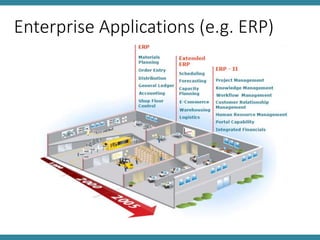
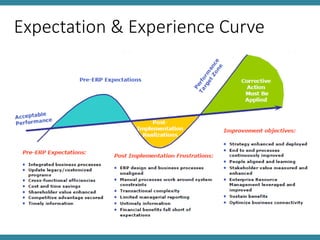
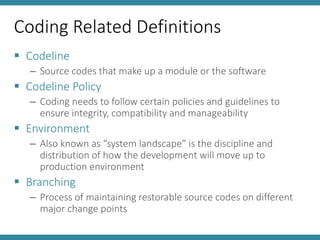
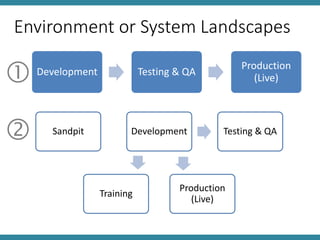
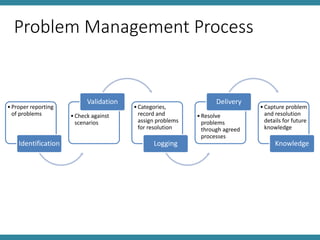
The document discusses IT asset management and software change control. It describes defining policies for IT systems management and outlines processes for efficient operations. Software changes should be tracked and tested as they move through development, testing, and production environments. Change management requires communication, training, and identifying leaders to drive changes. Problems should be properly reported, validated, logged, and resolved according to agreed upon processes, with details captured for future knowledge. Metrics and management review are important for monitoring performance.