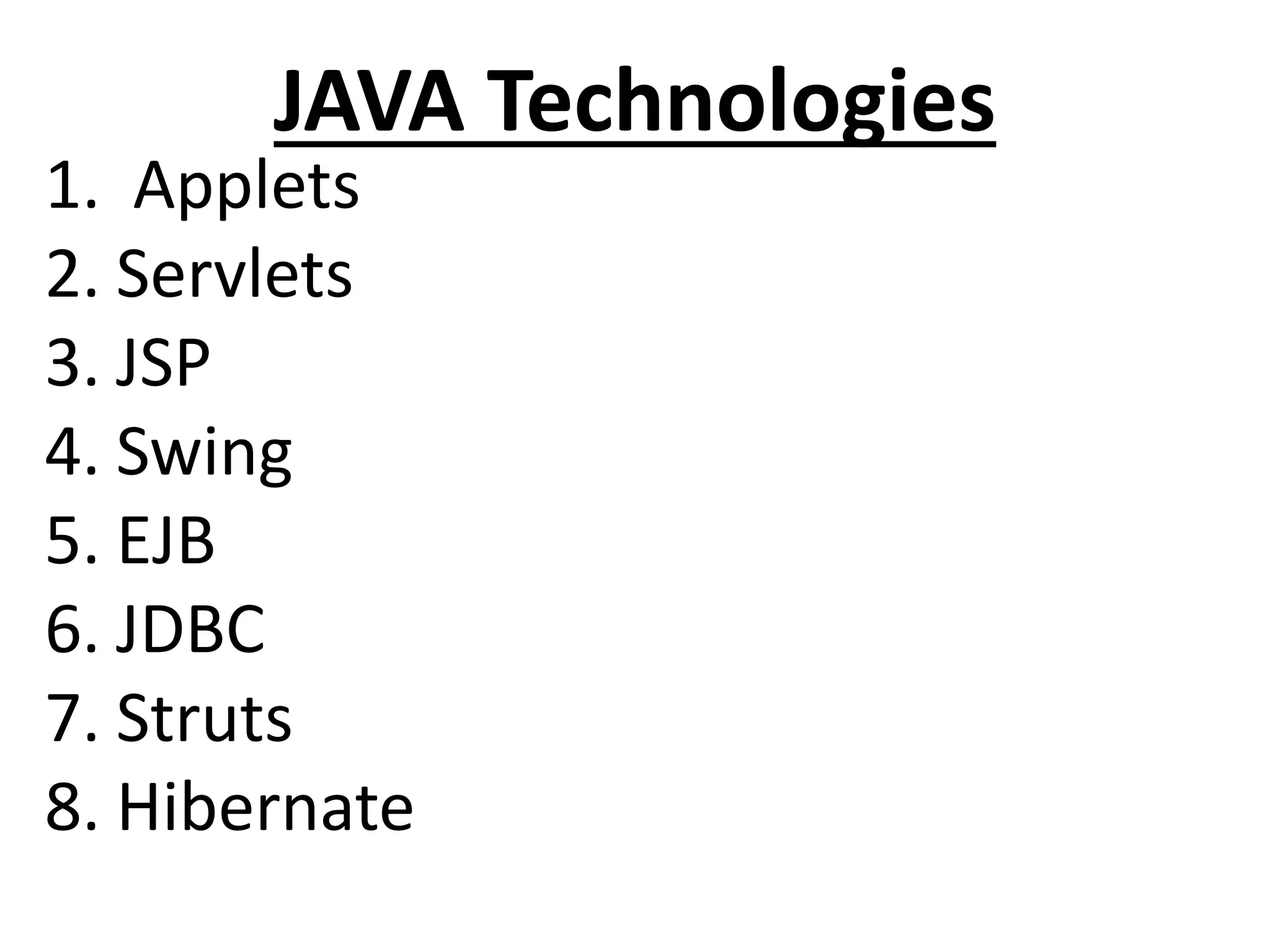
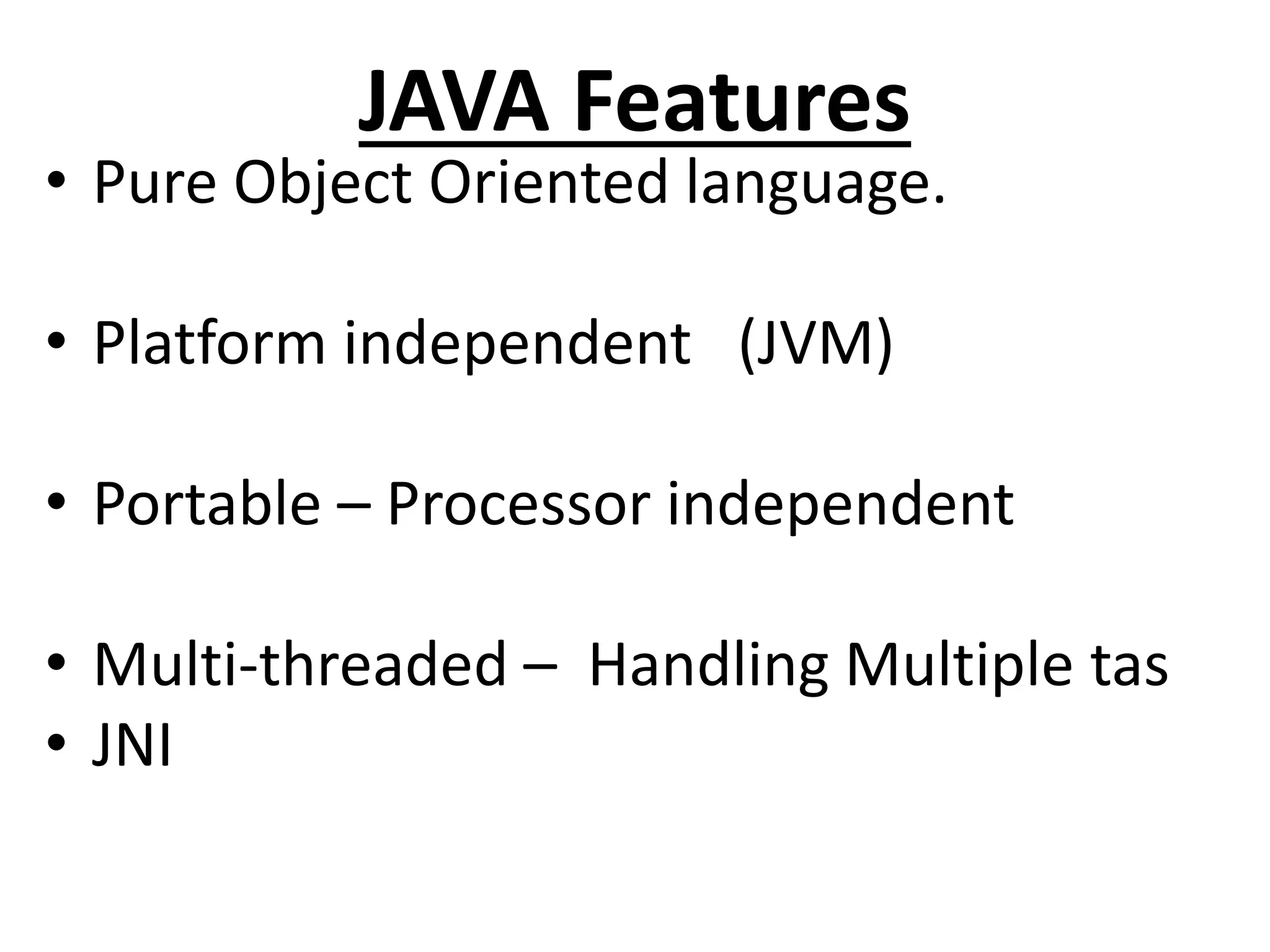
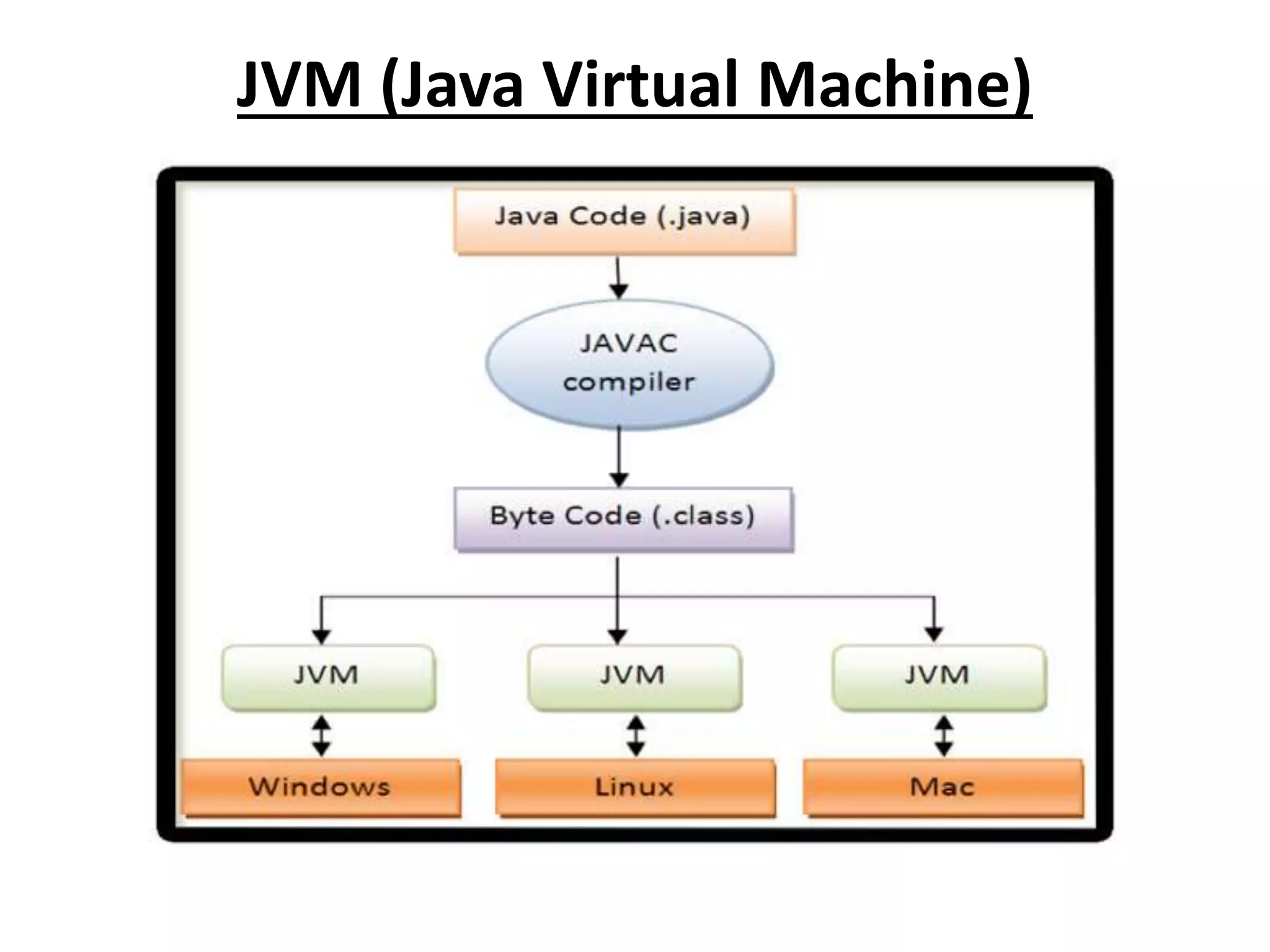
Java is an object-oriented programming language created by James Gosling. It was originally called Oak but was later renamed to Java. The document discusses the different editions of Java including J2SE, J2EE, and J2ME. It also covers key Java technologies like applets, servlets, JSP, and Swing. The document provides an overview of Java features such as being platform independent, portable, multi-threaded, and having a Java Virtual Machine. It also discusses concepts like inheritance, interfaces, packages, exceptions, and input/output in Java.



