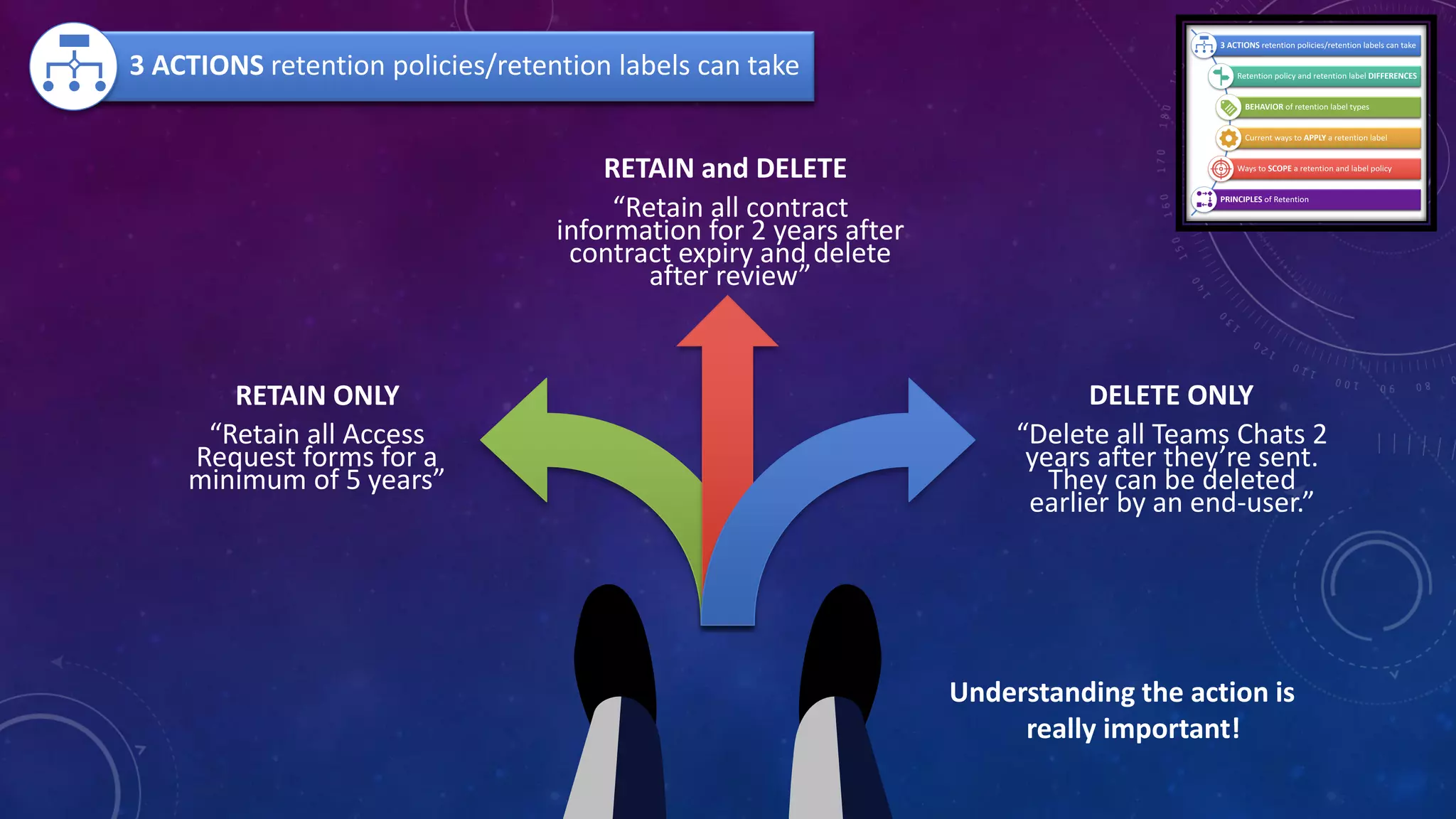
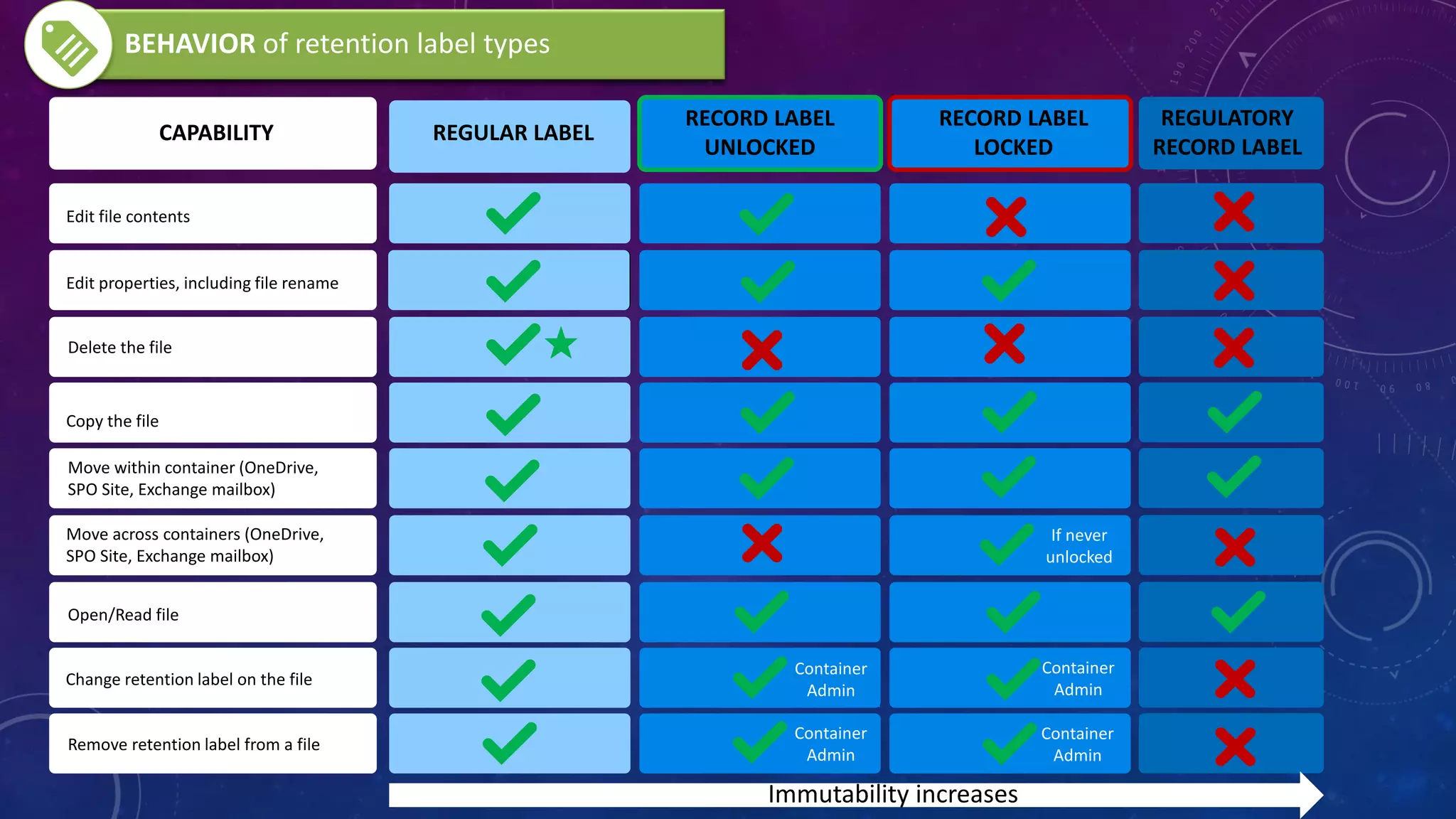
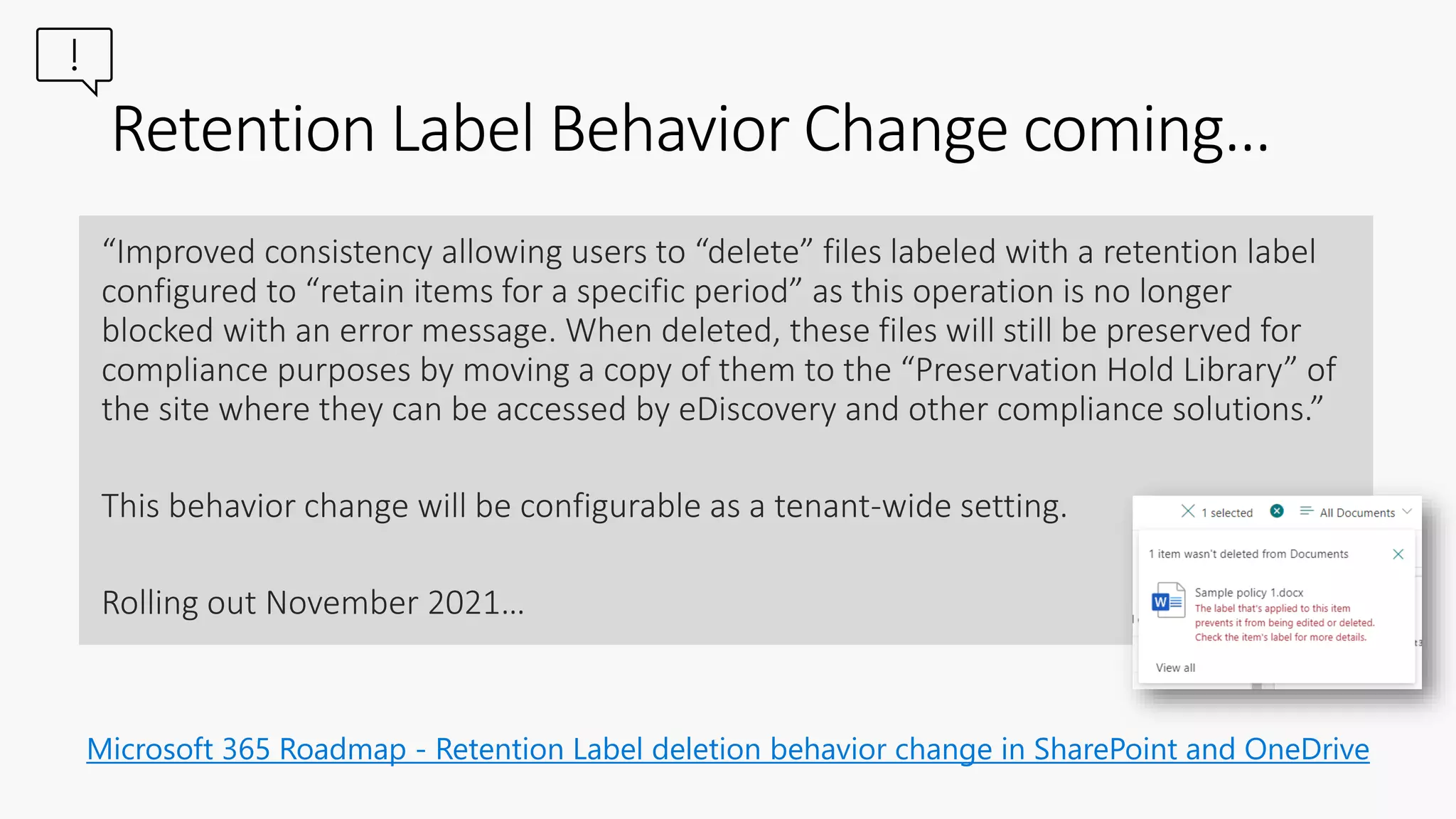
