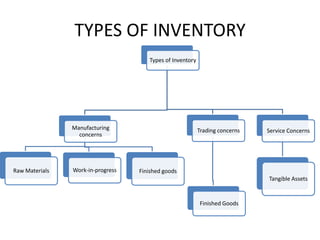
This document discusses inventory accounting systems. It describes two main systems - periodic and perpetual inventory systems. The periodic system involves taking a physical count of inventory at the end of an accounting period, while the perpetual system continuously records inventory receipts and issues in a stock ledger. The document also outlines the key differences between the two systems and various inventory valuation methods like FIFO, LIFO, weighted average cost.