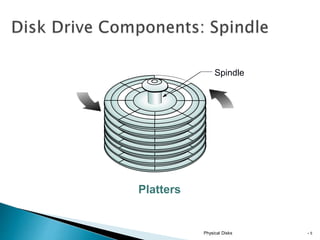
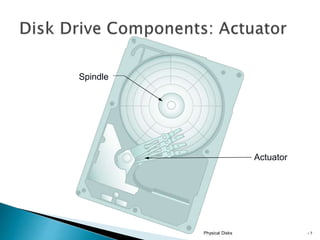
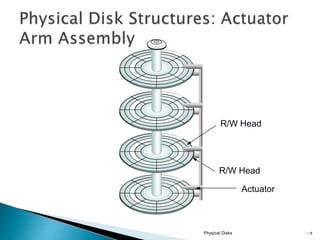
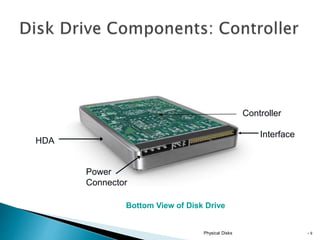
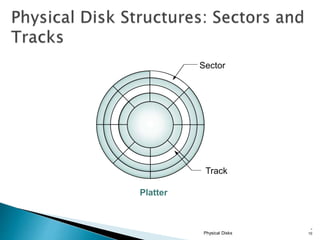
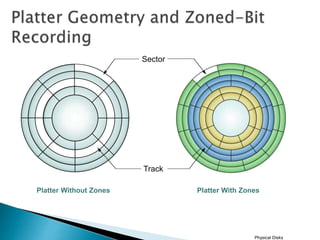
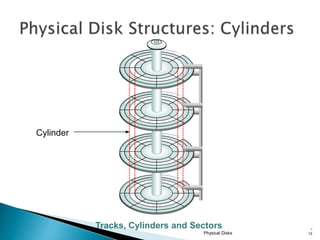
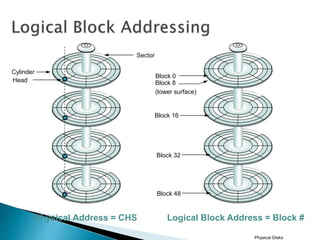
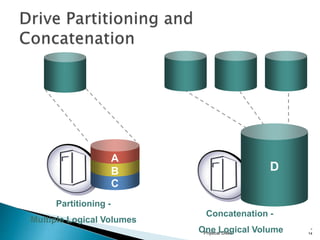
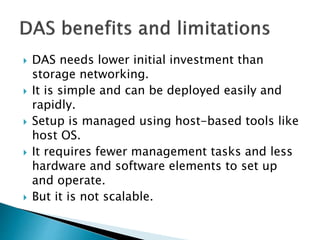
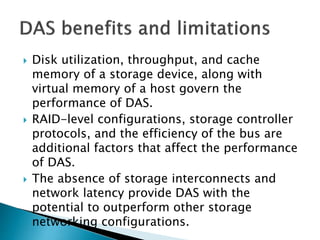
This document discusses direct-attached storage (DAS), which connects storage devices directly to servers. It describes the internal and external DAS architectures, with internal DAS having the storage device inside the host and external DAS connecting the storage device externally via interfaces like SCSI. DAS has benefits like lower cost and simpler setup than networked storage but lacks scalability and can be limited by bus bandwidth and distance restrictions. Performance depends on factors like disk utilization, cache memory, RAID configuration, and controller protocols.