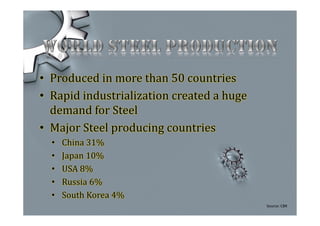
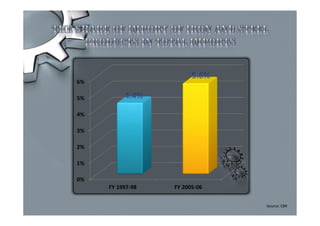
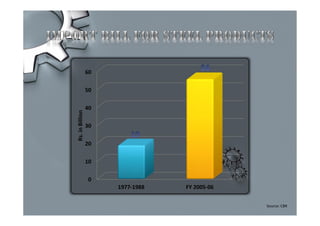
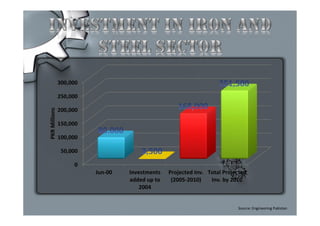
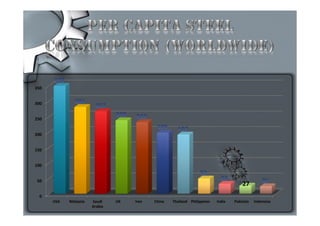
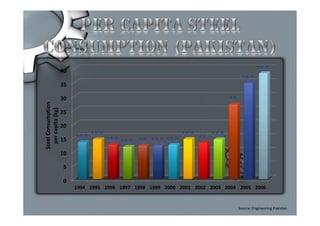
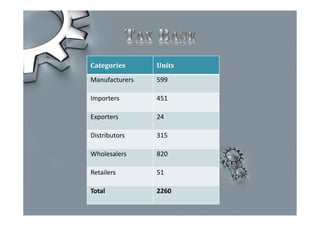
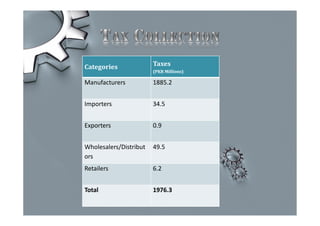
Steel is one of the most widely used metals globally and is produced in over 50 countries. China is the largest producer at 31% of the world's supply. The steel industry in Pakistan has grown at an average rate of 5% annually and employs over 92,000 people directly. However, the industry faces challenges of outdated plants, low per capita consumption, and lack of training/research programs. Increased investment, utilization of iron ore reserves, and improved policies are needed to further develop Pakistan's steel sector.