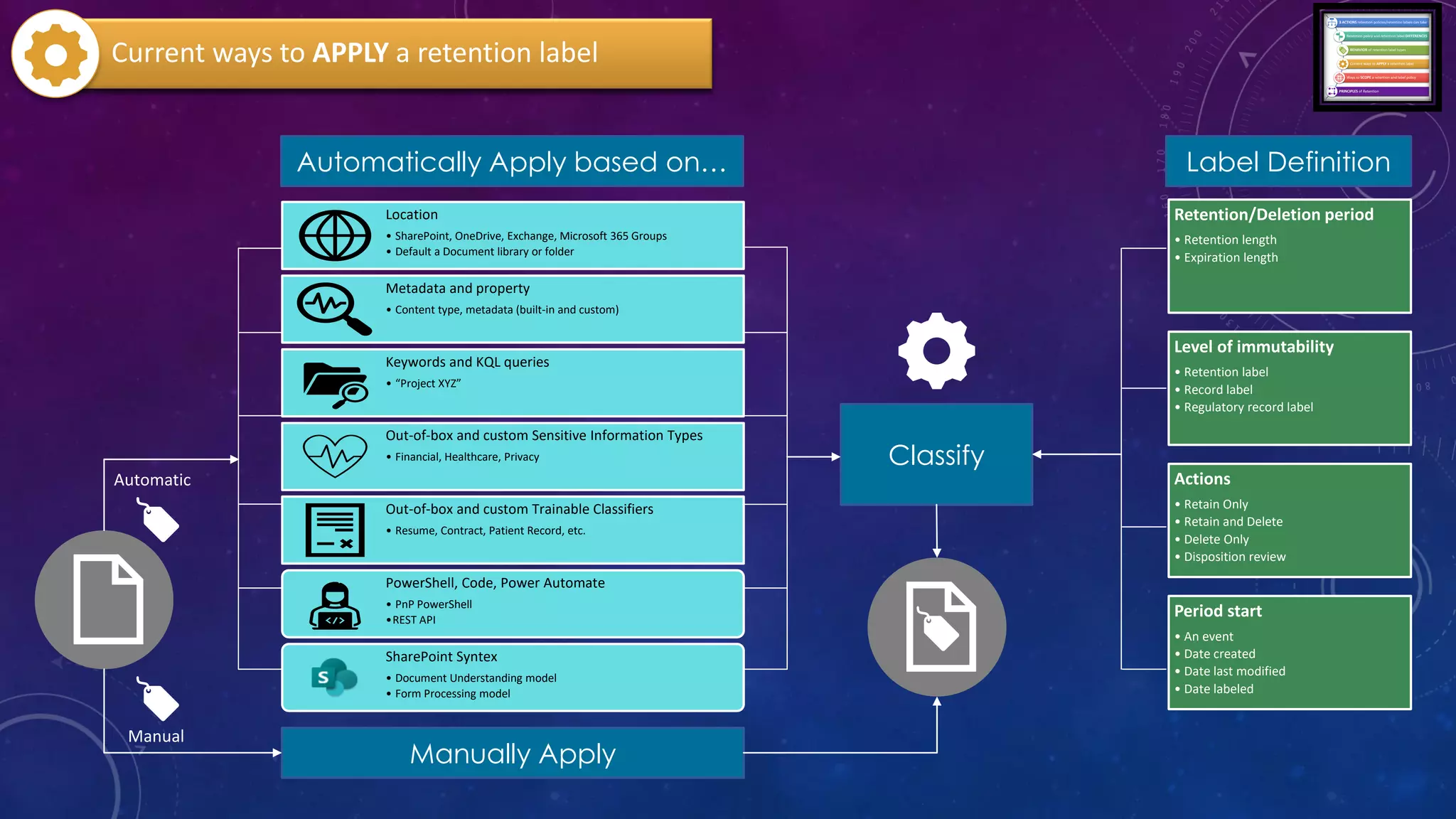
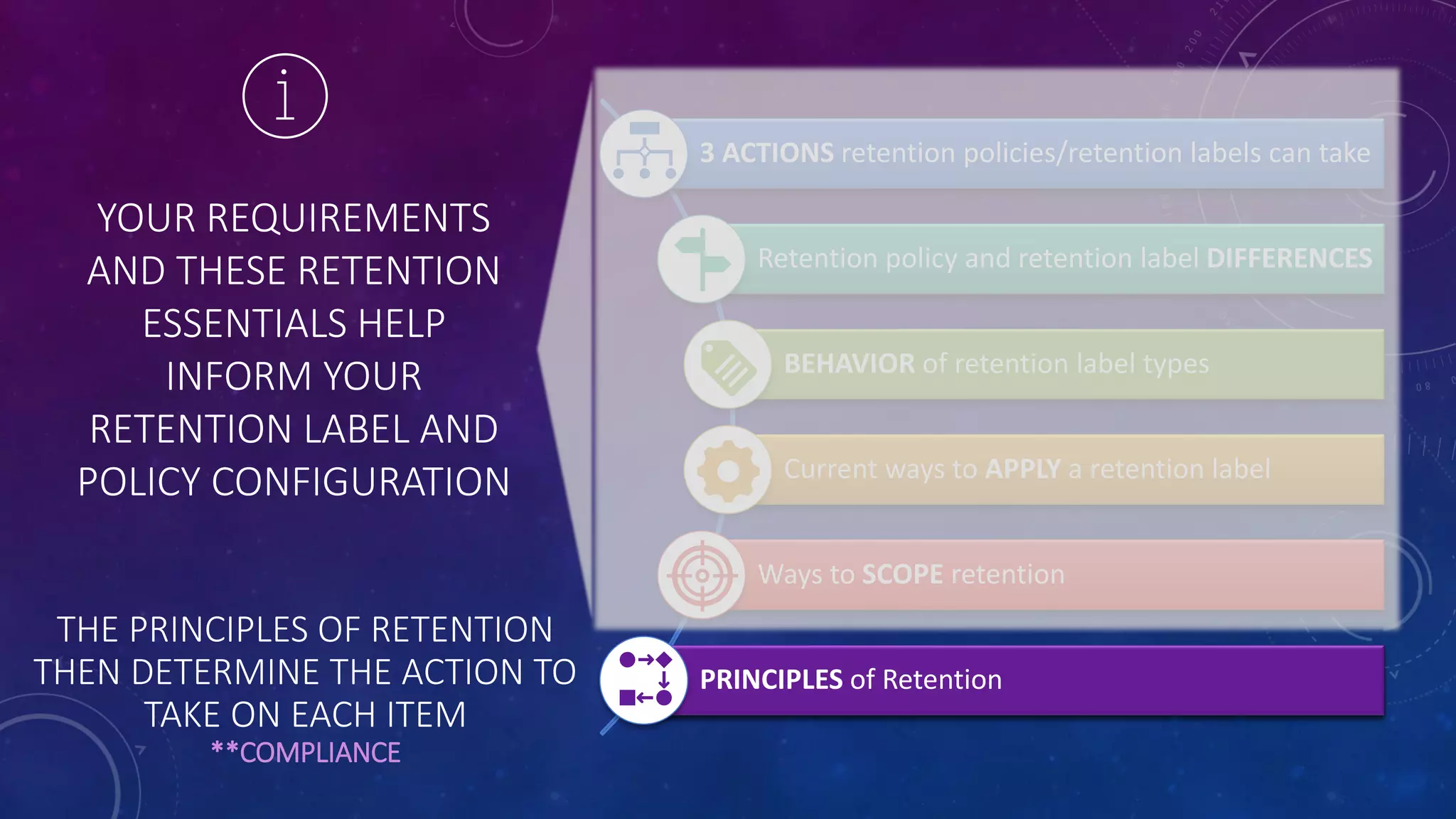
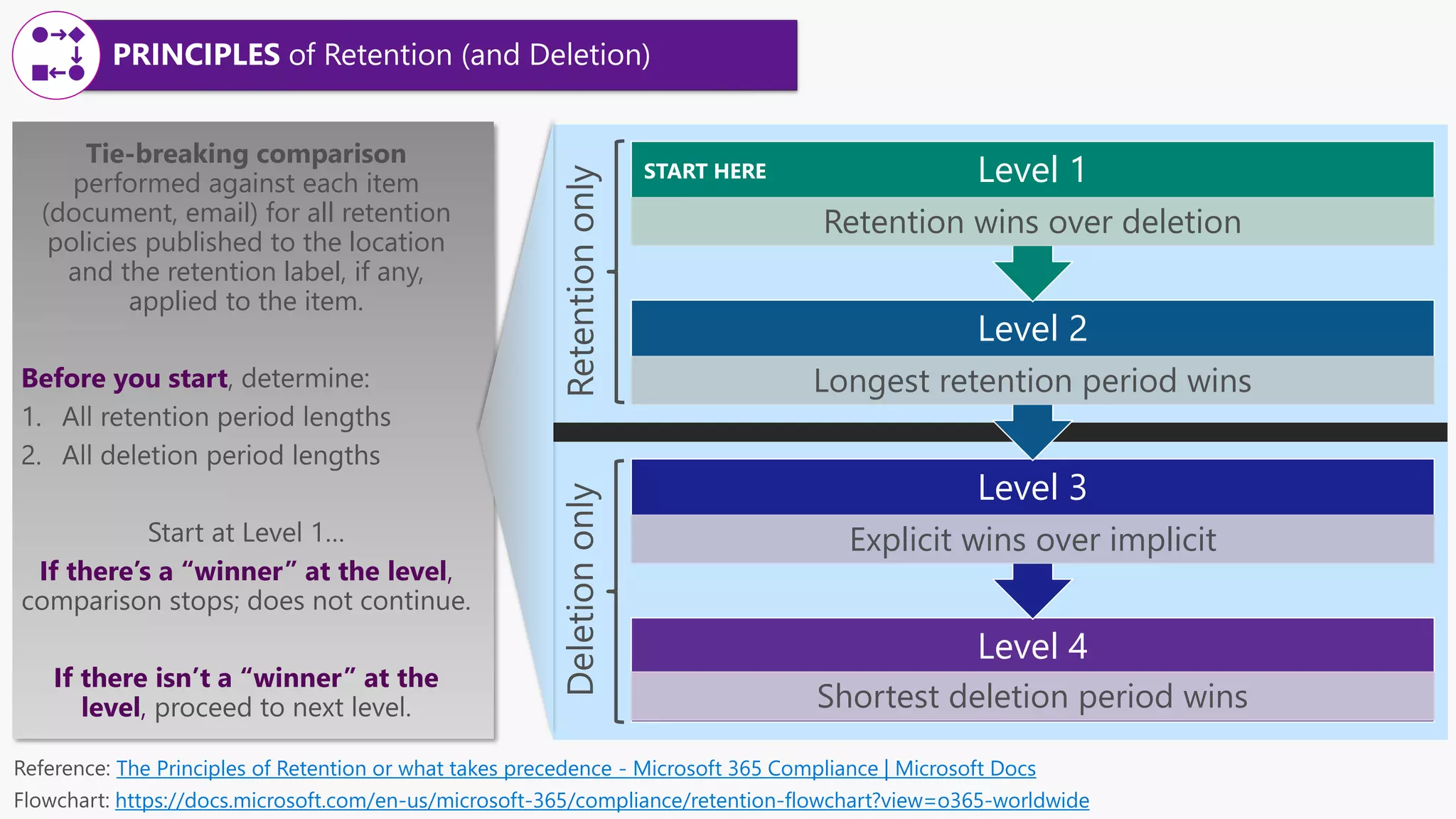
