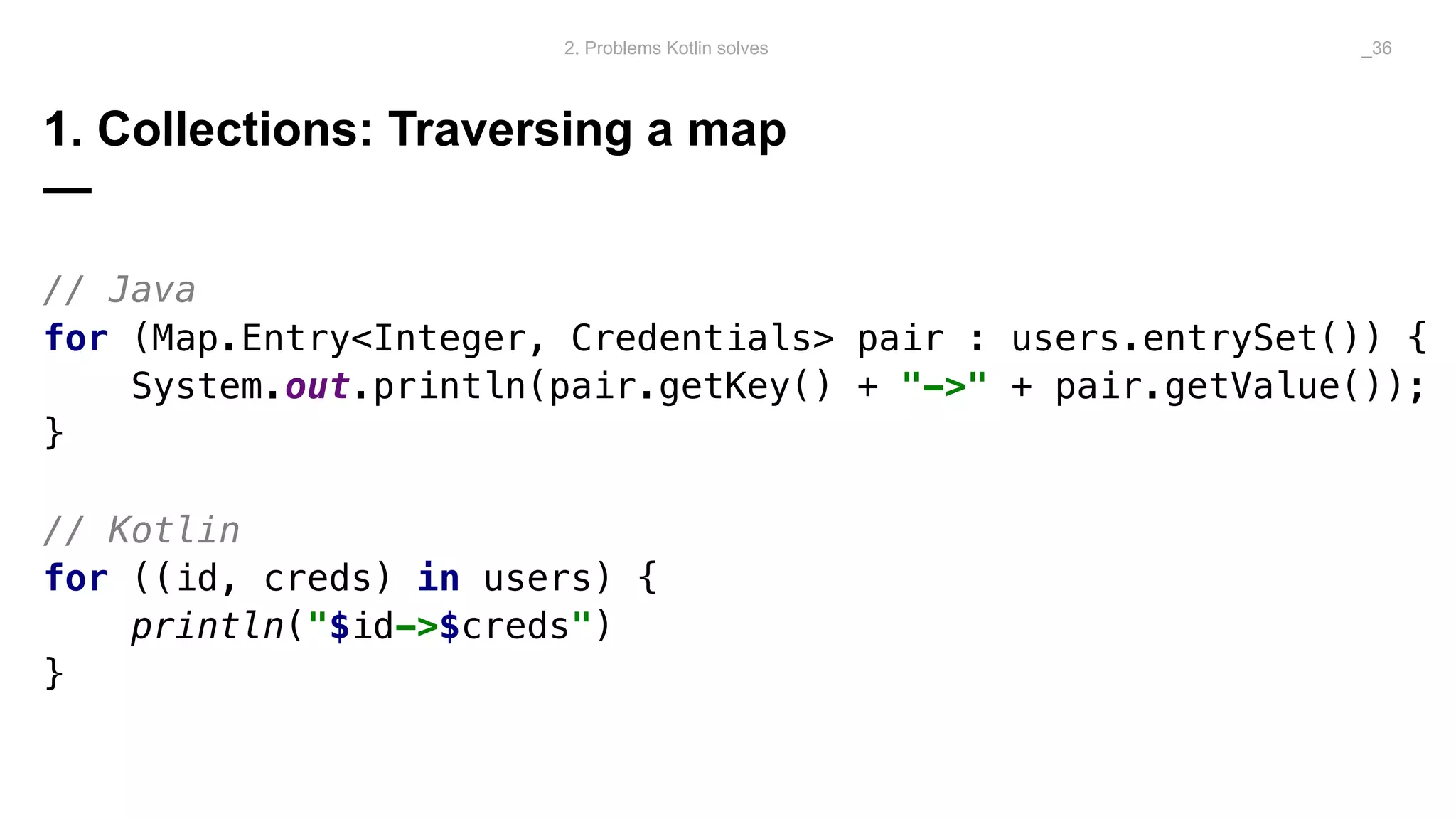
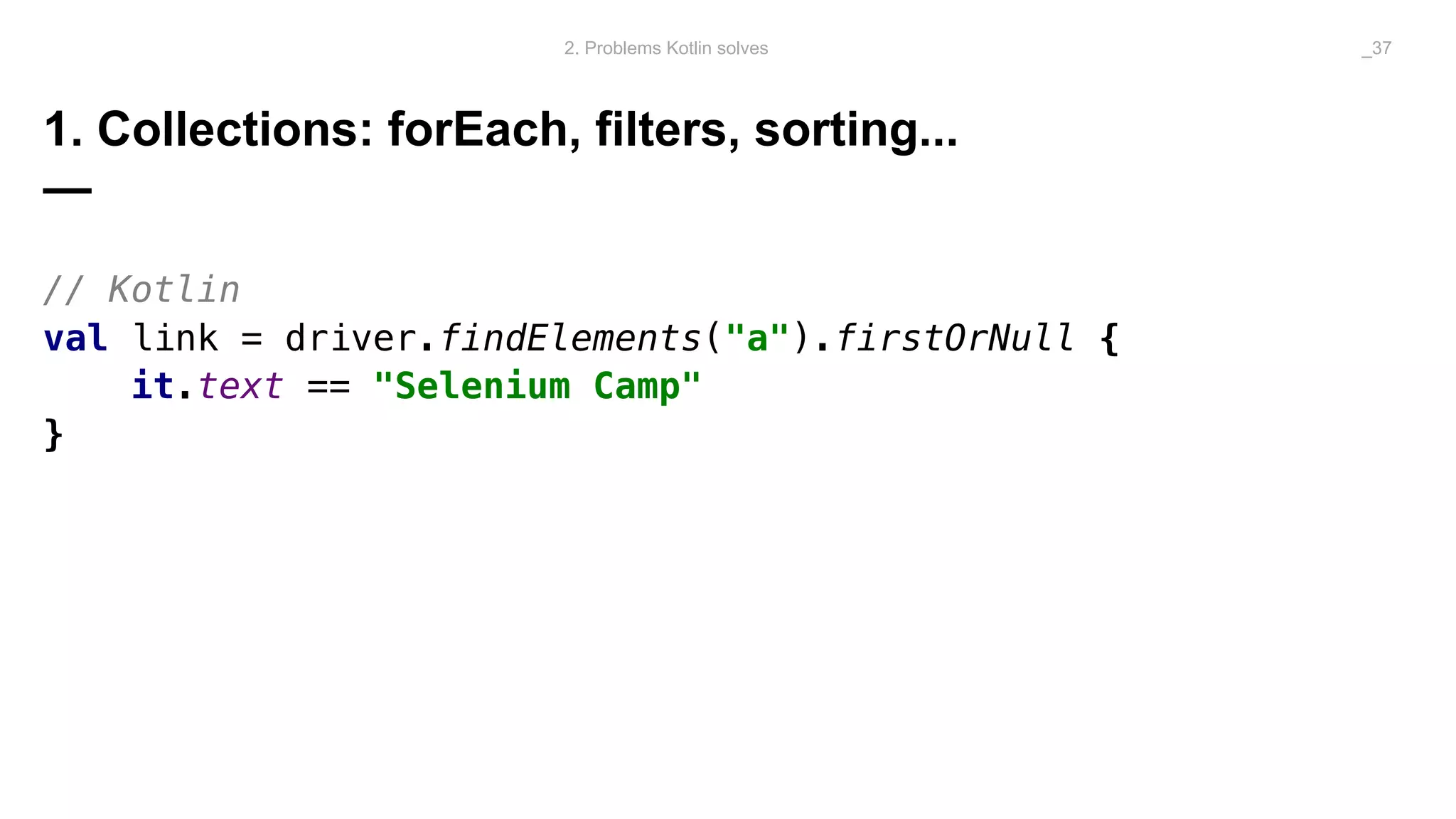
