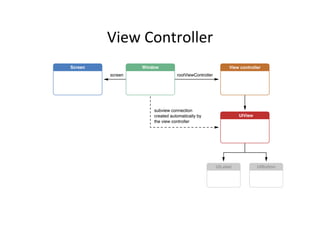
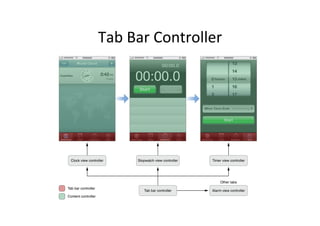
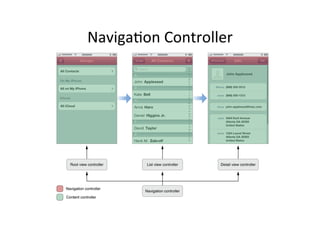
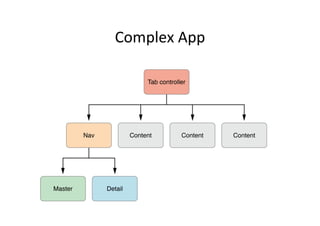
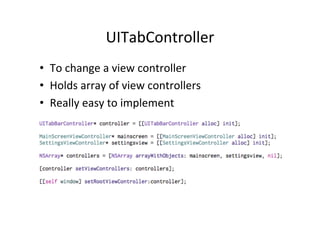
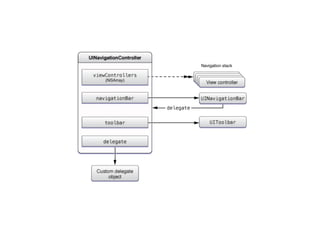
The document discusses iOS view controllers. It explains that a typical iOS app has multiple screens, each implemented with a view controller class. A view controller holds a reference to the UIView that is visible on screen. It describes how to add a button to a view controller's view. It also discusses setting a view controller as the root controller of a window, and implementing the UI in a XIB file. It differentiates between content and container view controllers. It provides an overview of tab bar controllers and navigation controllers, and how they are used to manage multiple screens and hierarchical data in an app.




![Adding
a
BuIon
to
the
View
of
ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// Initialize a view, this could be a custom view also..
UIButton* button =
[UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeRoundedRect];
[button setTitle:@"Main1" forState: UIControlStateNormal];
// Add the view to the controller
[self setView: button];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/view-controllers-pptx-121111034544-phpapp01/85/iOS-View-Controllers-6-320.jpg)
![Root
Controller
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:
(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen mainScreen] bounds]];
// Override point for customization after application launch.
MainScreenViewController* mainscreen = [[MainScreenViewController alloc] init];
[[self window] setRootViewController:mainscreen];
self.window.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];
return YES;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/view-controllers-pptx-121111034544-phpapp01/85/iOS-View-Controllers-7-320.jpg)







![Init
in
more
detail
• When
iniMalizing
the
controller
–
SettingsViewController* settingsview =
[[SettingsViewController alloc] init];
• This
is
equivalent
to
this!
– SettingsViewController* settingsview =
[[SettingsViewController alloc]
initWithNibName:nil bundle:nil];
• What
happens
if
nibname
is
nil?
– Search
for
a
xib
file
whose
name
is
the
same
as
your
class
and
search
inside
of
this
app
bundle!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/view-controllers-pptx-121111034544-phpapp01/85/iOS-View-Controllers-19-320.jpg)



![CreaMng
a
UINavigaMonController
// Create view controller
SettingsViewController* settingsview = [[SettingsViewController
alloc] init];
// Create navigation controller.
// Initialize it with the first screen
UINavigationController* navController =
[[UINavigationController alloc]
initWithRootViewController:settingsview];
// Add navigation controller to window
[[self window] setRootViewController:navController];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/view-controllers-pptx-121111034544-phpapp01/85/iOS-View-Controllers-24-320.jpg)
![Modifying
NavigaMon
Stack
• Add
another
view
to
stack
– [navController
pushViewController:otherViewController
animated:YES];
• To
get
pointer
to
navController
in
ViewController,
use
• [[self
navigationController] pushViewController:otherV
iewController animated:YES];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/view-controllers-pptx-121111034544-phpapp01/85/iOS-View-Controllers-25-320.jpg)
![Passing
informaMon
// Get text from UITextField
NSString* myText = [[self someTextField] text];
// Create the view controller
SettingsView1Controller* sv1 = [[SettingsView1Controller alloc] init];
// Pass the text to the view controller
[sv1 setText: myText];
// Push the view controller to nav controller. viewDidLoad is
// called!
[[self navigationController] pushViewController:sv1 animated:YES];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/view-controllers-pptx-121111034544-phpapp01/85/iOS-View-Controllers-26-320.jpg)
![Receiving
informaMon
@interface SettingsView1Controller : UIViewController
{
}
// Attribute and set+get methods for text
@property NSString* text;
@property IBOutlet UILabel* label;
* * *
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view from its nib.
// Set the given text to label:
[[self label] setText: [self text]];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/view-controllers-pptx-121111034544-phpapp01/85/iOS-View-Controllers-27-320.jpg)


![UINavigaMonItem
• Set
a
Mtle
– UINavigationItem *n = [self navigationItem];
– [n setTitle:@"Settings"];
• Other
properMes
– MtleView
-‐>
Can
have
any
view
on
navigaMon
bar
– rightBarBuIonItem
-‐>
another
buIon
to
the
right
– See
documentaMon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/view-controllers-pptx-121111034544-phpapp01/85/iOS-View-Controllers-30-320.jpg)
