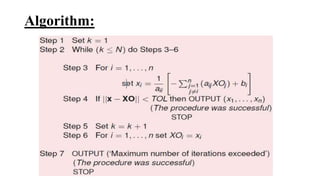
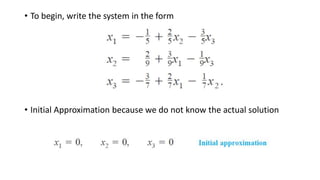
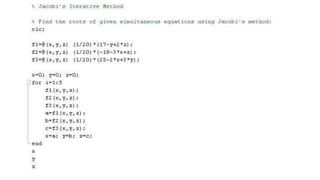
This document provides an overview of the Jacobi method for solving systems of linear equations. It includes the algorithm, an example, MATLAB code to implement the method, and applications in engineering. The Jacobi method makes approximations to solve systems of equations by iteratively solving for each variable. It converges to the solution when the last two iterations are identical. The method is useful for engineering problems involving linear systems and has advantages of being simple to program and stable, though it is slow compared to other methods.