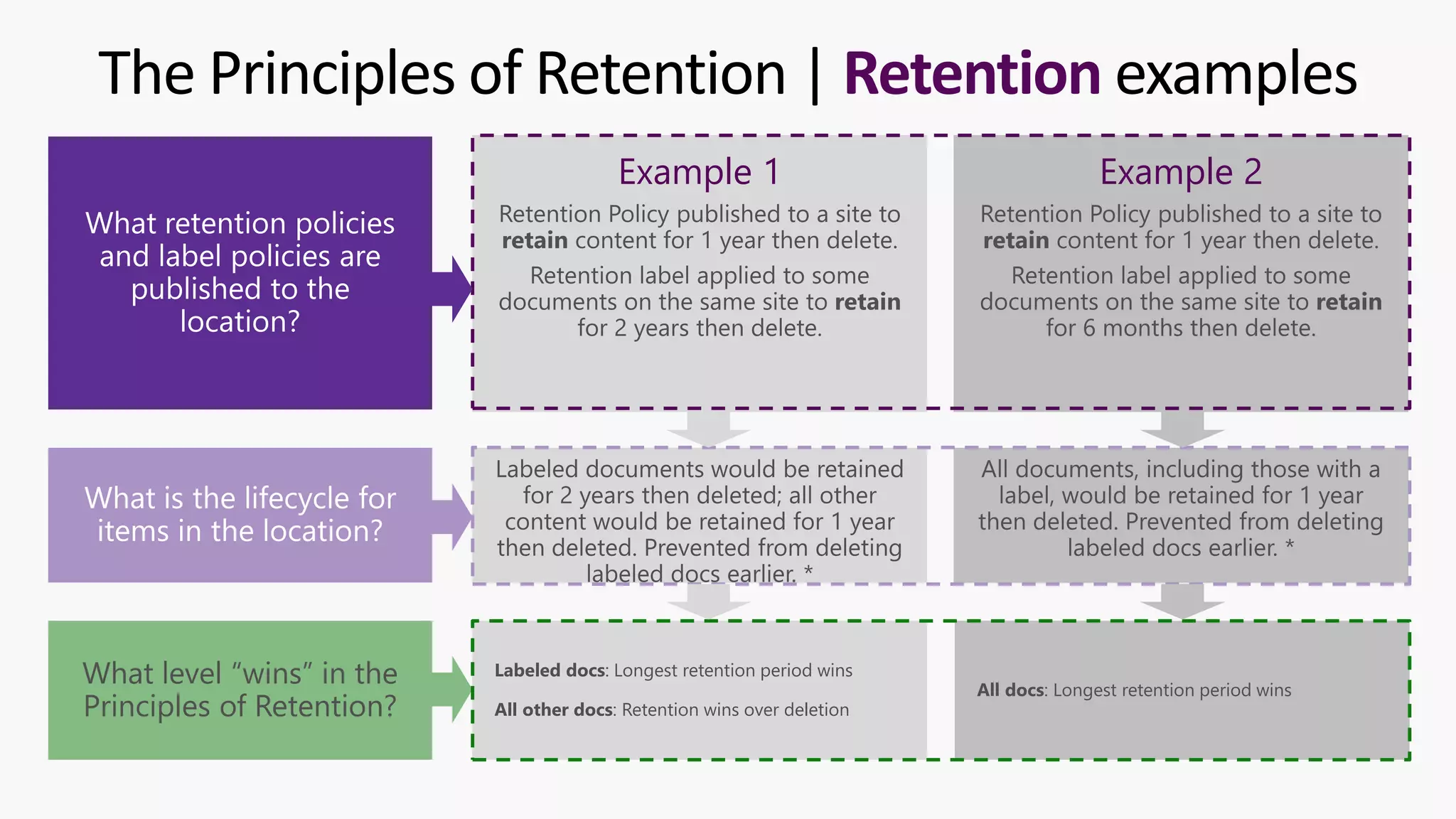
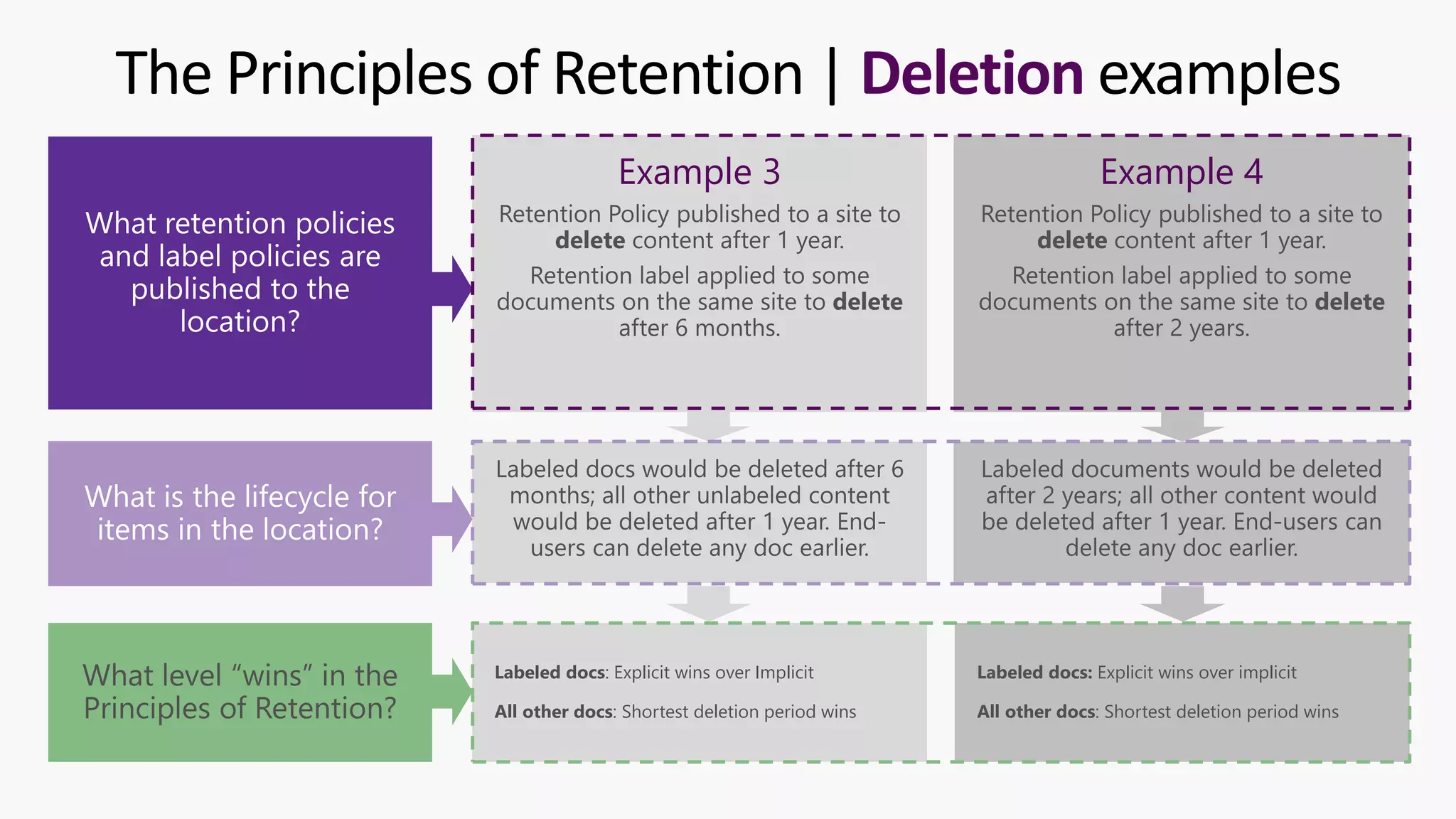
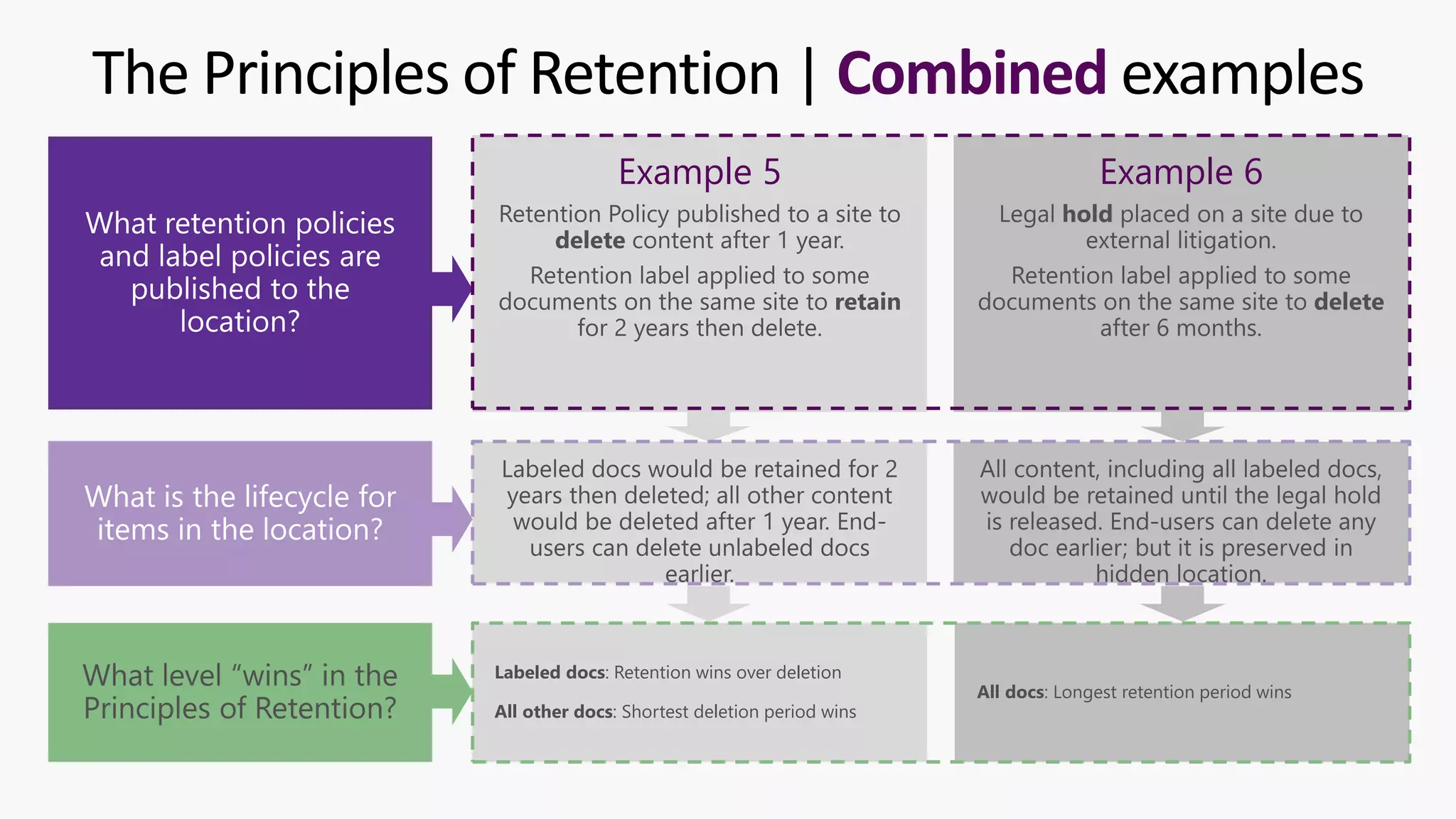
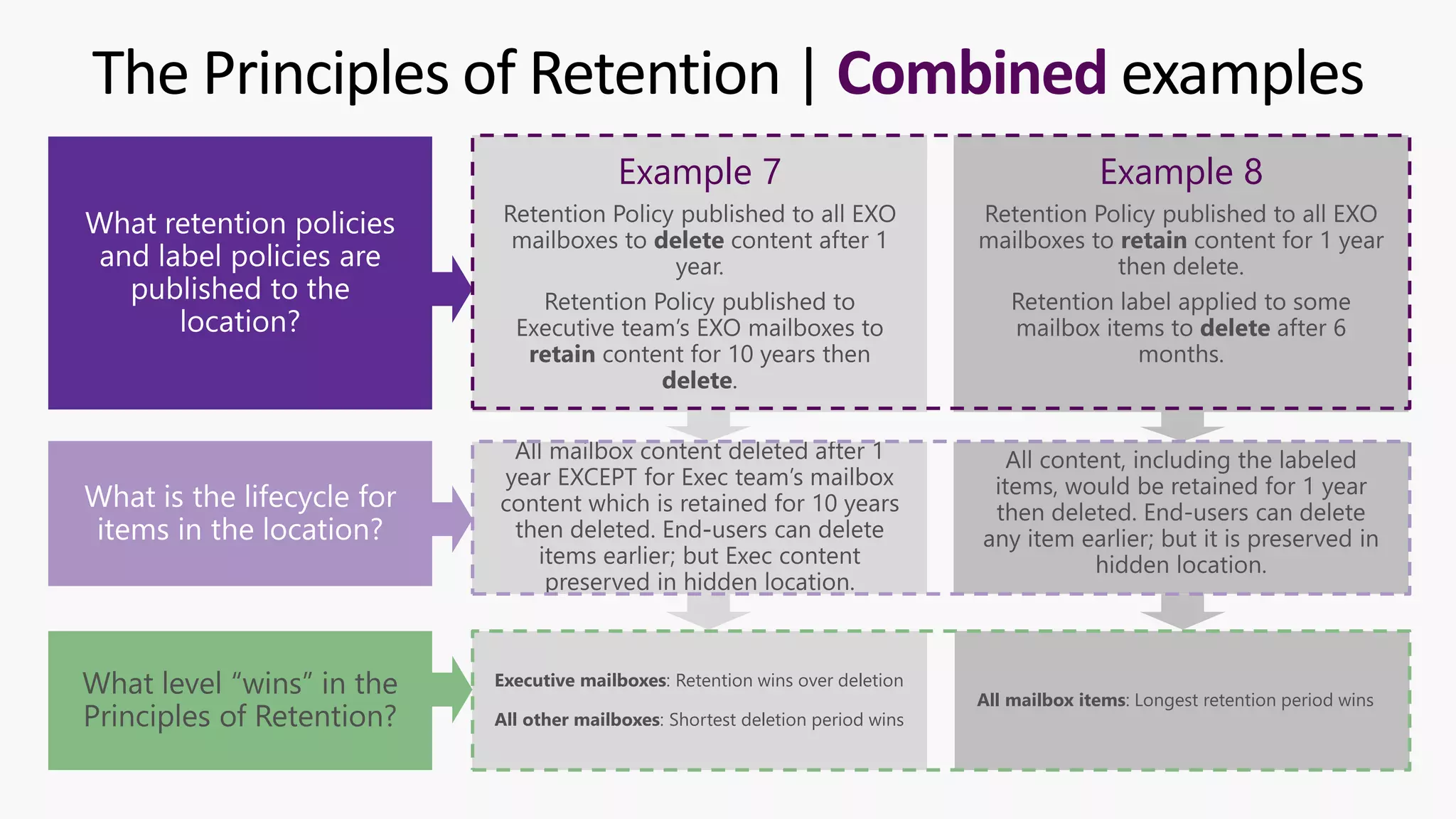
This document provides a summary of a presentation on the principles of retention in Microsoft 365. It discusses why understanding the principles is important for ensuring compliance with retention requirements. The presentation covers the essentials to understand before learning the principles, including how retention policies and labels differ and how they can be applied. It then walks through the four principles of retention - that retention wins over deletion, the longest retention period wins, explicit settings win over implicit ones, and the shortest deletion period wins. Examples are provided to illustrate how the principles are applied.