![Test.java
class Test
{
public static void main(String b[])
{
System.out.println(“Welcome”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-7-2048.jpg)

![Different name for java file and class
Sample.java
class Test
{
public static void main(String []a)
{
System.out.println(“Welcome”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-9-2048.jpg)



![import java.io.*;
class Test
{
public static void main(String []ar) throws Exception
{
int age;
DataInputStream d = new DataInputStream(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your Age");
age = Integer.parseInt(d.readLine());
System.out.println("Age:"+ age);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-13-2048.jpg)
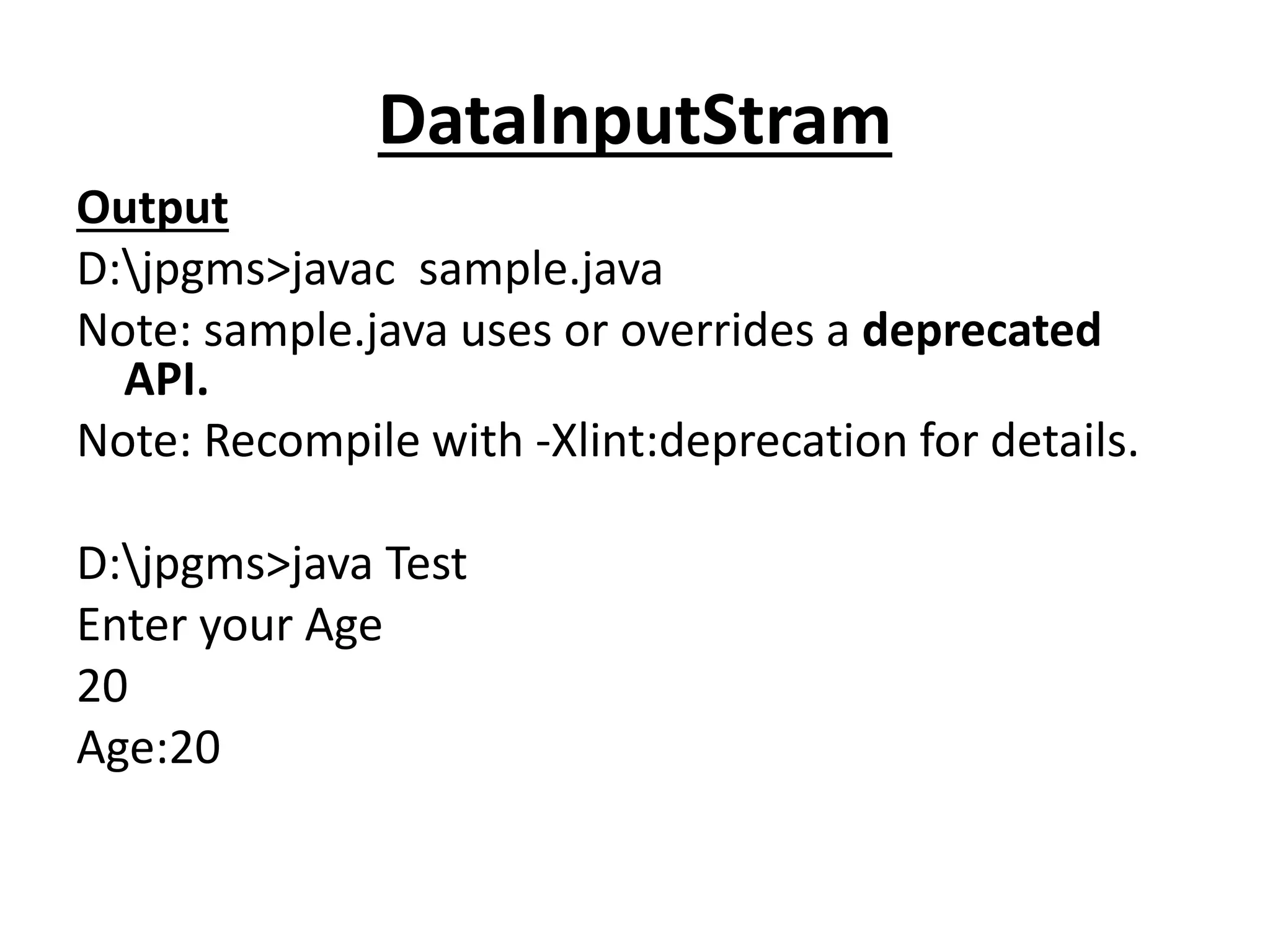
![import java.io.*;
class Test
{
public static void main(String []ar) throws Exception
{
int age;
BufferedReader d = new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Enter your Age");
age = Integer.parseInt(d.readLine());
System.out.println("Age:"+ age);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-15-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.Scanner;
class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your rollno");
