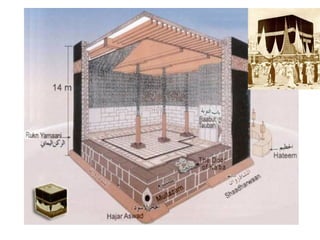
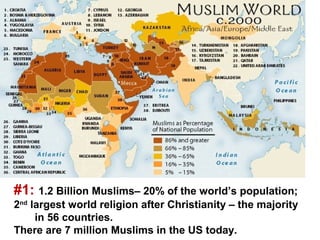
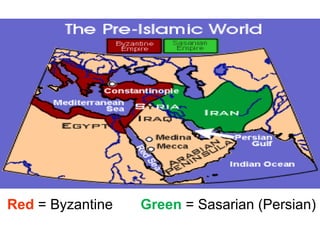
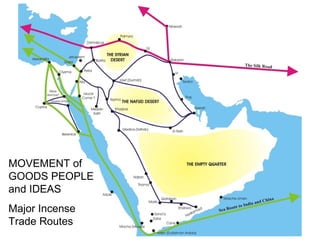
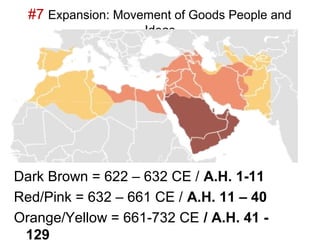
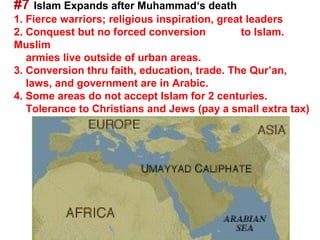
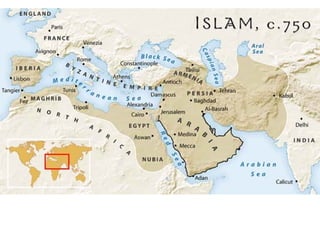
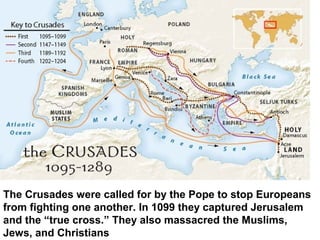
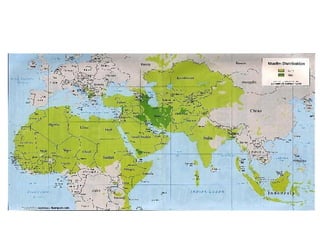
Here are a few key images related to education in Islam:
- Students studying the Quran. Memorizing and understanding the holy text is a central part of Islamic education.
- A madrasa, or Islamic religious school. Madrasas traditionally taught Islamic theology, law, jurisprudence, and other subjects.
- Students of all backgrounds learning together. Islam promotes education for both men and women of all social classes.
- A teacher leading a discussion. Traditional Islamic education emphasizes memorization as well as questioning, reasoning, and debate.
- Books and manuscripts. Islam places great value on the preservation and study of knowledge. Many classical Greek and other texts were preserved by Islamic scholars.
- A