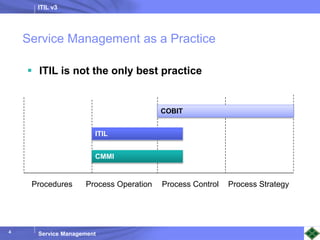
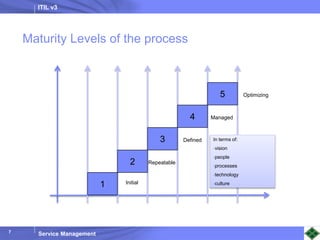
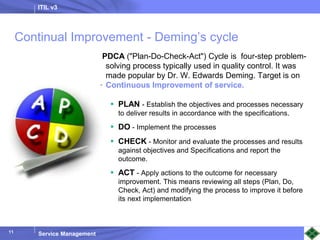
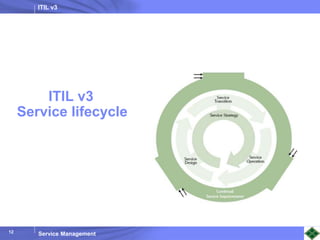
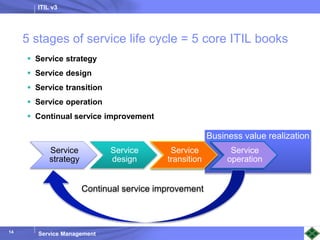
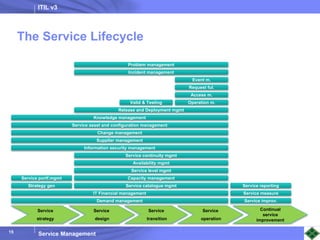
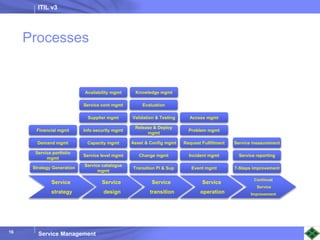
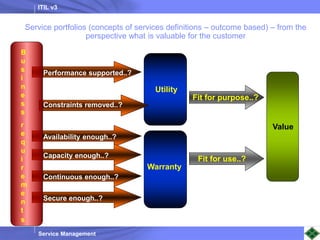
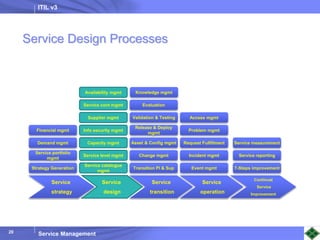
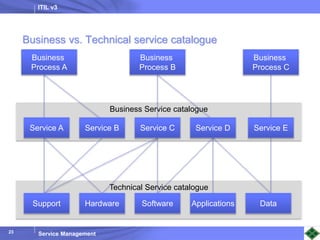
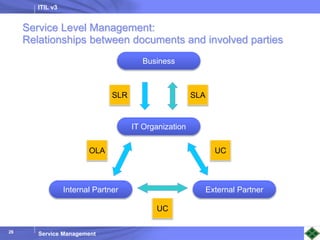
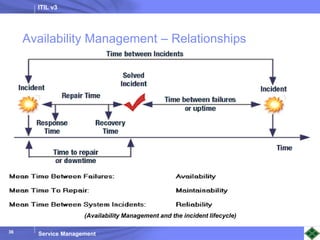
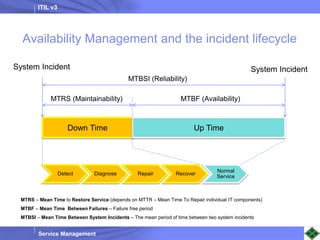
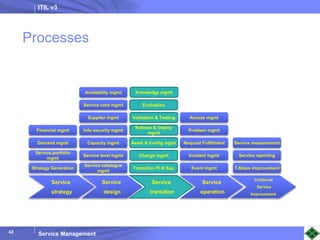
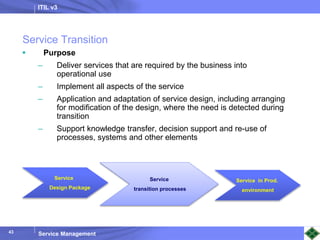
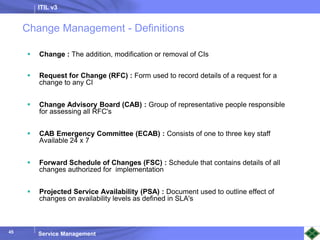
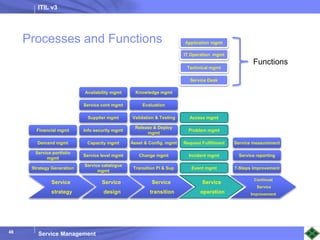
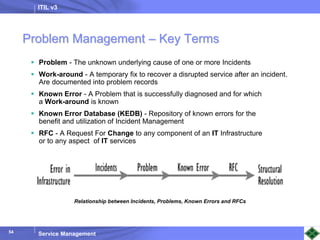
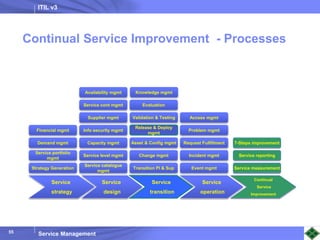
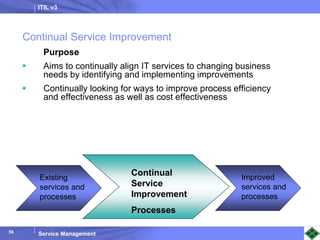
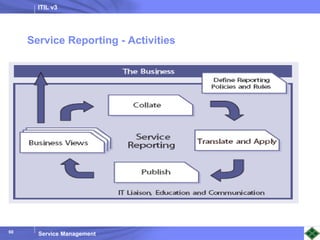
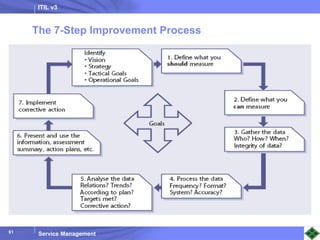
ITIL v3 provides guidance on best practices for IT service management. It describes key concepts like the service lifecycle, consisting of service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement. The document outlines various ITIL processes that fall within each stage of the lifecycle. It also discusses service management principles like having a service catalog, defining utility and warranty for services, and using metrics and key performance indicators to measure processes and drive improvement.