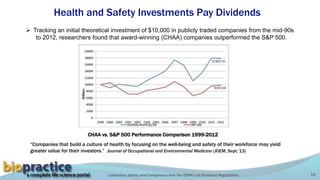
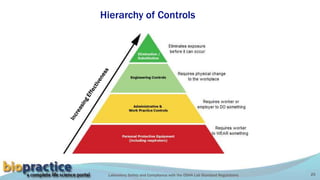
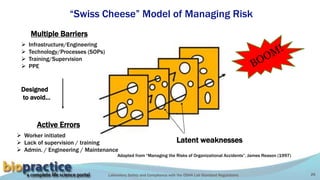
This document outlines the key requirements of the OSHA Lab Standard regulations. It discusses common causes of laboratory accidents like inadequate training and safety protocols. It summarizes statistics on laboratory accidents and fatalities. It also reviews several high-profile laboratory accident cases and the systemic deficiencies that led to the incidents. The document explains the hierarchy of hazard controls and the "Swiss cheese" model for managing risk. Finally, it details the main sections of the OSHA Lab Standard, including requirements for chemical hygiene plans, personal protective equipment, employee training, medical consultations, and recordkeeping.