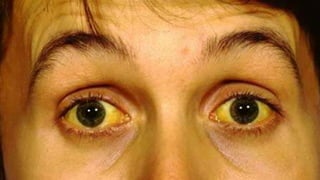
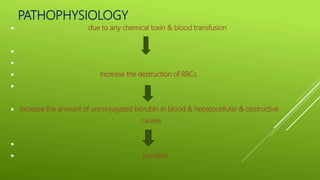
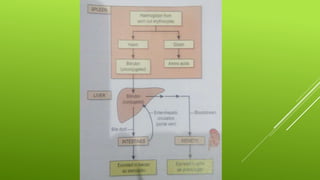
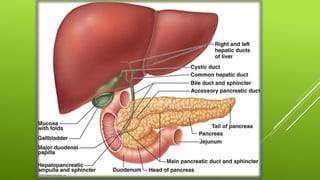
This document provides an overview of jaundice including its definition, types and causes, clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, diagnostic evaluation, medical management, dietary management, and nursing management. It defines jaundice as a yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes caused by an increased level of bilirubin in the blood. There are three main types - hemolytic, hepatocellular, and obstructive jaundice. Clinical manifestations include yellowish skin, gray stool, itchy skin, nausea, loss of appetite, and tea colored urine. Diagnostic evaluation focuses on measuring bilirubin levels while medical management includes antihistamines, sedatives, antibiotics, and dietary restrictions. Nursing management aims




![DEFINITION
Jaundice is a yellow discolouration of the skin,
mucus membrane and whites of eyes [
sclera ] caused by increase amount of bilirubin
in the blood
Bilirubin levels exceeds up to 3 times than
normal.
The normal value - 0.3 – 1.2 mg/dl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaundice-230407160905-e02f86c6/85/Jaundice-pdf-7-320.jpg)