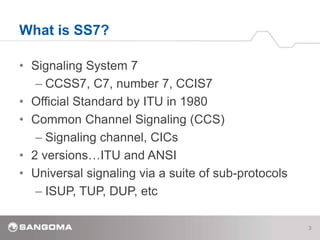
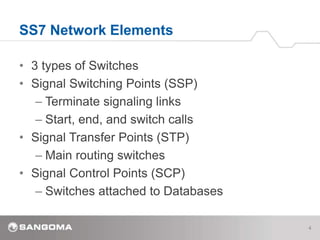
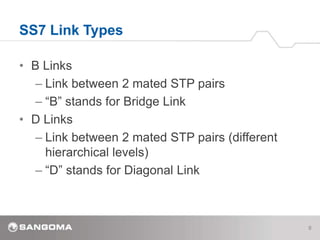
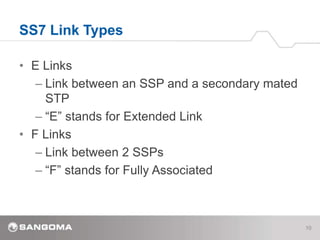
SS7 is a signaling protocol for establishing calls between two endpoints. It uses three main network elements - Signal Switching Points (SSPs) that originate and terminate calls, Signal Transfer Points (STPs) that route calls, and Signal Control Points (SCPs) connected to databases. The protocol has multiple layers including MTP1-3 for transport and routing, and ISUP for call setup. Key SS7 concepts are its link types (A-F links), basic call messages like IAM and REL, addressing using point codes, and signaling messages including MSUs that carry data between nodes.