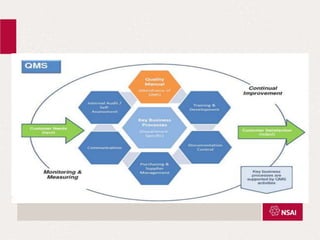
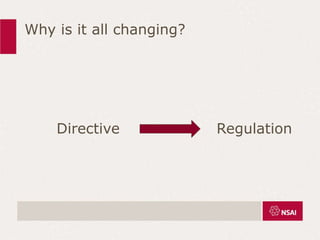
This document provides an overview of the key changes between ISO 13485:2003 and ISO 13485:2016 for quality management systems in the medical device industry. It discusses definitions, the timeline for transition, and what is new in each section of the updated standard, including expanded requirements for design and development, purchasing, production, and complaint handling. The changes are aimed at increasing risk-based approaches and ensuring continued compliance with evolving regulations.