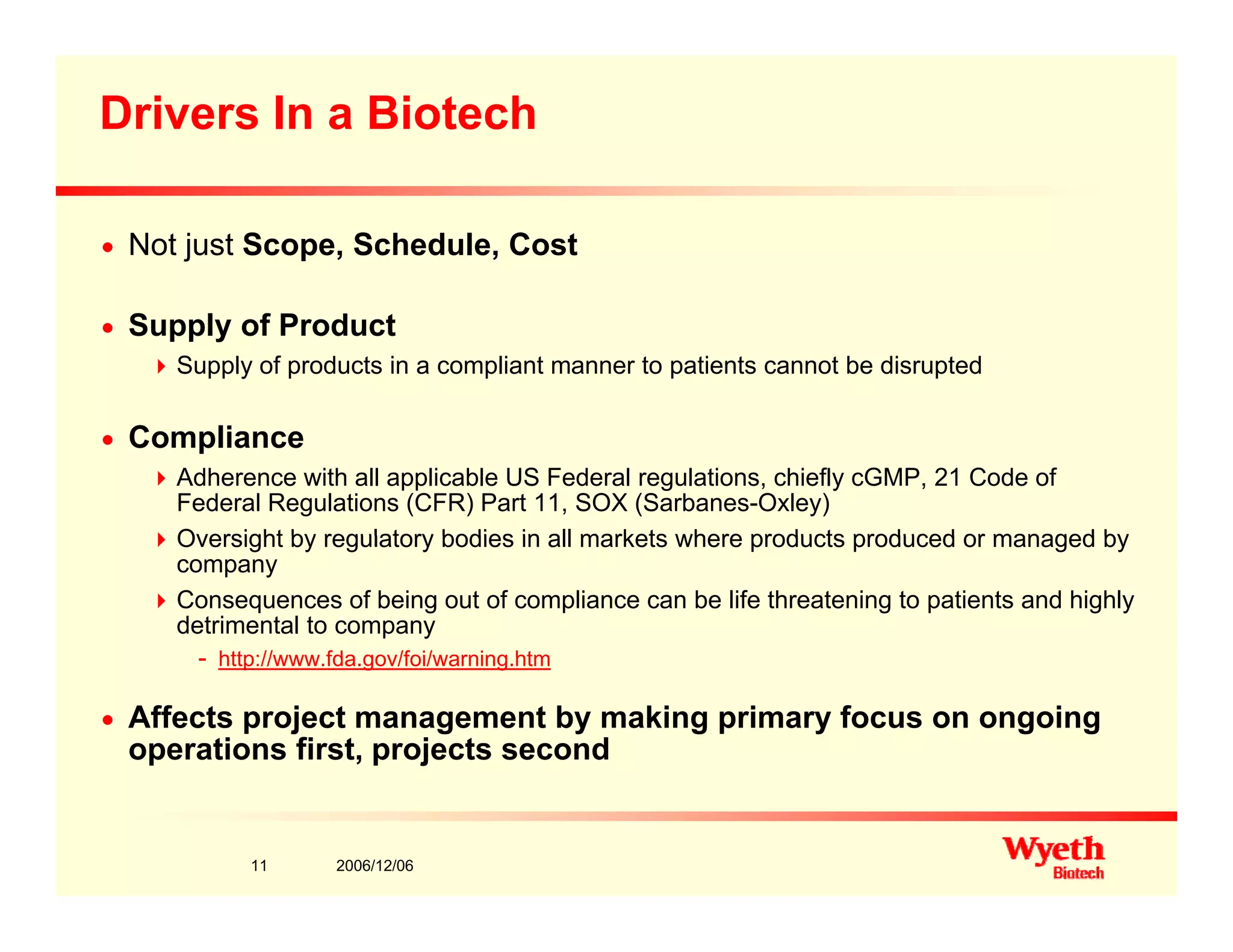
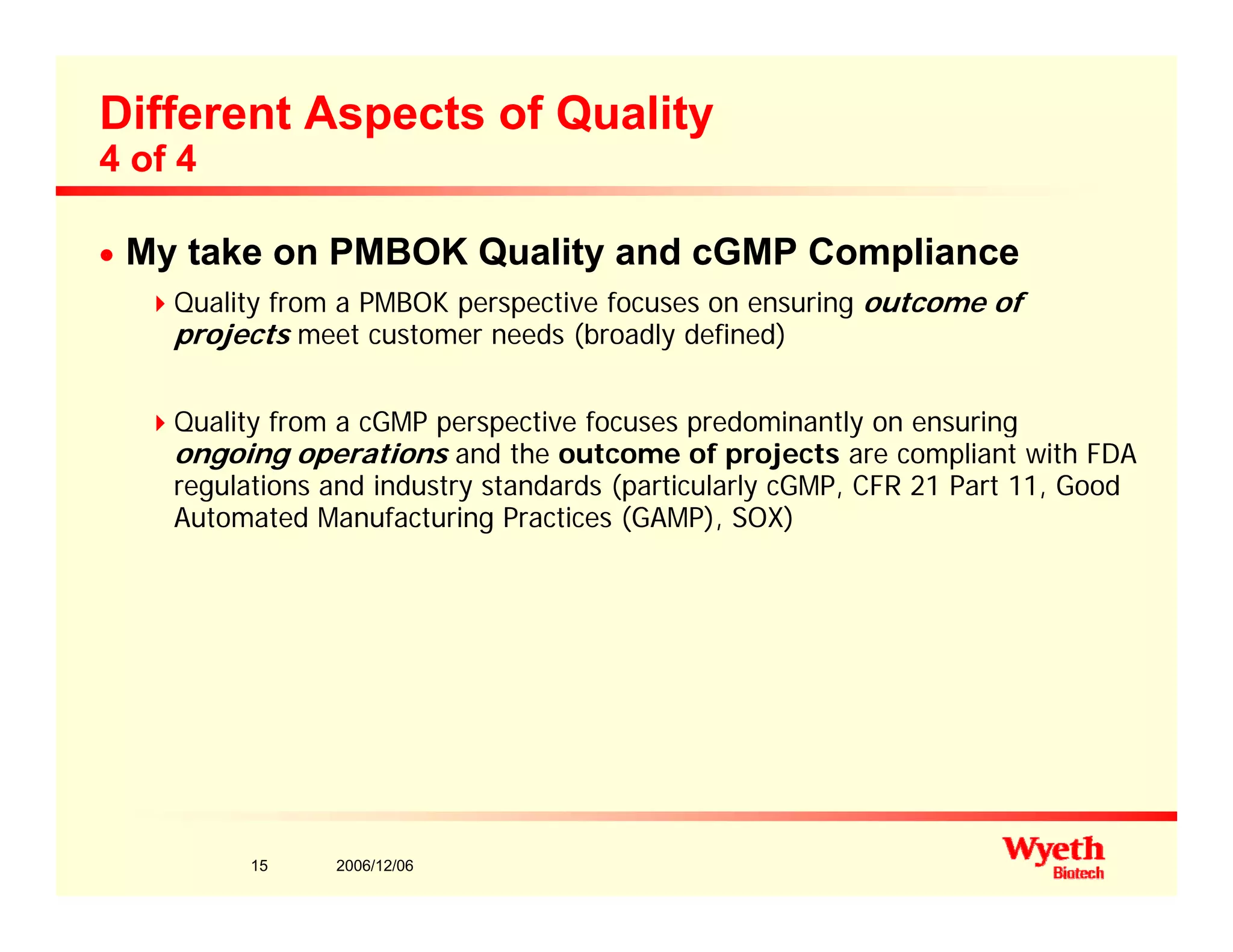
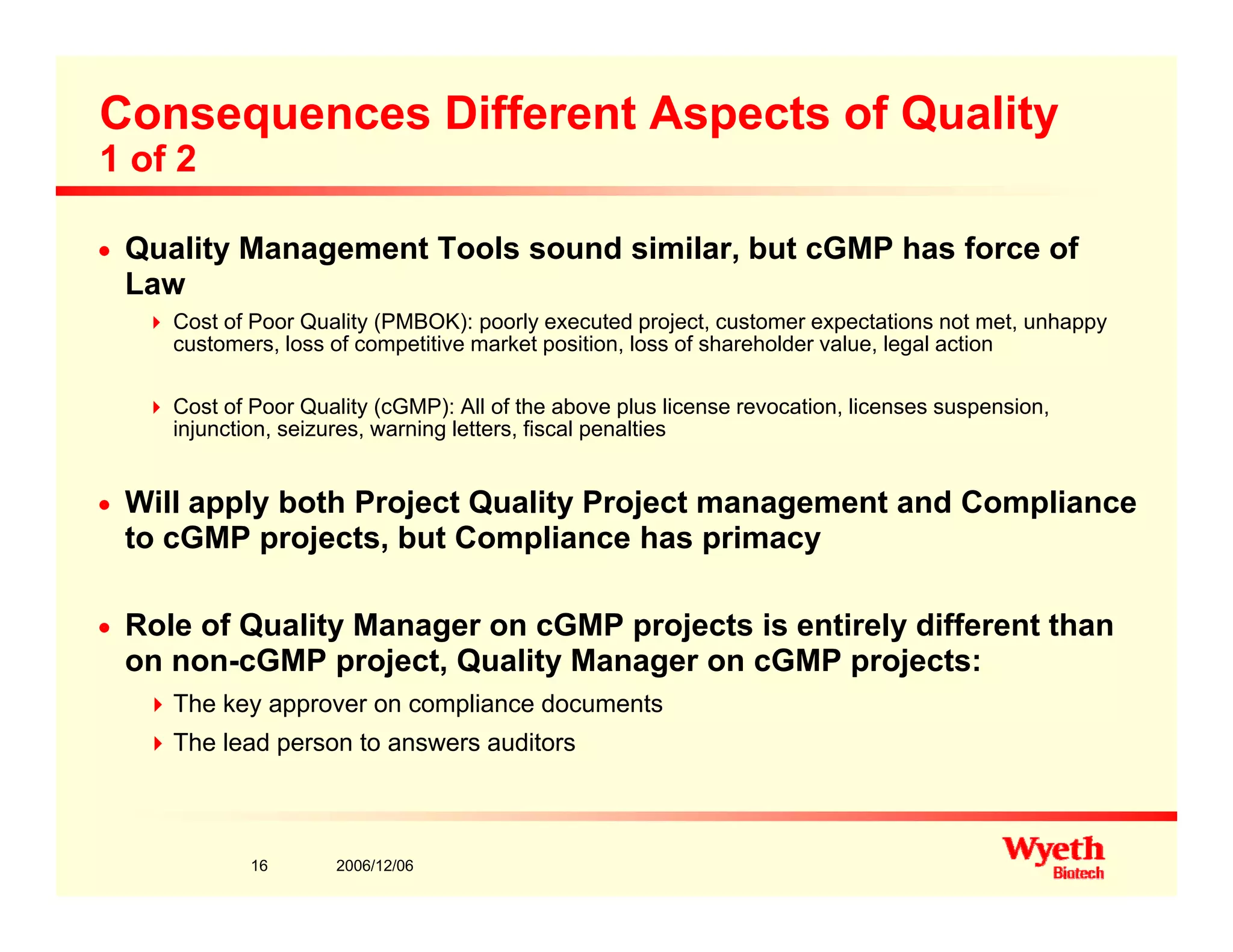
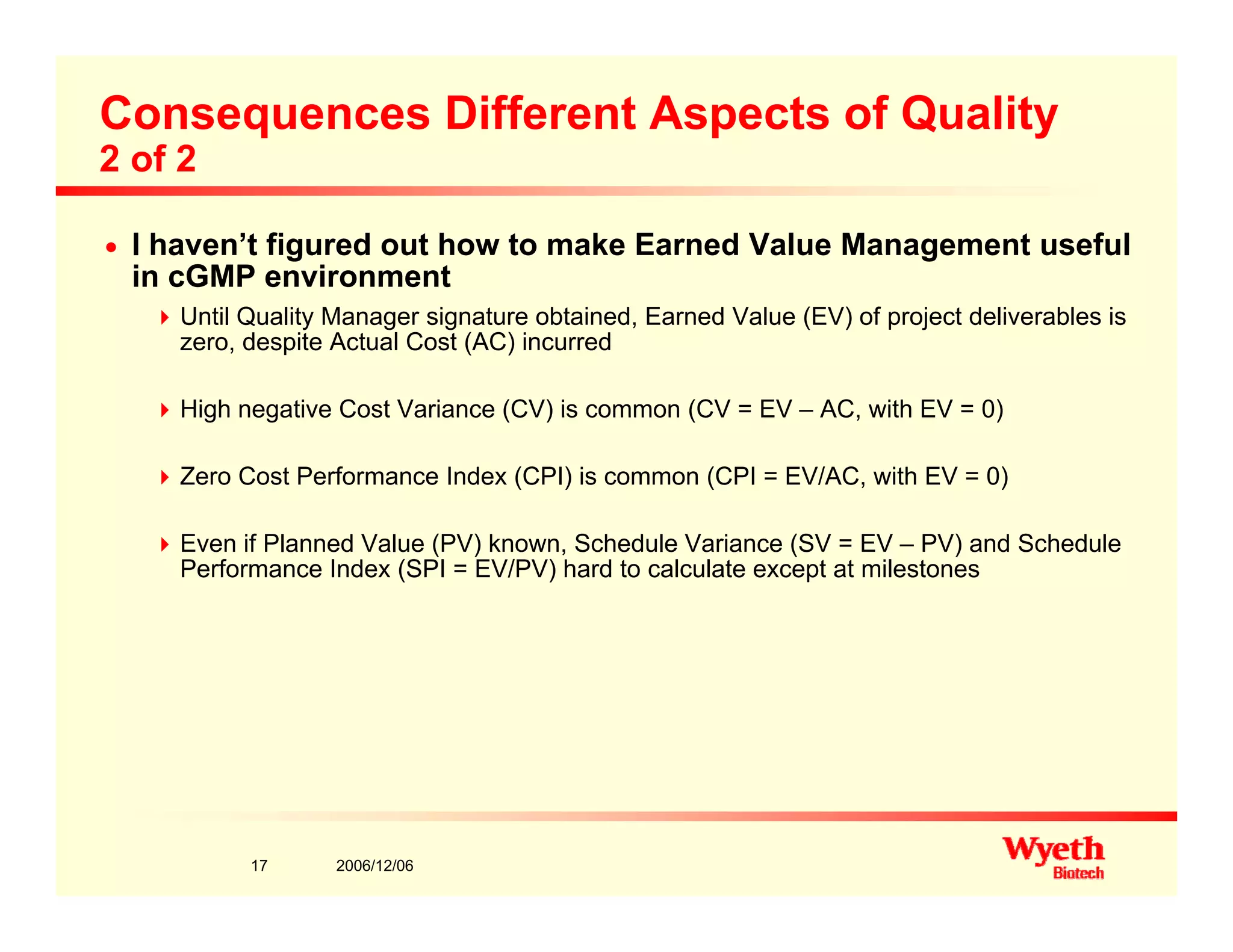
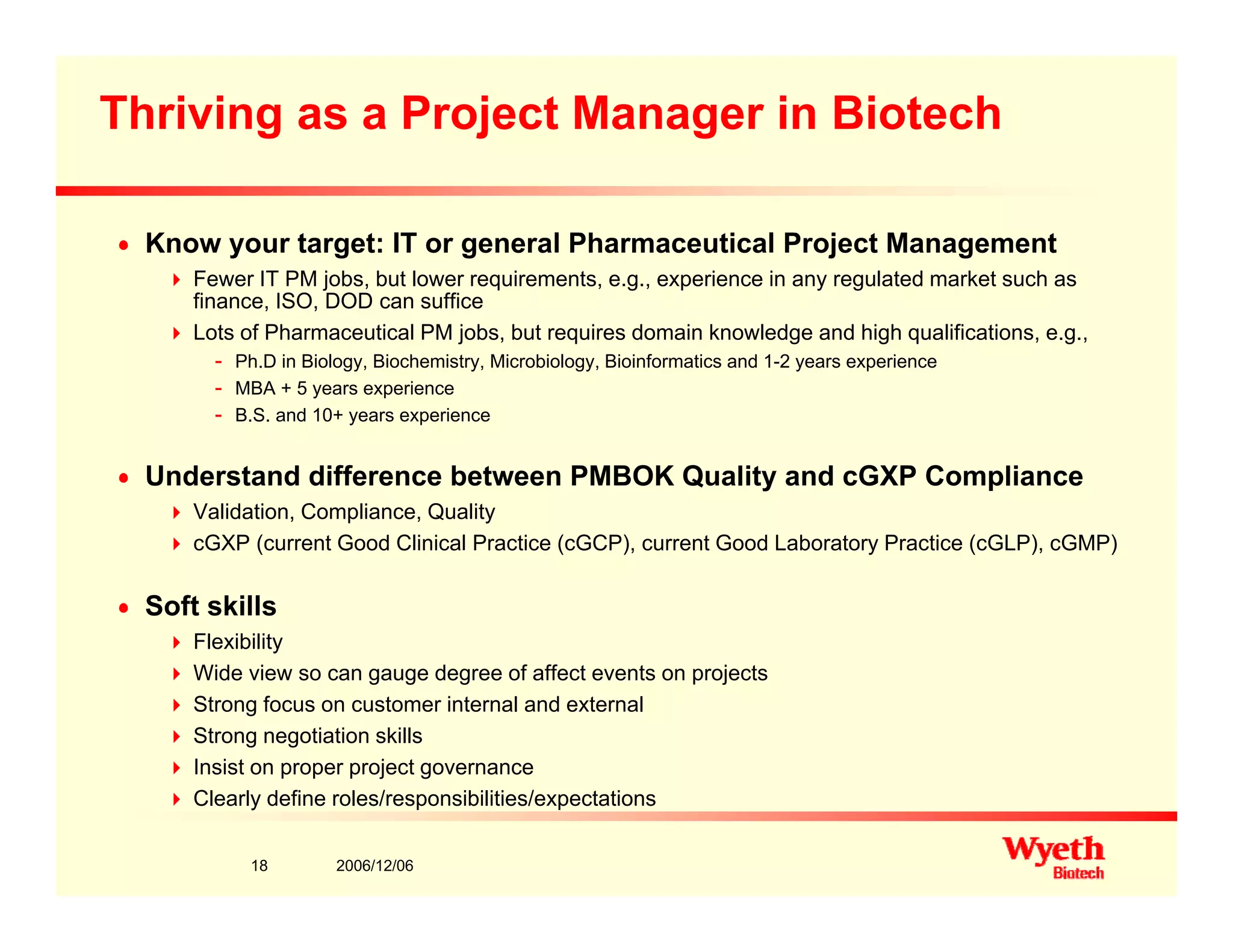
This document provides an overview of project management in a biopharmaceutical manufacturing environment. It discusses the key drivers in this environment beyond typical