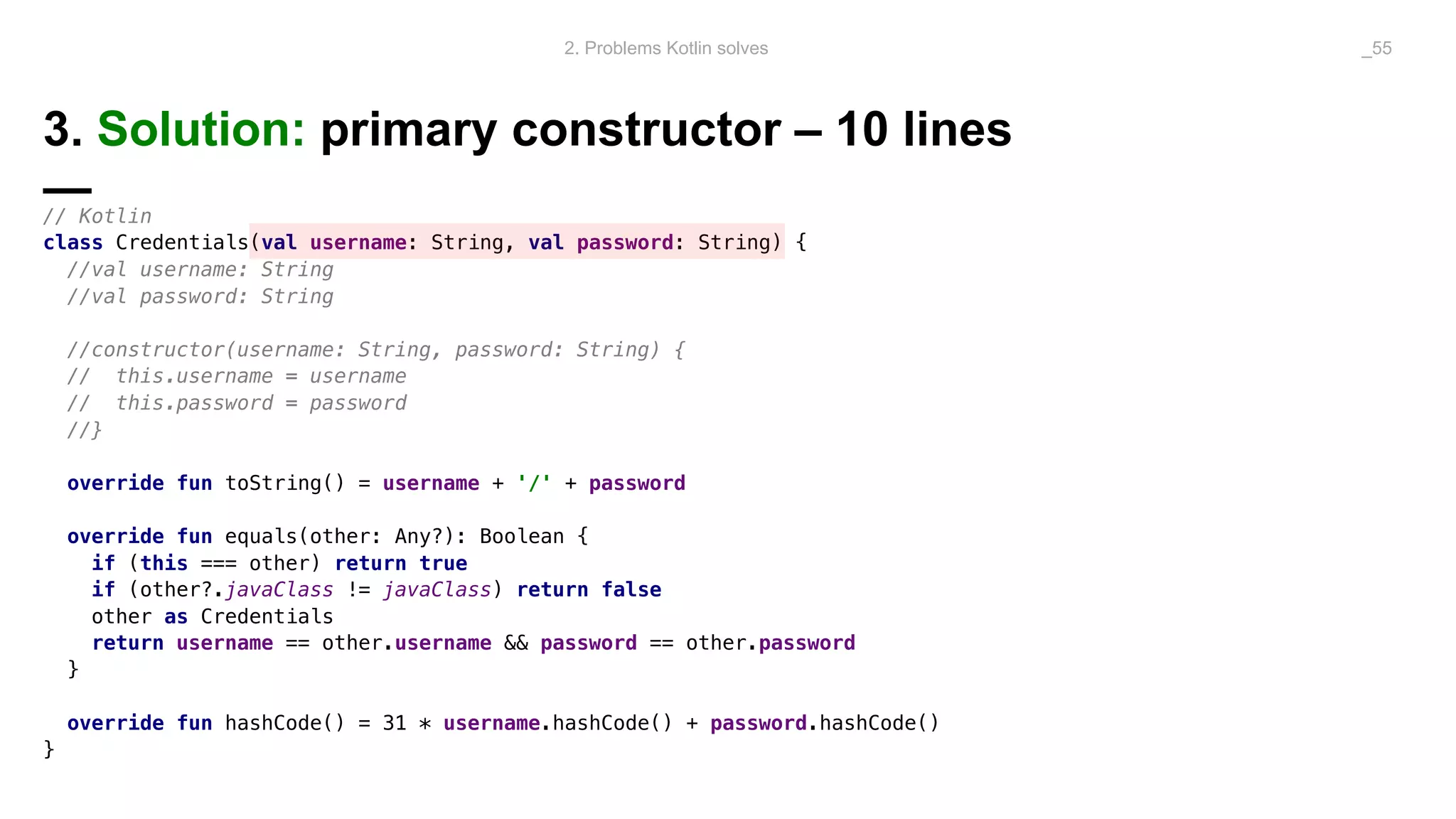
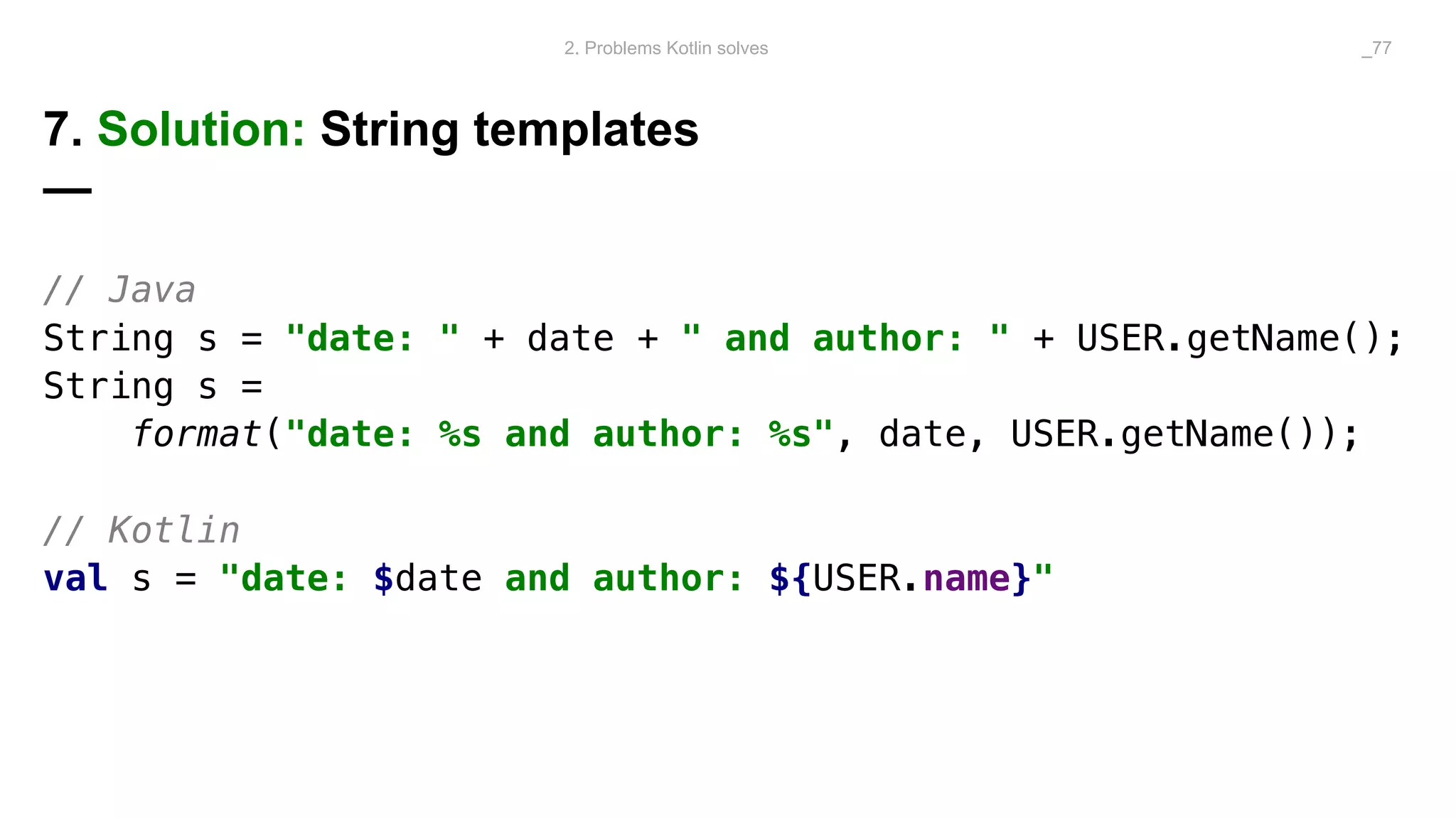
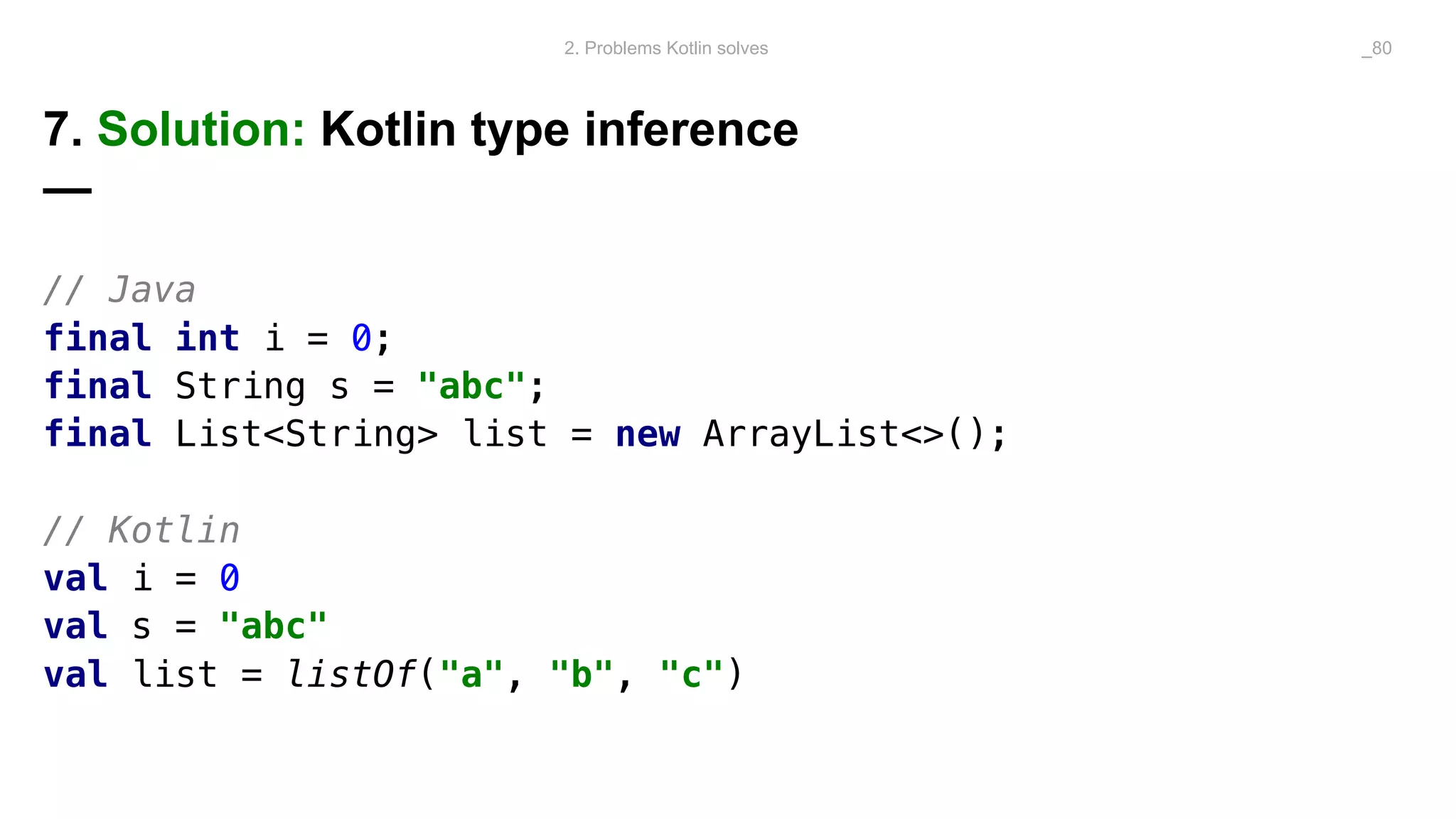
