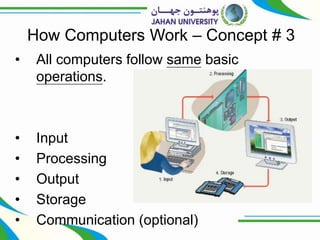
This document provides an introduction to computers, including definitions, how they work, and their basic components. It discusses that computers process data into useful information through hardware and software. The hardware includes the system unit, processor, memory, storage, input/output devices, and other components. It also explains the basic operations of input, processing, output, storage, and optional communication. Software includes system software that manages the computer and application software that allows users to perform tasks.