cost, schedule, and resource constraints, including supplying product to patients and compliance with regulations. The presentation focuses on an overview of a project to support manufacturing, differing aspects of quality between PMBOK and cGMP standards, and skills for project managers to thrive in a cGMP environment.





![Basic Notions of Compliance and
ValidationValidation
n Validation
Establishing documented evidence which provides a high degree of assurance that ag p g g
specific process will consistently produce a product meeting its predetermined
specifications and quality attributes
- http://www.fda.gov/ora/inspect_ref/igs/gloss.html
Validation coverage should be based on the software’s complexity and safety risk – notg p y y
on firm size or resource constraints.
- http://www.fda.gov/cdrh/comp/guidance/938.html#_Toc517237933 (section 4.8)
n What is [21 CFR] Part 11?n What is [21 CFR] Part 11?
Regulation allowing FDA to accept electronic records and signatures in place of paper
records and handwritten signatures.
Describes controls to ensure that electronic records and signatures are
- Trustworthy
- Reliable
- Compatible with FDA work
http://www.fda.gov/cder/regulatory/ersr/2002 11 05 standards1/sld003.htm
2006/12/0610
p // da go /cde / egu a o y/e s / 00 _ _05_s a da ds /s d003](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bykpmicentralmass2007-06-12v1-181104042939/75/IT-focused-Project-Management-in-a-Biopharmaceutical-Manufacturing-Environment-10-2048.jpg)