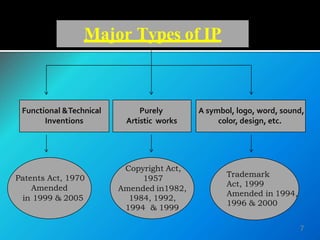
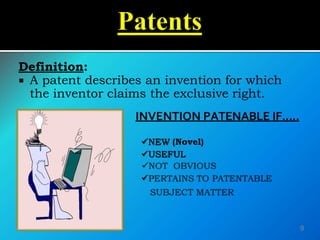
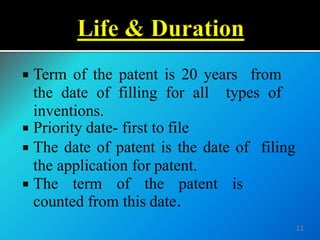
This document provides an overview of intellectual property (IP) laws in India. It discusses the main types of IP including patents, trademarks, copyright, and geographical indications. For each type of IP, it outlines the governing acts, eligibility requirements, rights and protections provided, infringement issues, and case studies. The purpose is to increase awareness and understanding of IP laws and how they can be utilized to legally protect creations and innovations.






![(1) It is covered under the Act called the
Patents Act, 1970 [Amended by
Patents Act, 2005]
(2) It extends to the whole of India.
(3) It shall come into force on such date
as the Central Government may
publish, by notification in
the Official Gazette.
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iprshatrughan-191112184357/85/IPR-8-320.jpg)











![ The Indian CopyrightAct,1957 governs
the system of copyrights in India.
[Amended in 1982, 1984, 1992, 1994
& 1999]
Meaning : It is a right which Grants
protection to the unique expression of
Ideas.
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iprshatrughan-191112184357/85/IPR-22-320.jpg)













