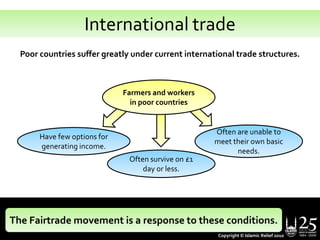
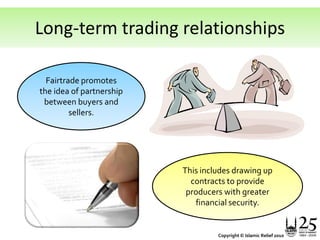
The document discusses the concepts of Fairtrade and its alignment with Islamic principles of justice and equity in trade. It provides information on Fairtrade standards such as minimum pricing and premiums that ensure farmers' and workers' livelihoods are supported. The document also highlights teachings from the Quran and hadith that promote fairness, workers' rights, environmental stewardship and contractual agreements. It encourages individuals to consider ethically sourced Fairtrade products and support farmers in poorer nations through their consumer choices.