int rno=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter your name");
String name=sc.next();
System.out.println("Rollno:"+rno);
System.out.println(" name:"+name);
sc.close();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-16-2048.jpg)

![Finally
Exception Handling
What is Exception? Runtime error
Eg:-
ArrayIndexoutofBounds Exception
int a = new int[10];
a[11]=123;
ClassNotFoundException](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-18-2048.jpg)

![import java.io.*; //for DataInputStream class
class Test
{
public static void main(String []ar) throws Exception
{
int age;
DataInputStream d = new DataInputStream(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your Age");
age = Integer.parseInt(d.readLine()); //IOException
System.out.println("Age:"+ age);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-20-2048.jpg)
![class Test
{
public static void main(String []ar)
{
try
{
int a=100,b=0,c;
c=a/b;
}
catch (Exception e) //ArithmeticException division by zero
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-21-2048.jpg)

![class Test
{
public static void main(String []ar)
{
try
{
int a=100,b=0,c;
c=a/b;
}
catch (Exception e) //ArithmeticException division by zero
{
System.out.println(e);
}
finally
{
System.out.println(“finally block”);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-23-2048.jpg)
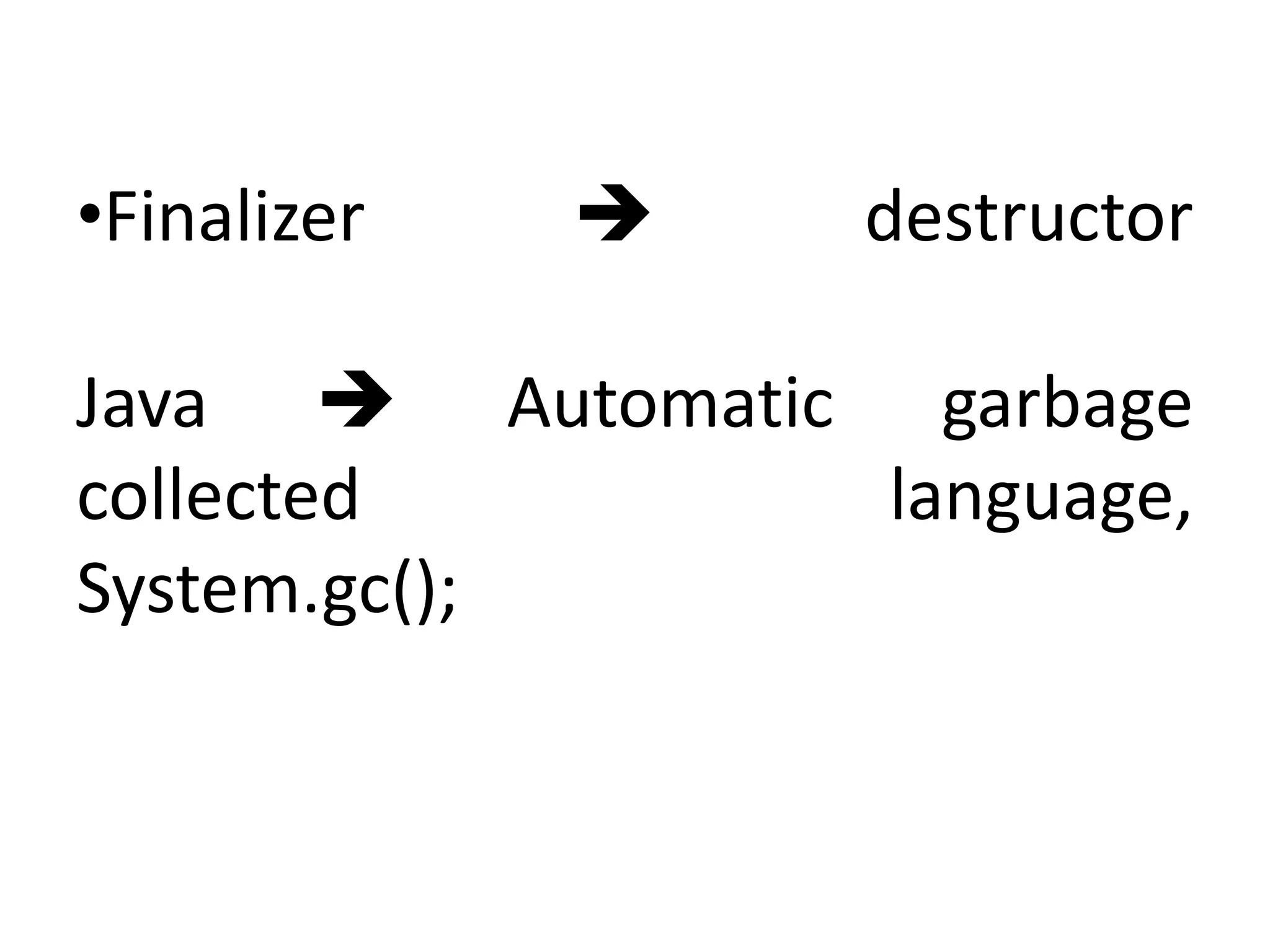
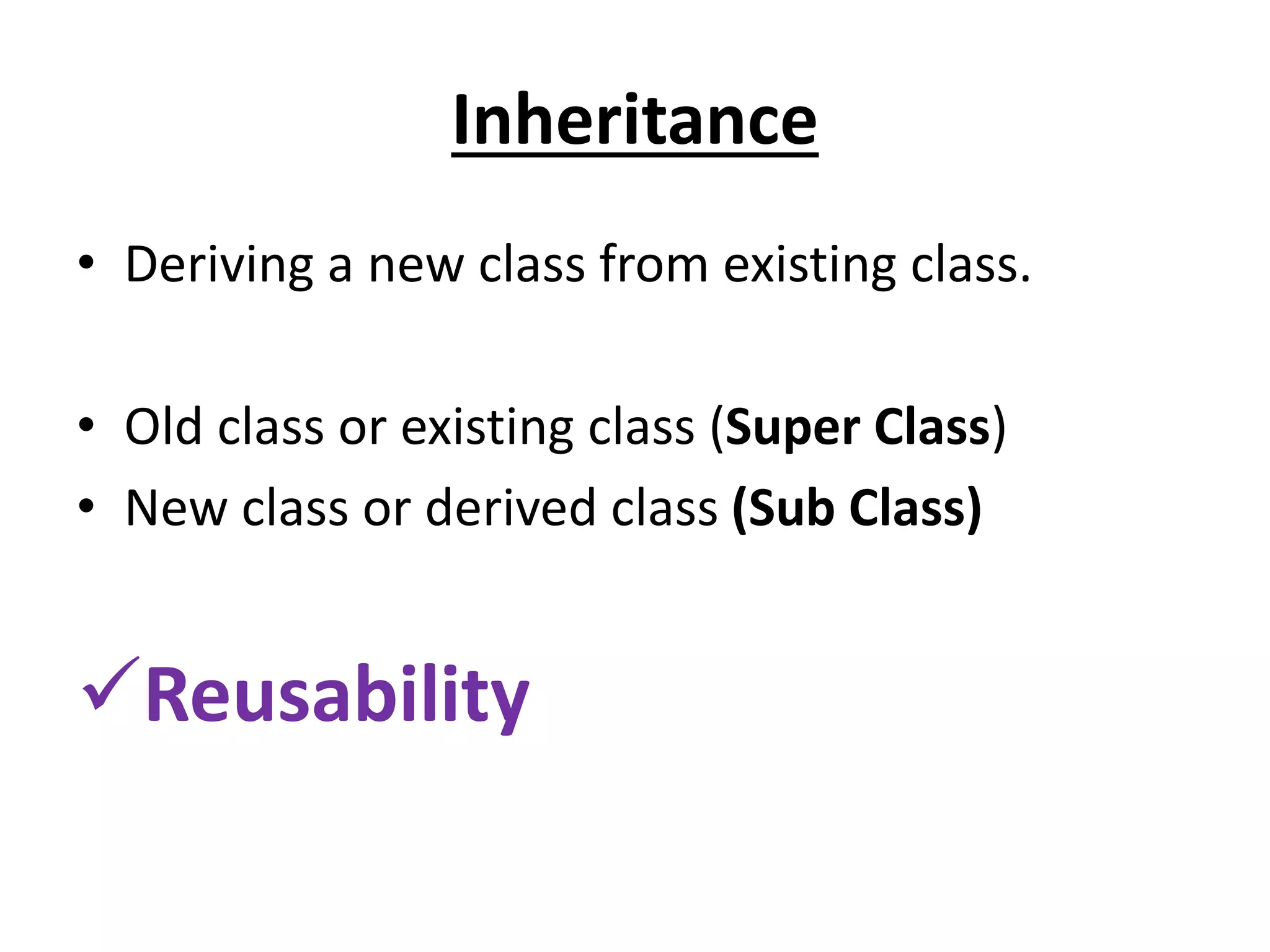
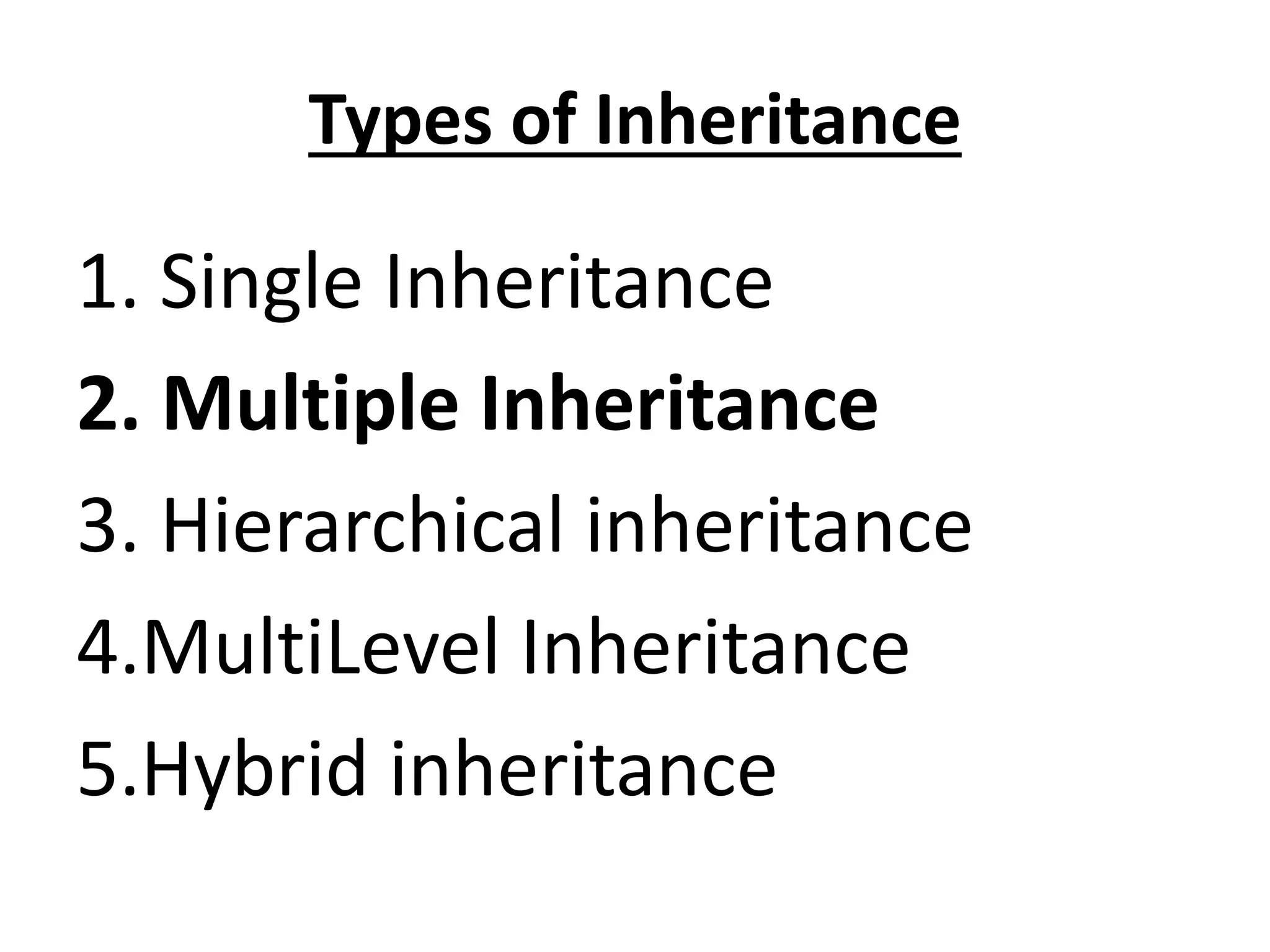
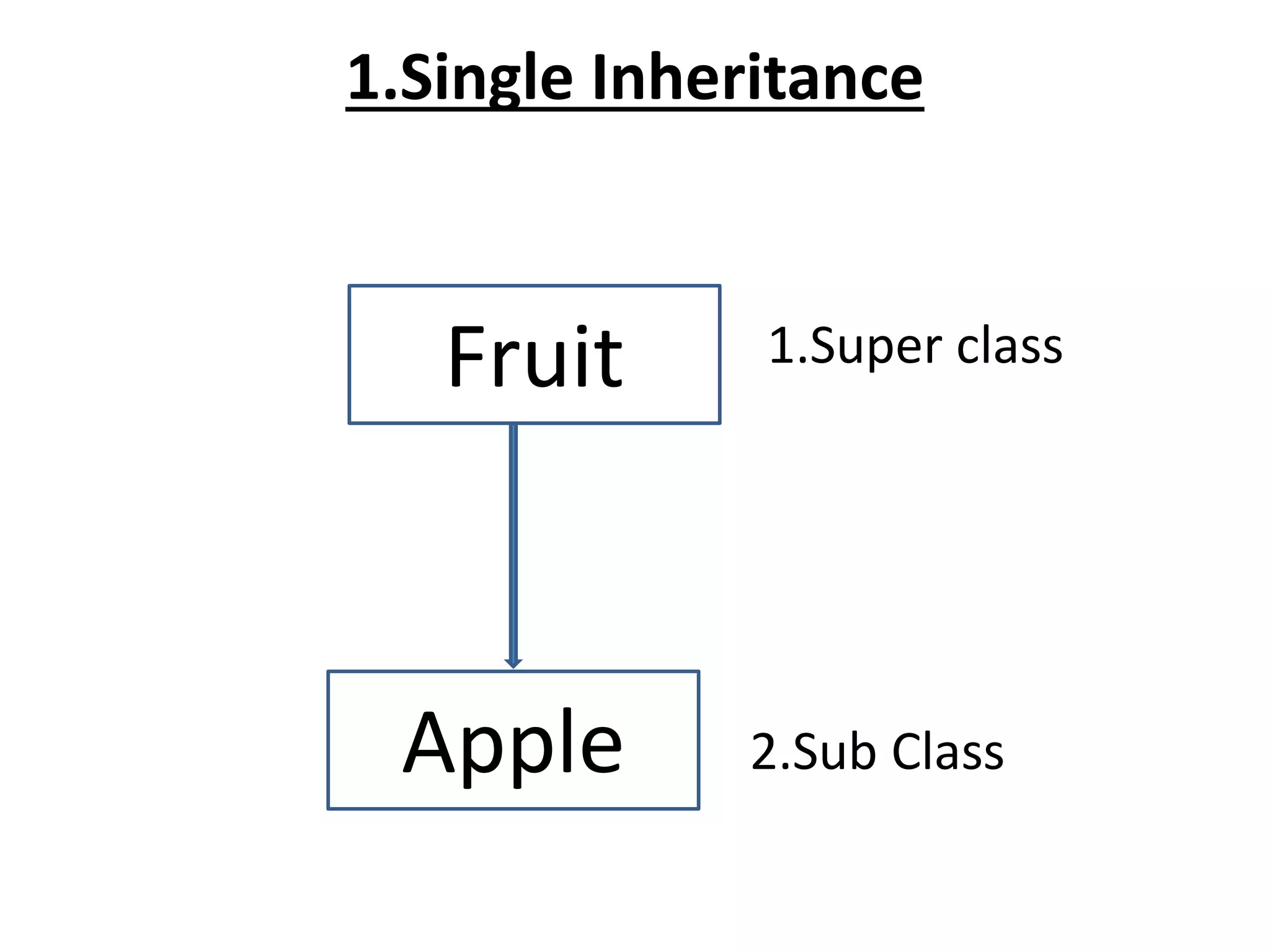
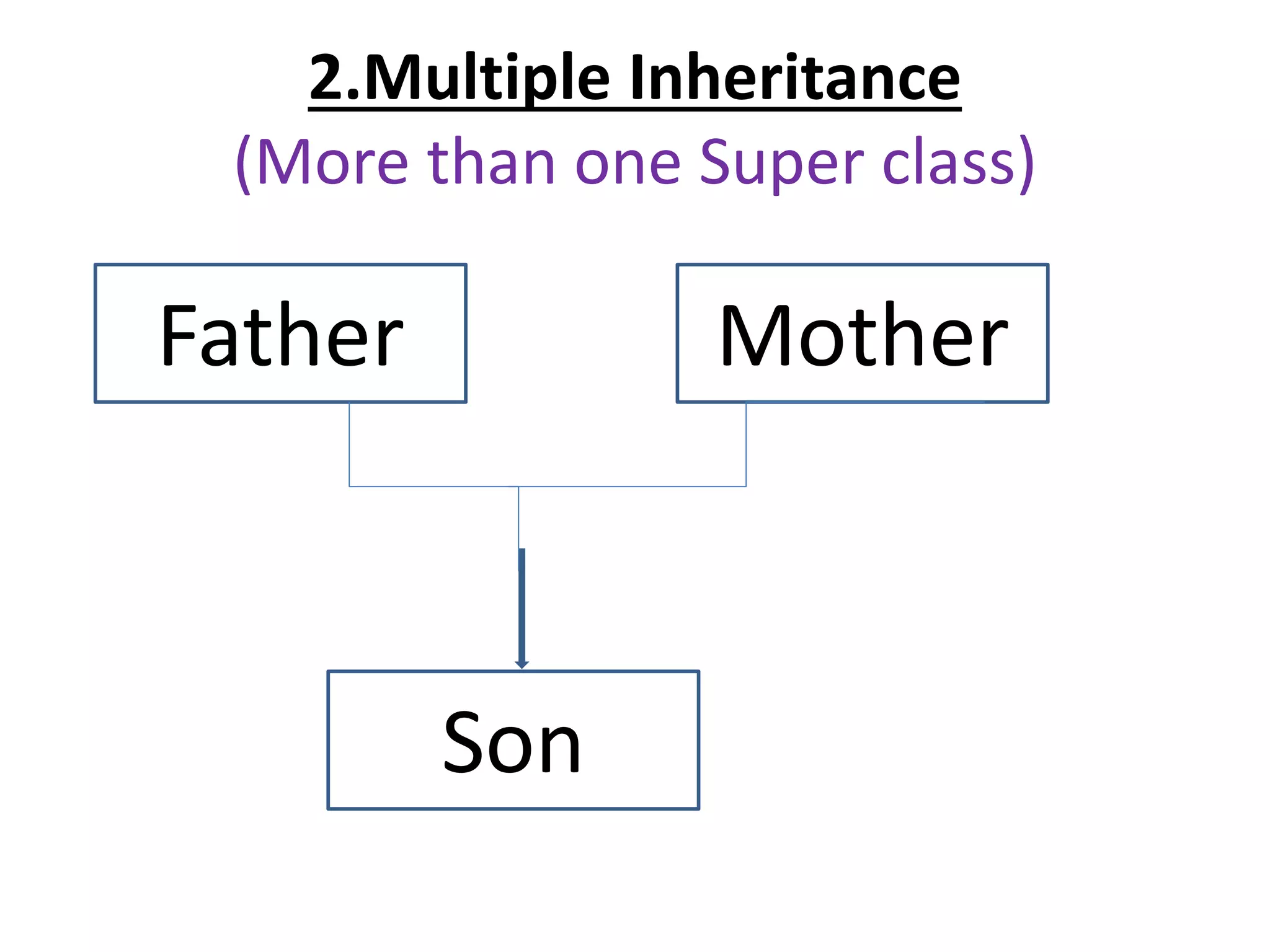

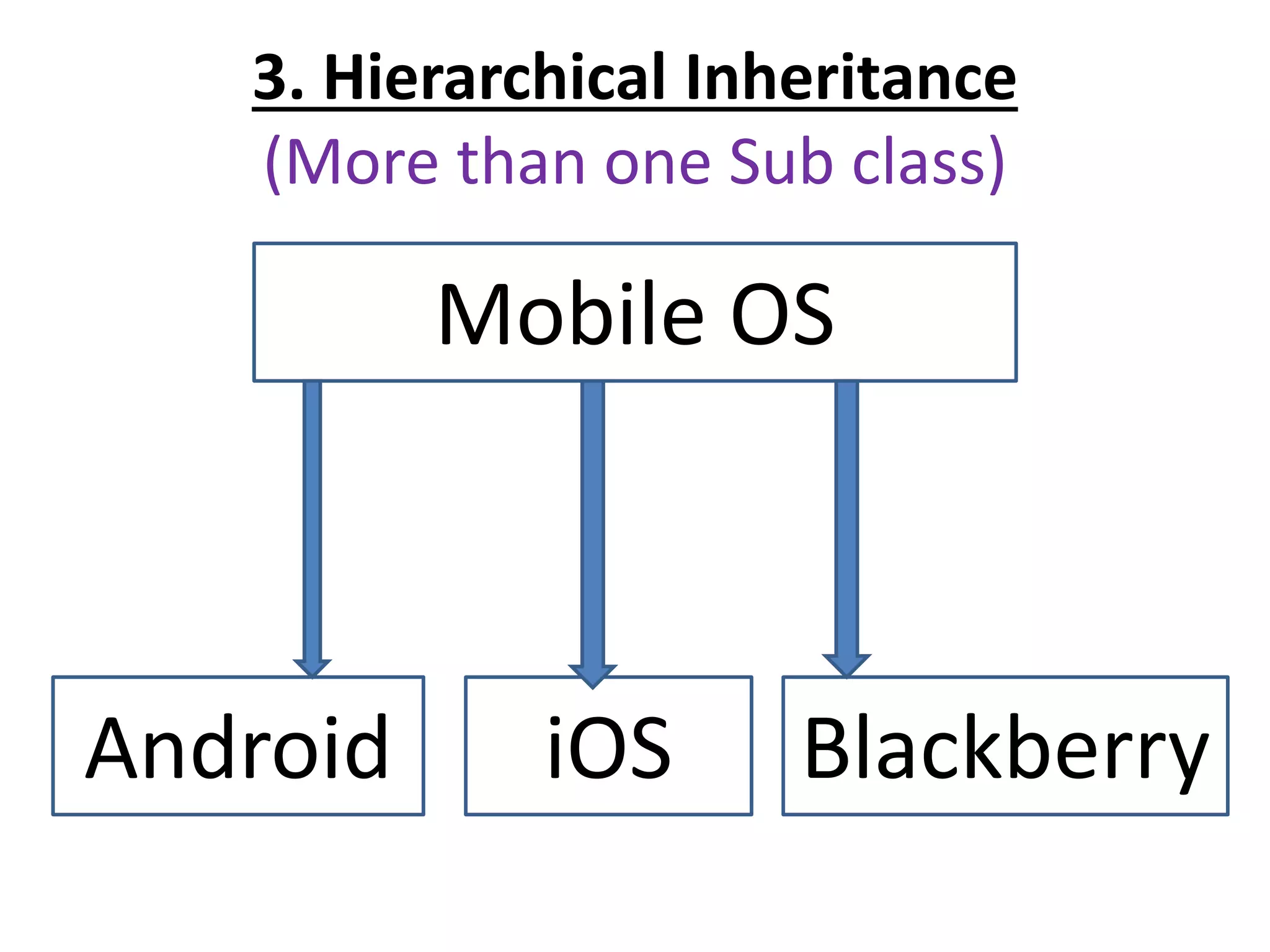
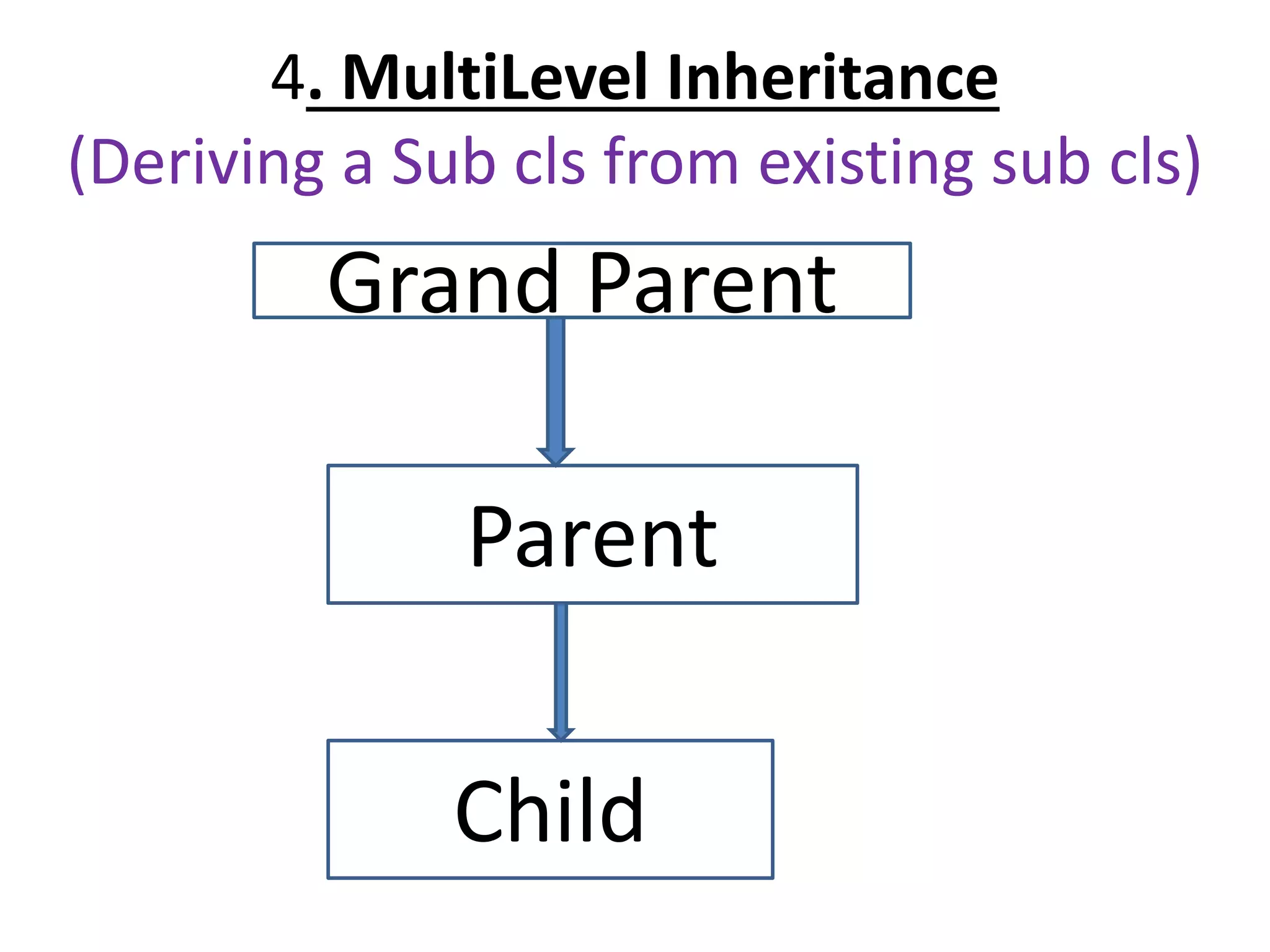
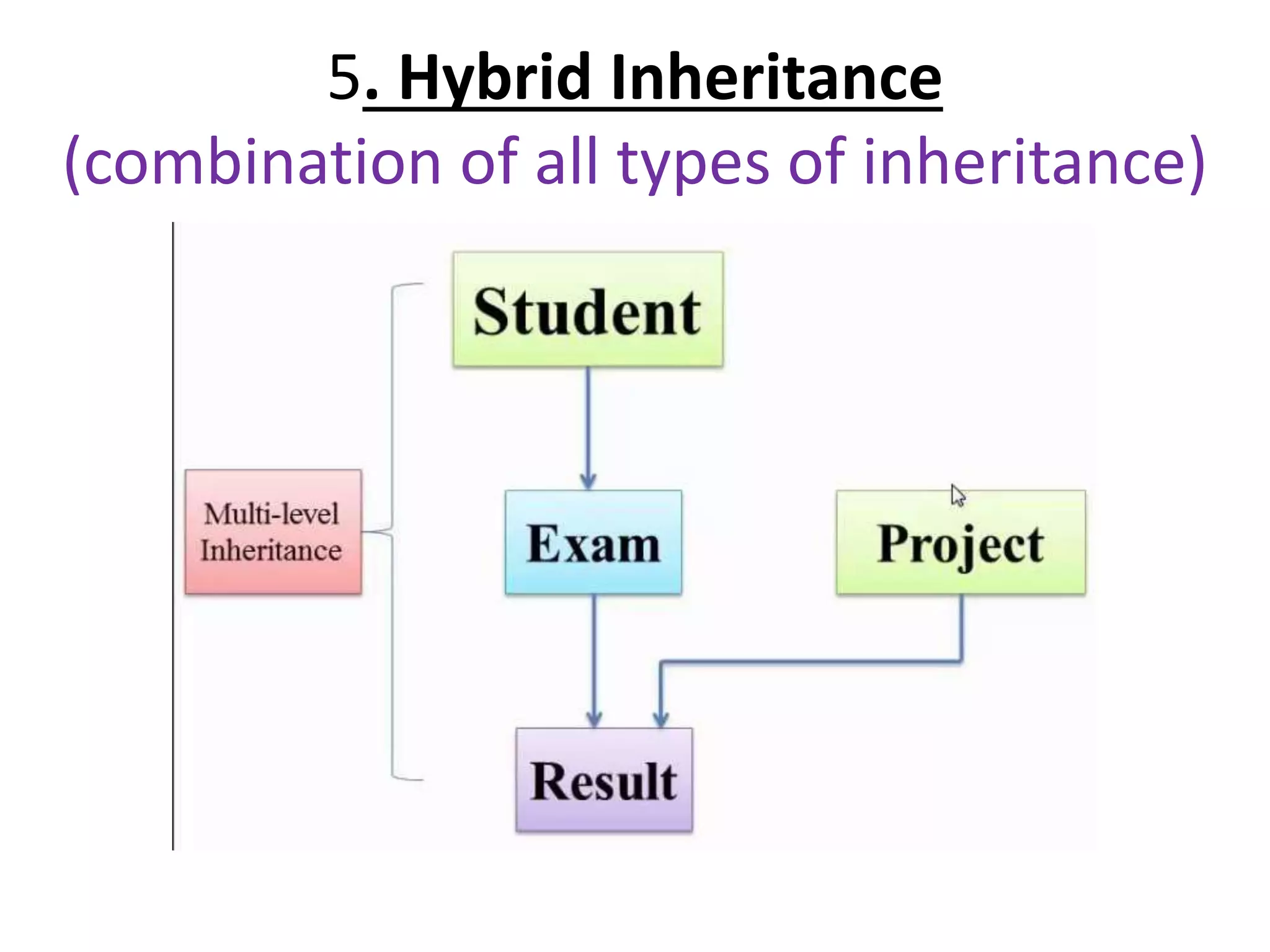
![Single Inheritance
class A
{
static int x=10;
static int y=20;
}
class B extends A
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int z=30;
int res=x+y+z;
System.out.println("Result:"+res);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-33-2048.jpg)
![class Shape
{ int l,b;
}
class Rectangle extends Shape
{
int a;
public int findArea()
{
a = l*b;
return (a);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
r.l = 10;
r.b = 20;
System.out.println("Area of rectangle is:" + r.findArea());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-34-2048.jpg)
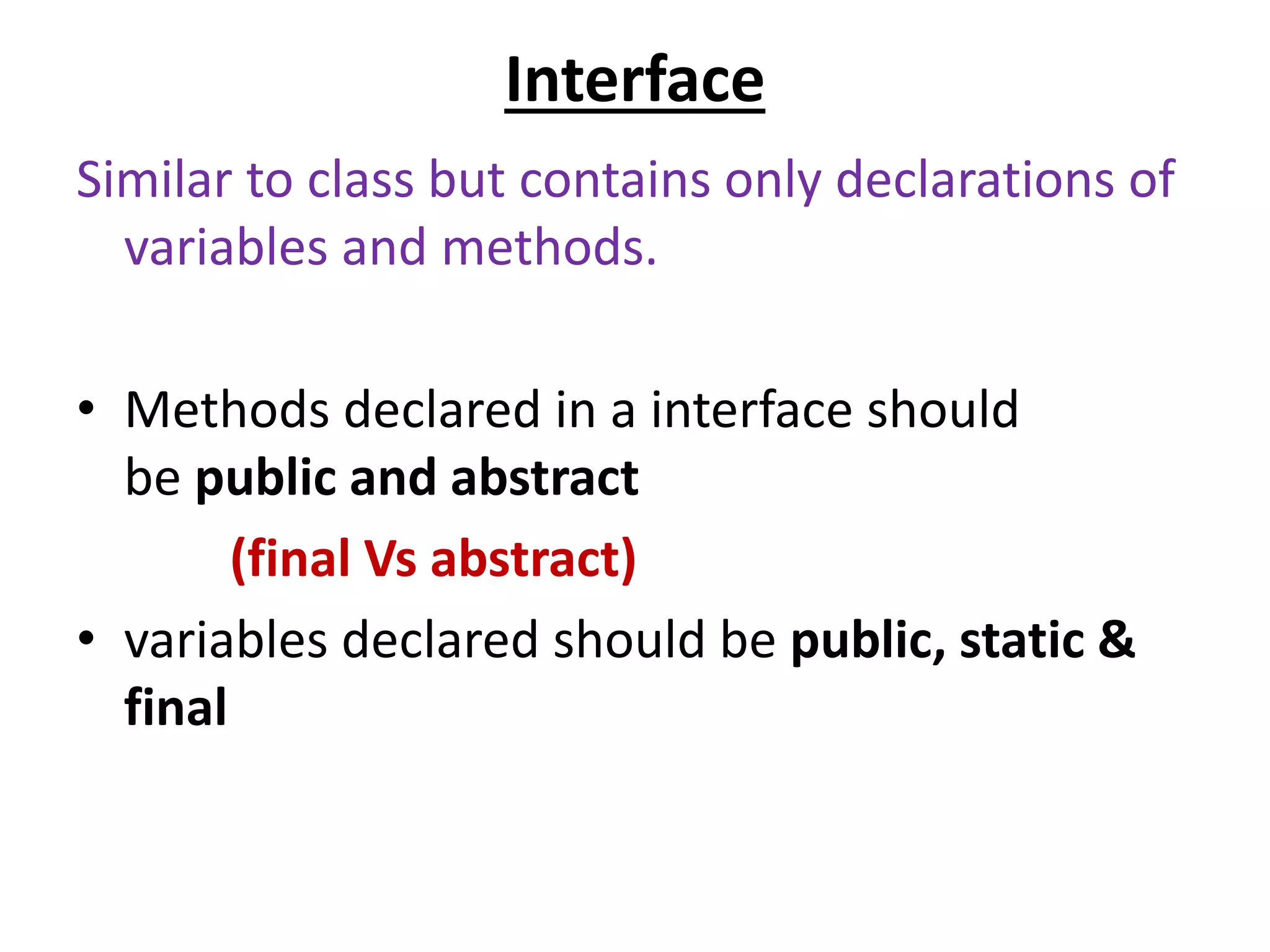
