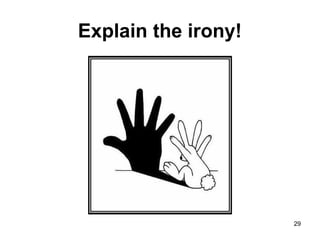
This document provides an overview of different types of irony and paradoxes in literature. It begins by defining verbal irony as when the intended meaning of words is contrary to their literal interpretation. It then gives several historical examples of irony in works by Chaucer, Shakespeare, and Swift. Dramatic irony occurs when the audience knows something characters do not. The document distinguishes between linguistic, situational, and tragic irony. It also discusses paradoxes, Catch-22 situations, and irony in signs and real life. In summary, the document covers the concepts and techniques of irony, paradox, and dark humor as used in literature.