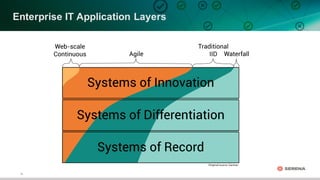
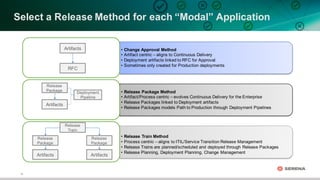
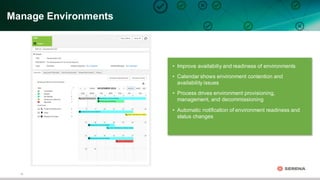
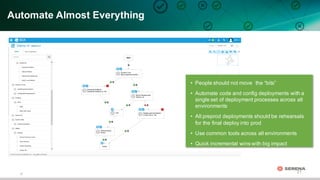
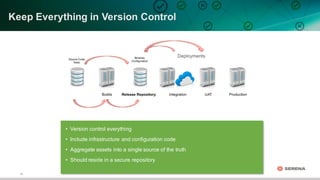
This document discusses leveraging DevOps principles for improving software release and deployment processes. It notes that while agile development has increased innovation speed, it has pushed bottlenecks to IT operations due to differing goals between development and operations teams. To address this, the document recommends applying DevOps principles such as automating processes, keeping all code and configurations in version control, integrating release and deployment tools, and establishing continuous delivery practices to create repeatable, reliable processes that improve responsiveness to business needs.