- The Intellectual Property Office is an executive agency within the Department of Business, Innovation and Skills that helps stimulate innovation and raise competitiveness through intellectual property rights.
- An IP baseline survey found that most UK businesses do not understand or utilize intellectual property properly - they do not know the value of their IP, have IP policies, or correctly identify ownership.
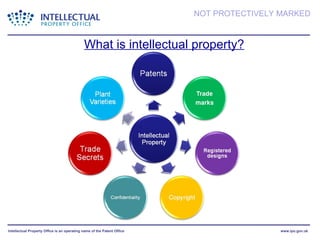
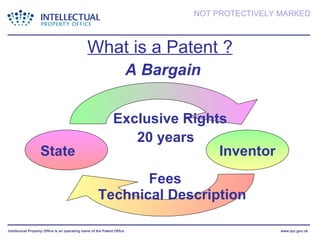
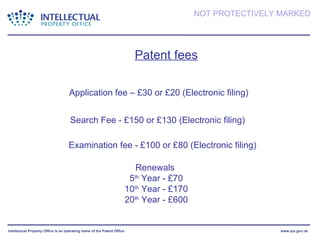
- The presentation discusses trademarks, registered designs, patents, and copyright - what they protect, requirements for registration, fees, and duration of protection. It emphasizes the importance of intellectual property for businesses.






































![Thank you Gary Townley [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipo-120215071642-phpapp01/85/An-Introduction-To-Intellectual-Property-By-Intellectual-Property-Office-44-320.jpg)