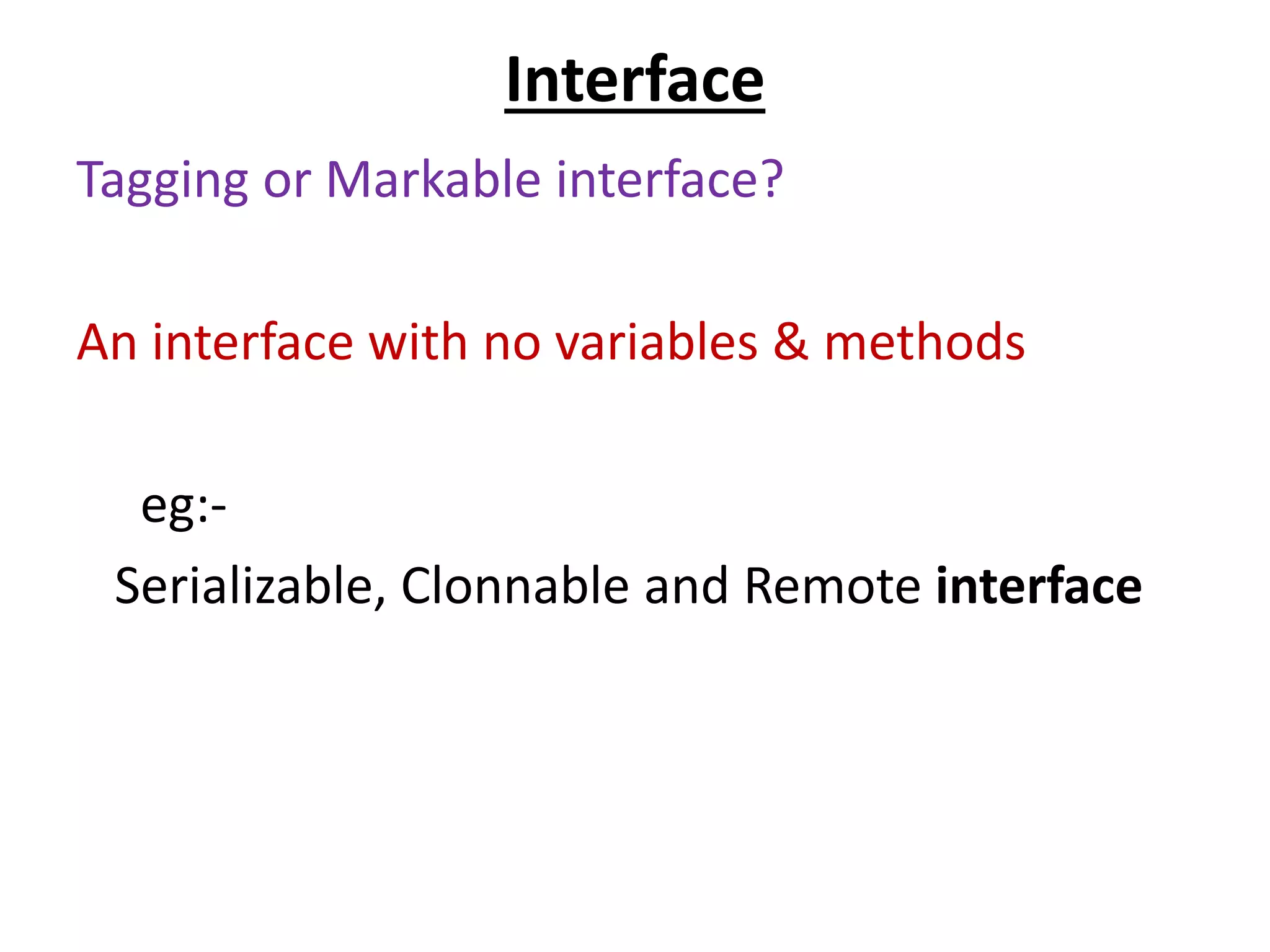
![Interface pgm
interface P
{
void print();
}
class A implements P
{
public void print()
{ System.out.println("Hello"); }
public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj = new A();
obj.print();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-37-2048.jpg)
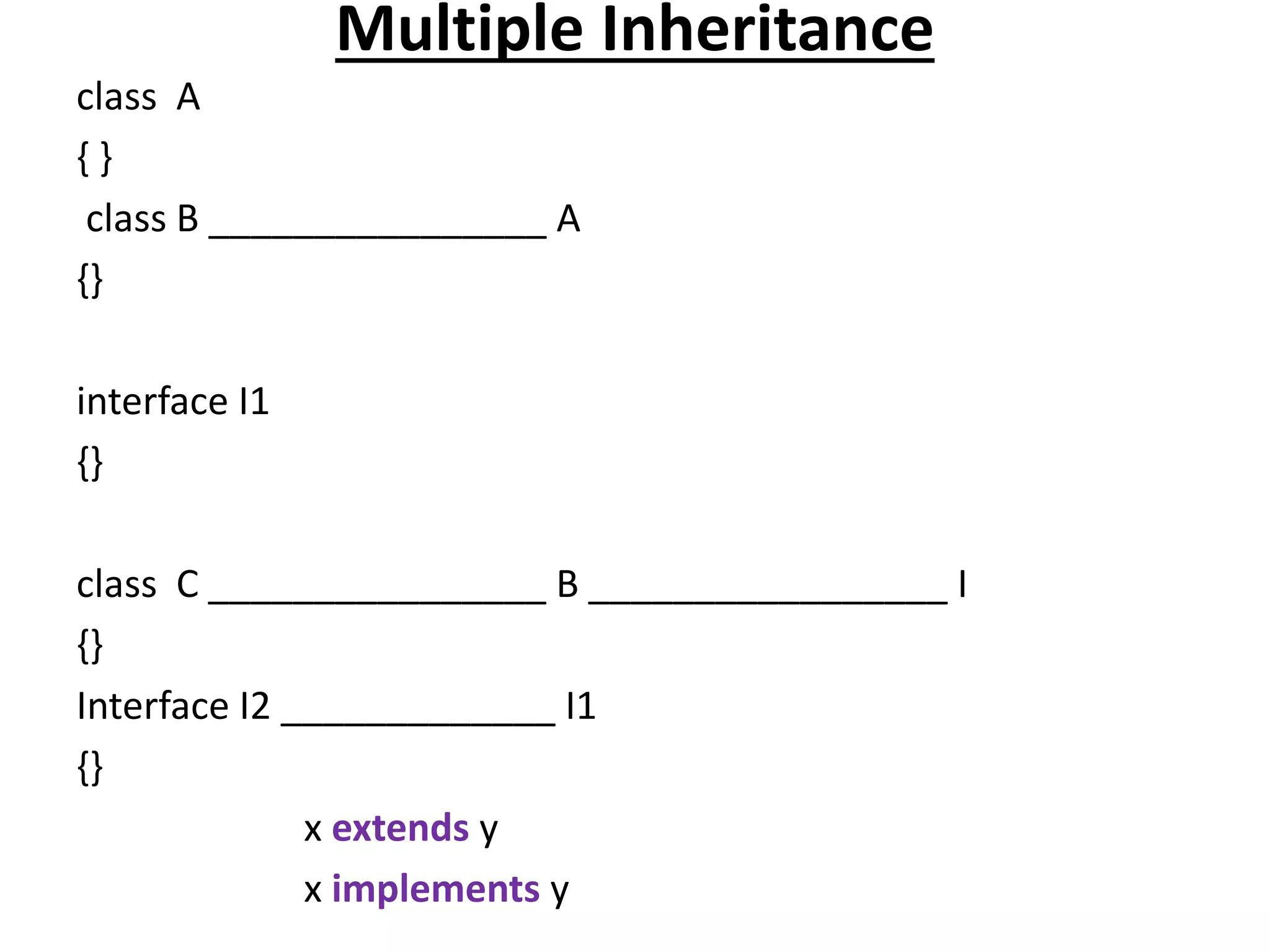
![Multiple Inheritance
class A
{
static int x=10;
}
interface B
{
static int y=20;
}
class C extends A implements B
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Multiplication:"+ x*y);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-38-2048.jpg)

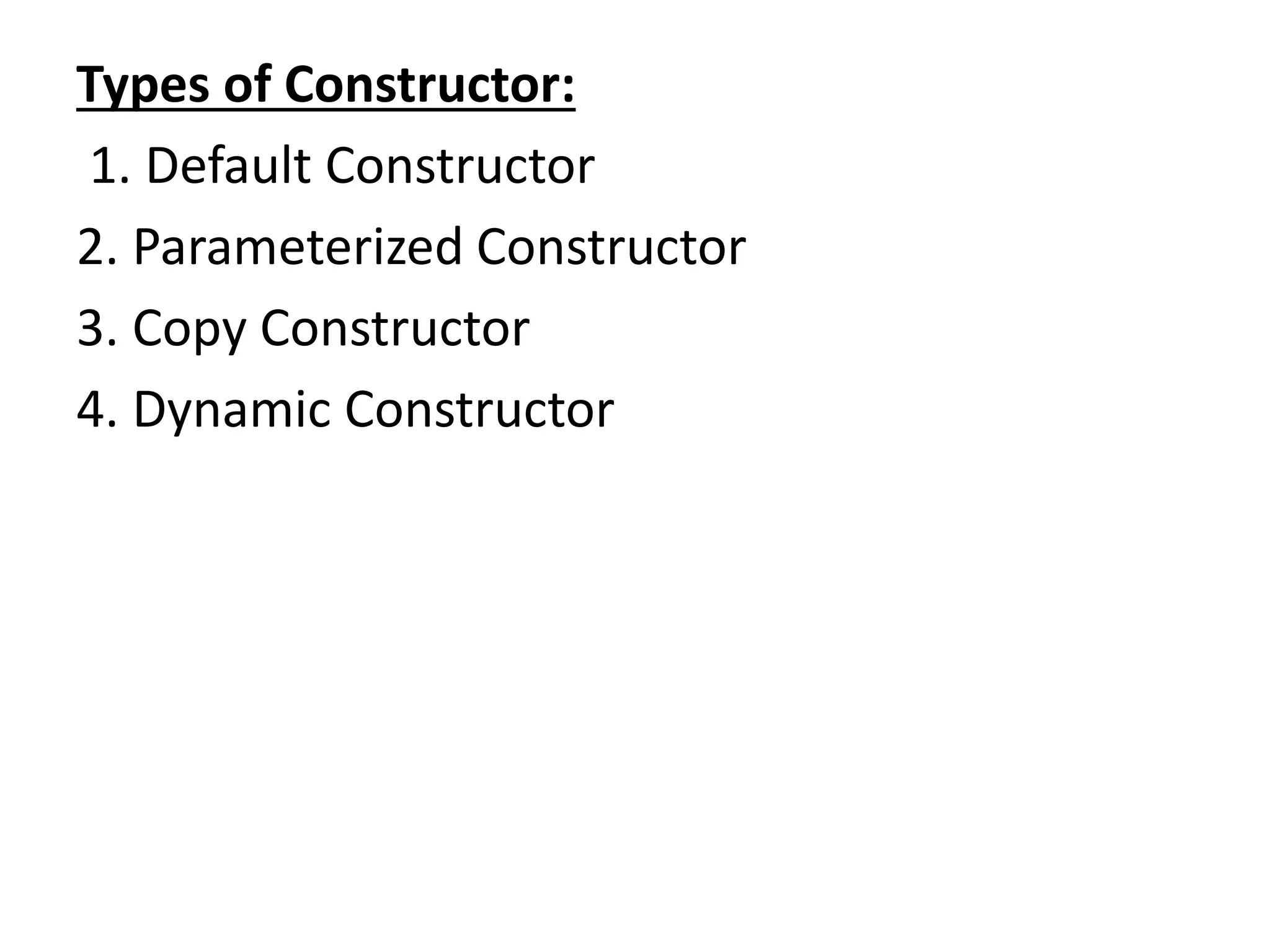
![Default constructorclass Student
{
int rno;
String name;
void display()
{
System.out.println("Name:"+name);
System.out.println("RollNO:"+rno);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s1=new Student();//default constructor
s1.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-42-2048.jpg)
![2. Parameterized Constructor
class Student
{
int rno;
String name;
Student(int r,String s)
{
rno=r;
name=s;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println("Name:"+name);
