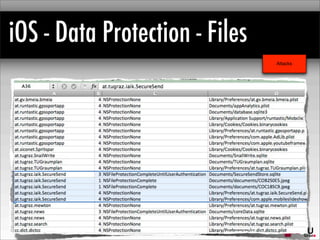
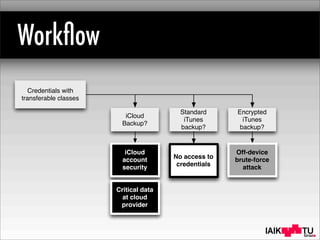
The document provides a comprehensive analysis of iOS encryption systems, focusing on device encryption and data protection for files and credentials. It discusses the mechanisms of encryption, key derivation, and security considerations, including potential attack vectors such as jailbreaking and brute-force attacks. Additionally, it covers backup strategies through iTunes and iCloud, highlighting the implications of encryption for user data security.