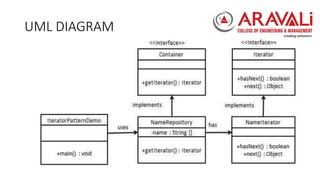
The iterator pattern allows for sequential access to elements in a collection without exposing its underlying implementation. It defines an interface for accessing and traversing elements with methods like hasNext() and next(). Concrete classes implement the iterator interface and container interface which returns the iterator. The demo class uses a name repository container to get an iterator and print out each name.





![Step 2
Create concrete class implementing the Container interface. This
class has inner class NameIterator implementing
the Iterator interface.
• NameRepository.java
public class NameRepository implements Container
{
public String names[] = {"Robert" , "John" ,"Julie" , "Lora"};
@
Override
public Iterator getIterator()
{
return new NameIterator();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iteratorpattern-201016082747/85/Iterator-pattern-7-320.jpg)

![@Override
Public Object next()
{
if(this.hasNext()
{
return names[index++];
}
return null;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iteratorpattern-201016082747/85/Iterator-pattern-9-320.jpg)
![Step 3
Use the NameRepository to get iterator and print
names.
• IteratorPatternDemo.java
public class IteratorPatternDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
NameRepository namesRepository = new NameRepository();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iteratorpattern-201016082747/85/Iterator-pattern-10-320.jpg)