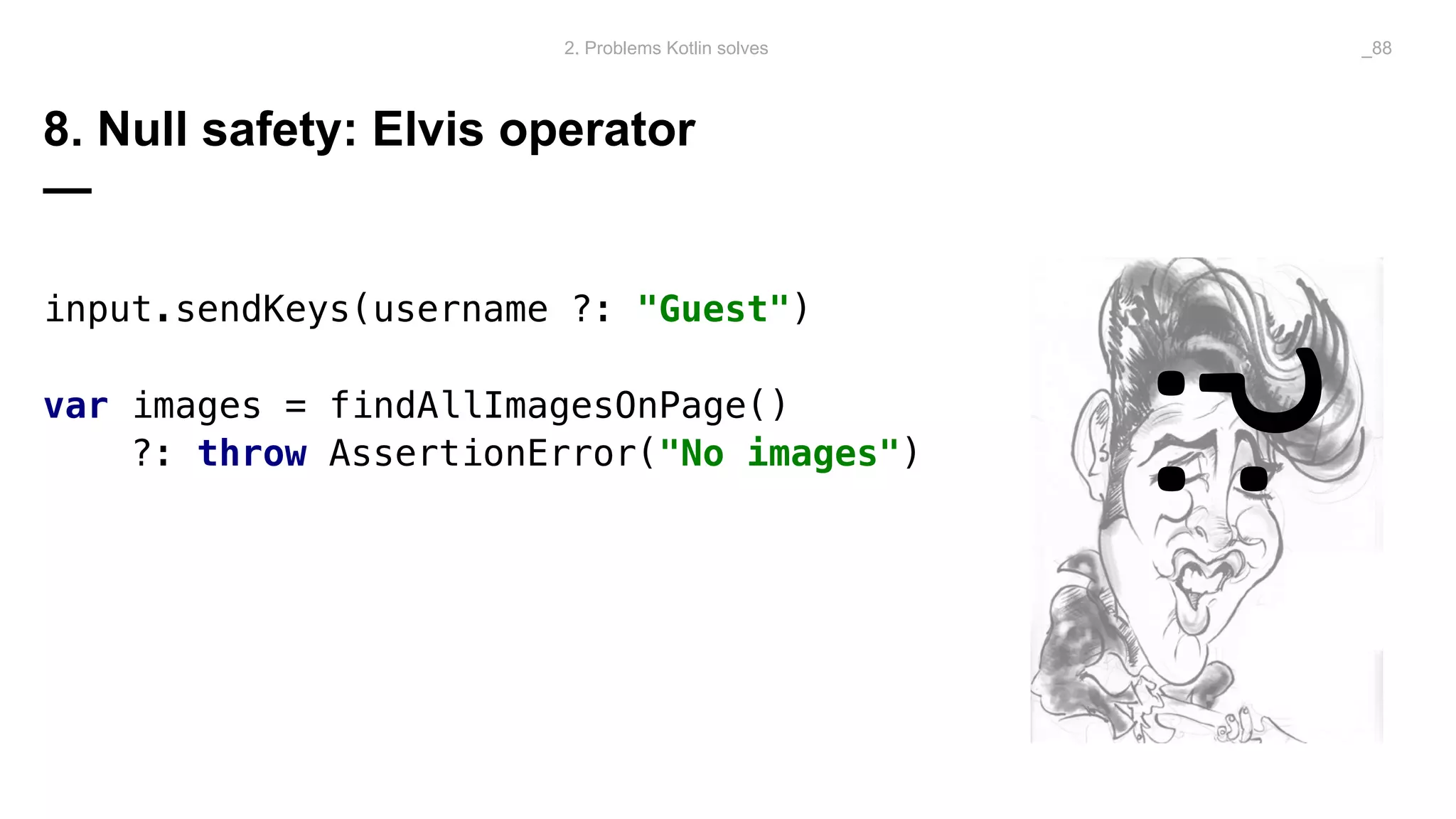
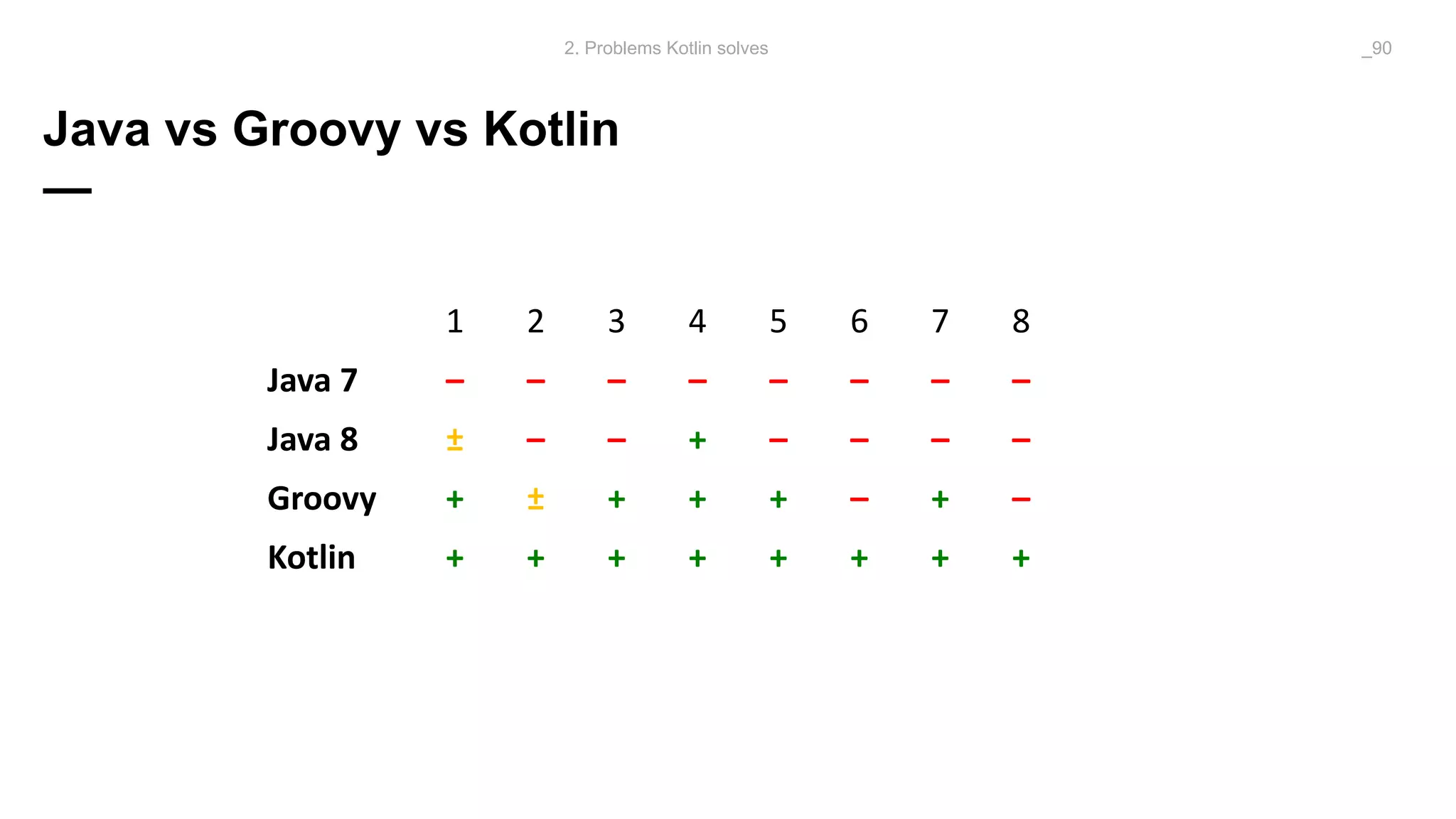
