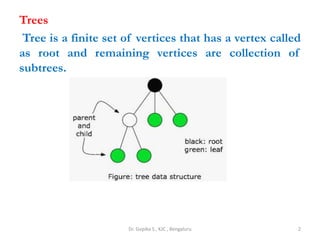
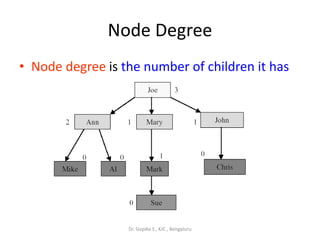
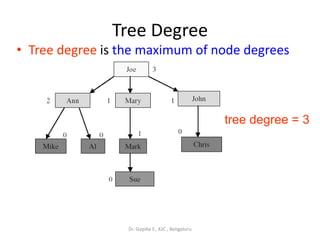
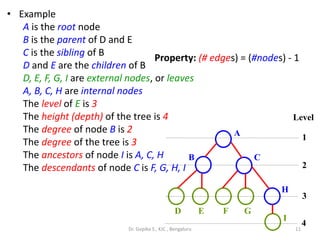
This document defines common tree terminology used in computer science. It explains that a tree is a set of vertices with one root vertex and other vertices arranged in subtrees. It defines key terms like nodes, degrees, edges, levels, ancestors and descendants. Examples are provided to illustrate a tree structure and how terms like root, parent, child, sibling apply to different nodes in the tree. Common tree traversal and processing concepts are also covered briefly.