System.out.println("RollNO:"+rno);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s1=new Student(101,"Sudha");//parameterized constructor
s1.display();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-43-2048.jpg)
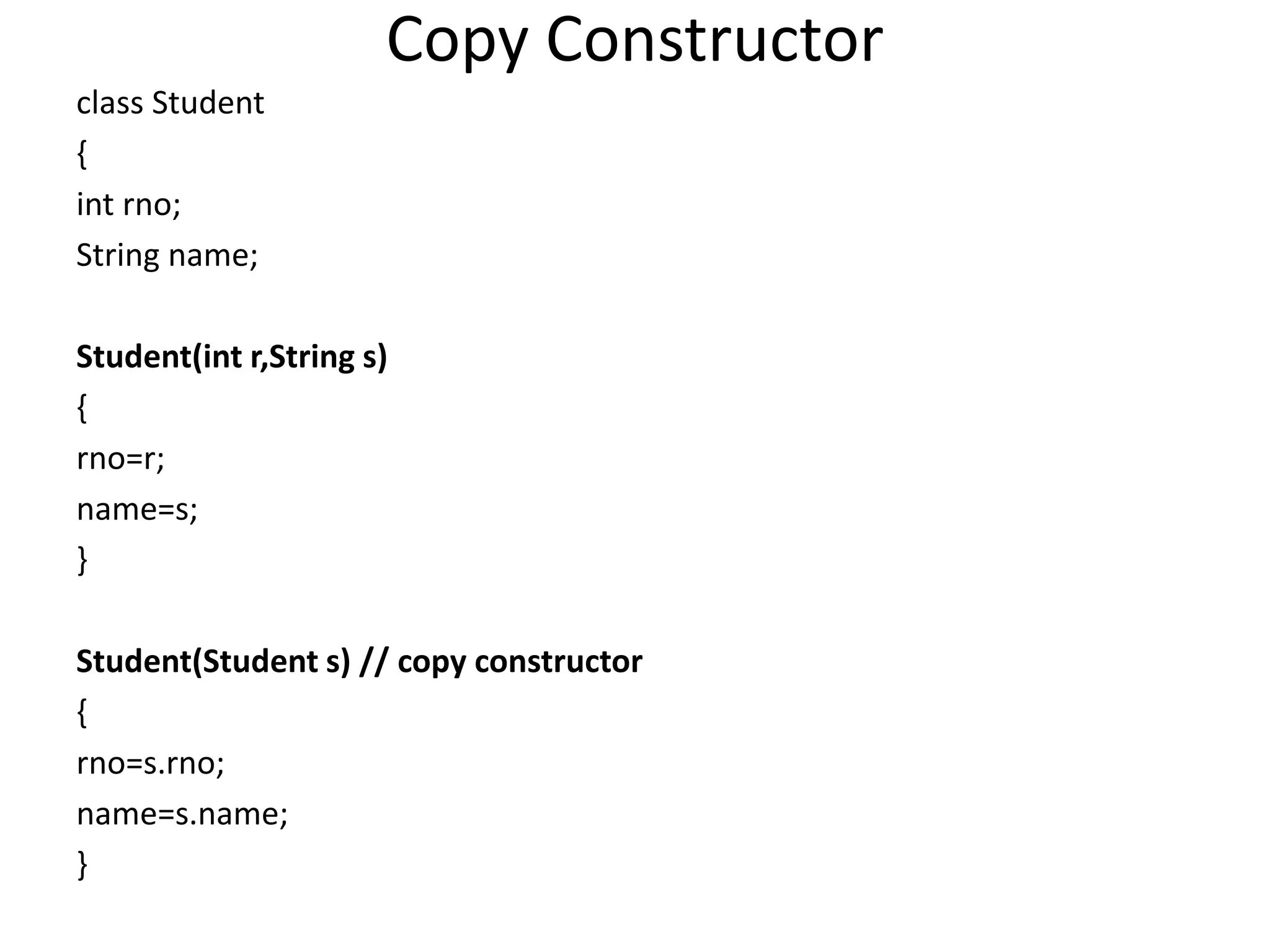
![void display()
{
System.out.println("Name:"+name);
System.out.println("RollNO:"+rno);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s1=new Student(101,"Sudha”);
Student s2 = new Student(s1); //Copy Constructor
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-45-2048.jpg)


![class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{ Apple a=new Apple();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-48-2048.jpg)
![this keywordclass A
{
int a,b;
int add(int x, int y)
{
a=x;
b=y;
return(a+b);
}
}
class B extends A
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
A a=new A();
System.out.println("Added Value:" + a.add(10,20));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-49-2048.jpg)
![class A
{
int x,y;
int add(int x, int y)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
return(x+y);
}
}
class B extends A
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
A a=new A();