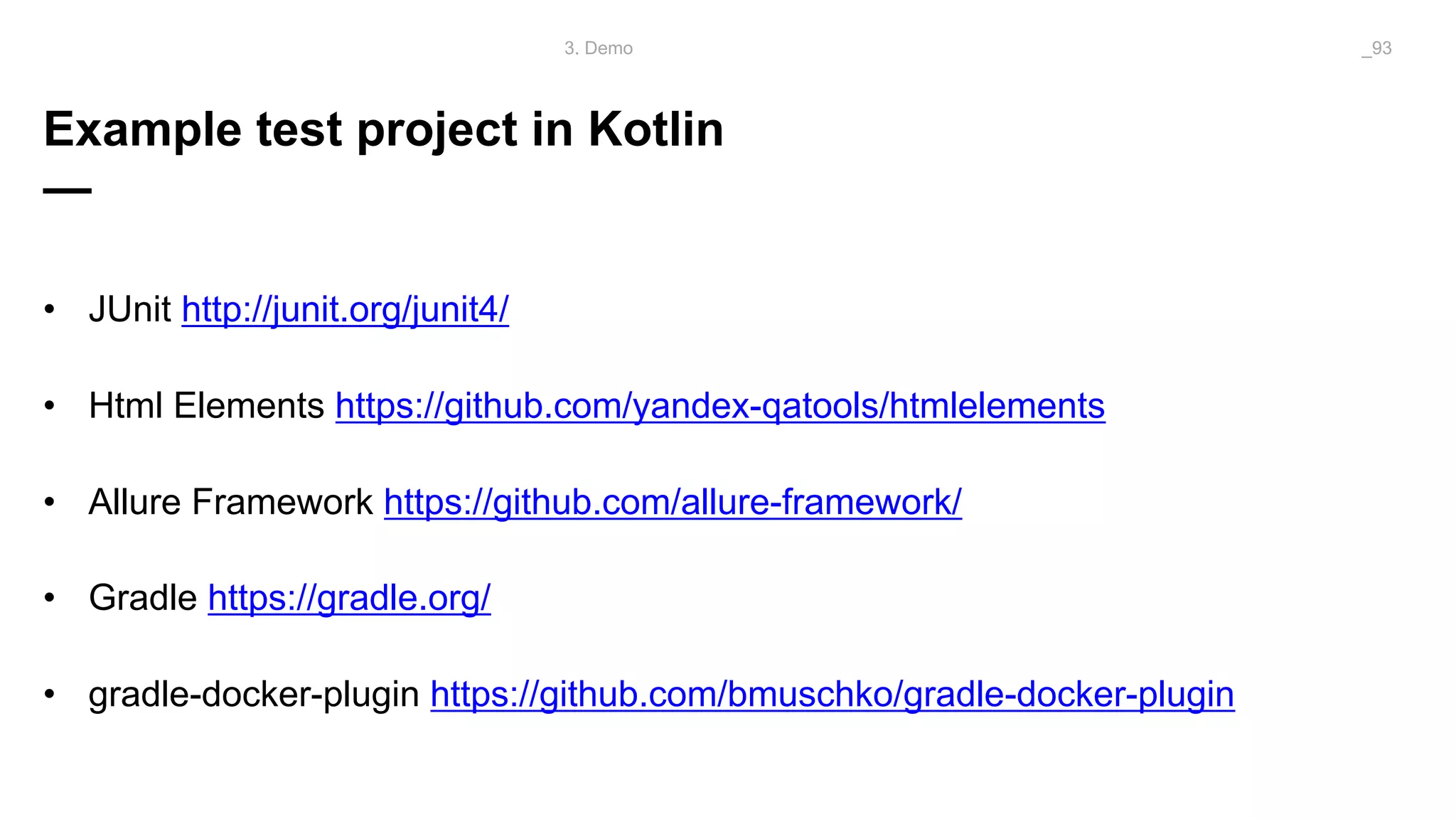
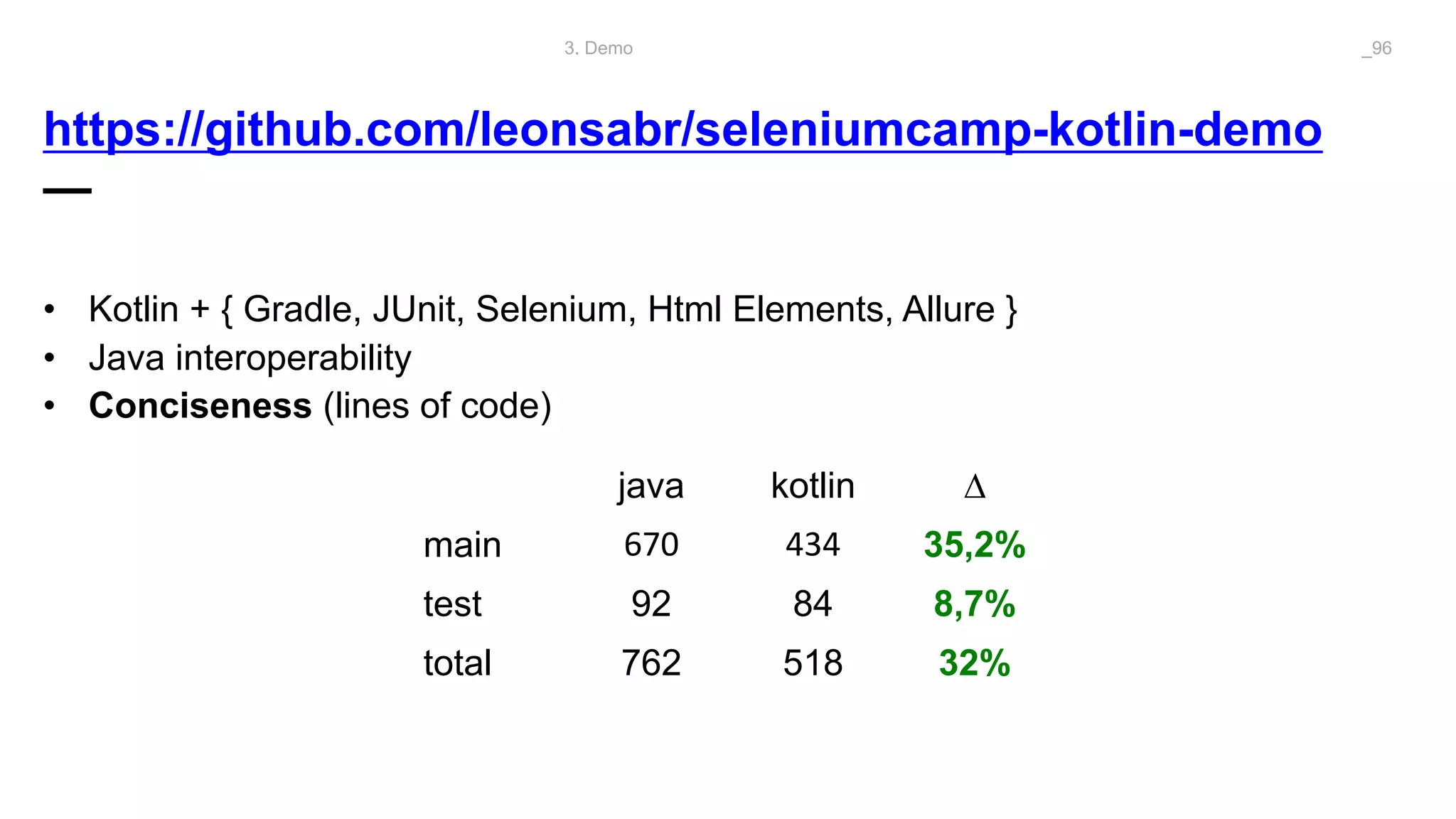
The document discusses problems solved by Kotlin for test automation. It summarizes Kotlin as a JVM language that is statically typed, multi-paradigm, pragmatic, safe, and concise. It then discusses problems Kotlin solves such as cleaner code for collections and maps, extension functions to add functionality, data classes to reduce boilerplate for small classes, and cleaner steps in Allure reports using lambda functions.