System.out.println("Added Value:" + a.add(10,20));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-50-2048.jpg)
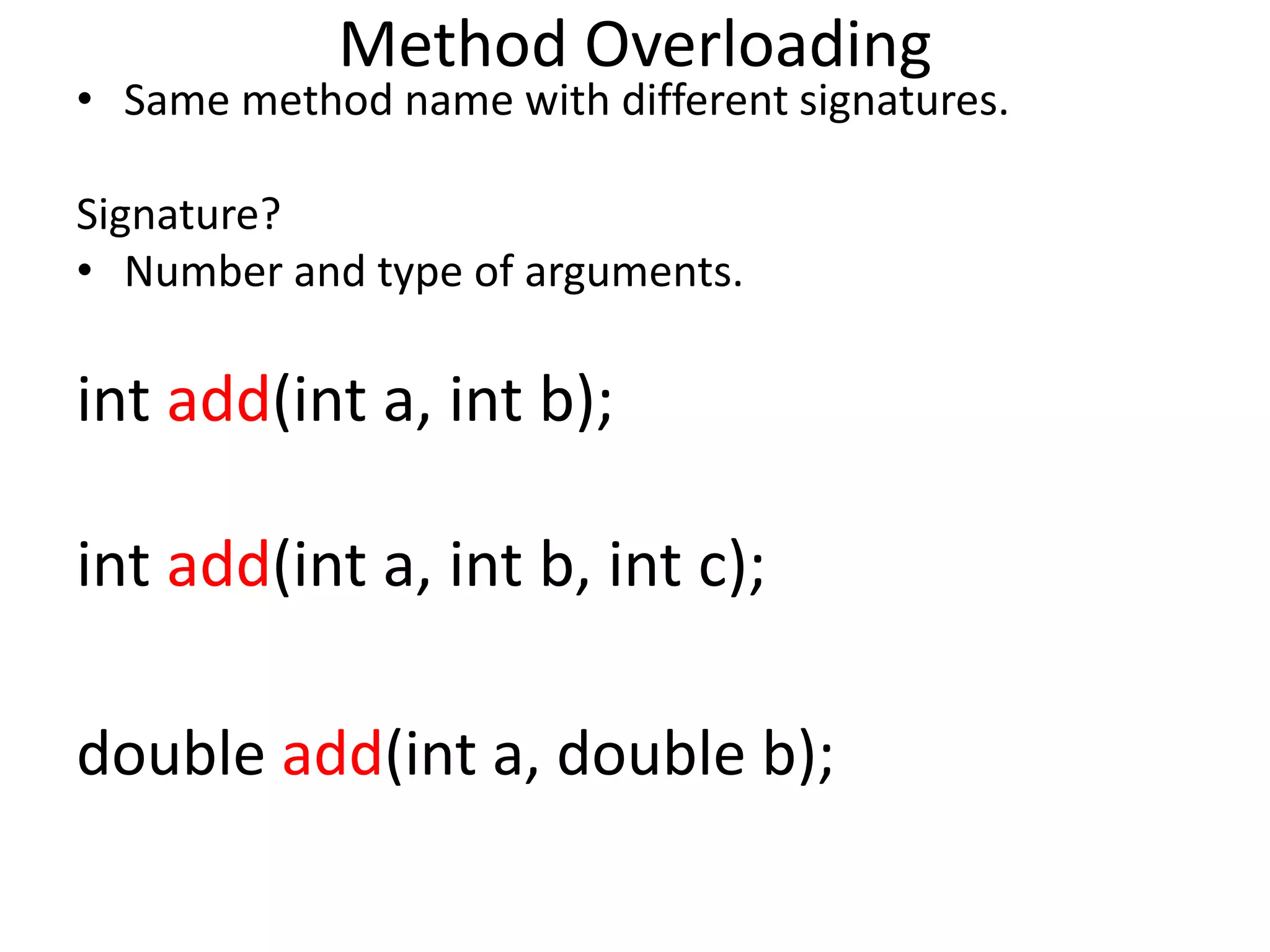

![class B extends A
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
A a=new A();
System.out.println("Added Value:" + a.add(10,20));
System.out.println("Added Value:" + a.add(10,20,30));
System.out.println("Added Value:" + a.add(1.2,20));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-53-2048.jpg)


![class Test
{
public static void main(String a[])
{
B b = new B();
b.show();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-56-2048.jpg)


![class TestBank
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Bank b;
b=new SBI();
System.out.println("Rate of Interest is: "+b.getInterest());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-59-2048.jpg)


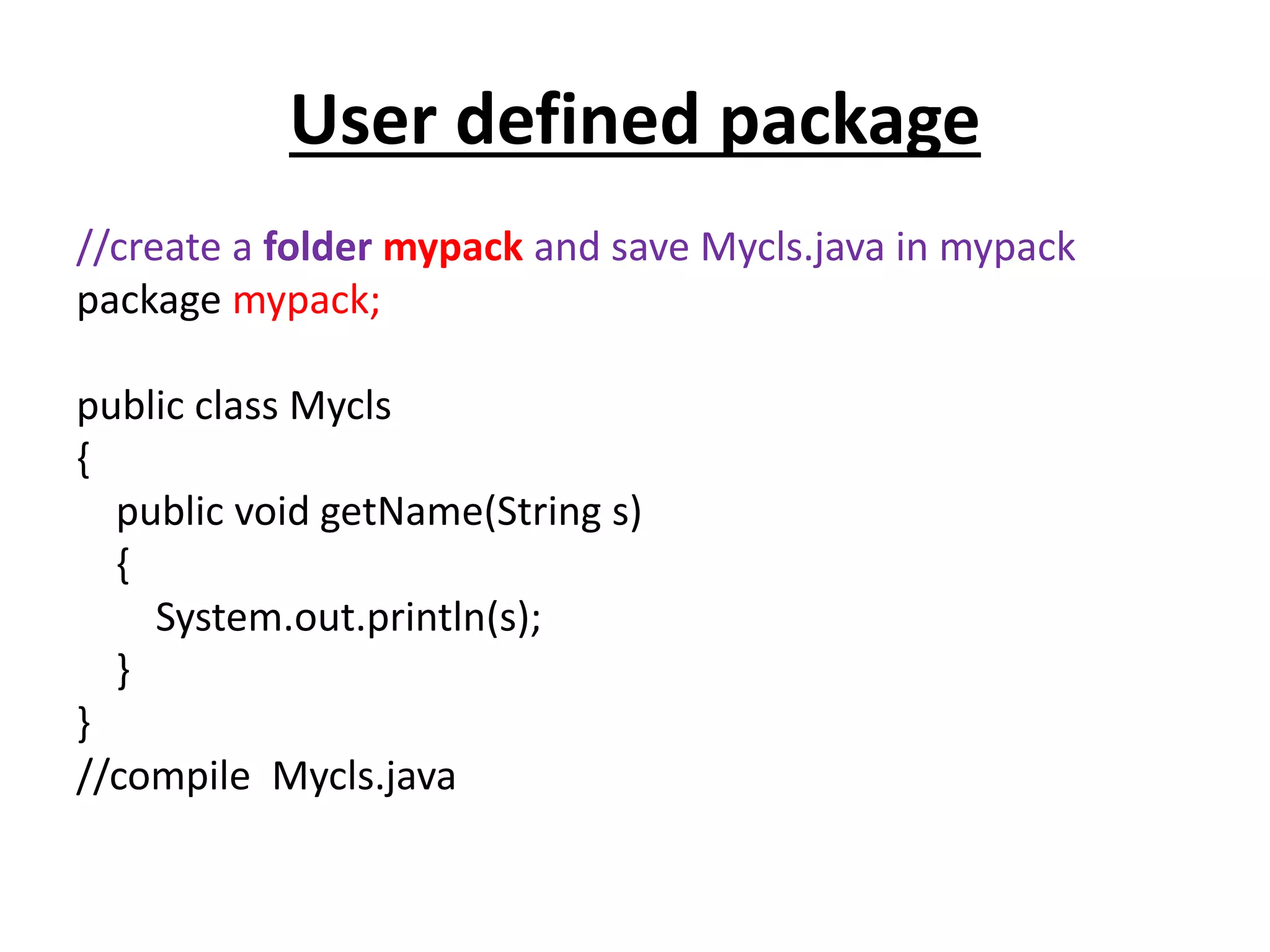
![import mypack.Mycls;
public class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mycls m = new Mycls();
m.getName("VIIMS");
}
}
//cd..
//compile Test.java & run
// Output:- VIIMS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-65-2048.jpg)
![//static keyword
import static java.lang.System.*;
class Test
{
public static void main(String b[])
{
out.println("Welcome");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-66-2048.jpg)






![Creating a Tableimport java.sql.*;
class Test
{
public static void main(String a[]) throws Exception
{
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection("Jdbc:Odbc:stucon");
String qs = "create table student(sname text,rno number)";
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(qs);
ps.executeUpdate();
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-76-2048.jpg)
![Select Queryimport java.sql.*;
class Test
{
public static void main(String a[]) throws Exception
{
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("Jdbc:Odbc:empcon");
String qs = "select * from EMPLOYEE";
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(qs);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next())
{
System.out.println("Employee No :" + rs.getString(1));
System.out.println("Employee Name:" + rs.getString(2));
System.out.println("Salary Rs :" + rs.getString(3));
}
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-170921202458/75/Core-java-Essentials-77-2048.jpg)
