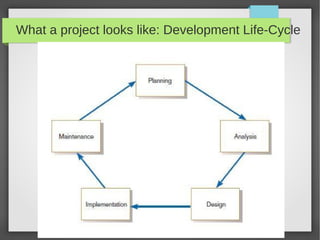
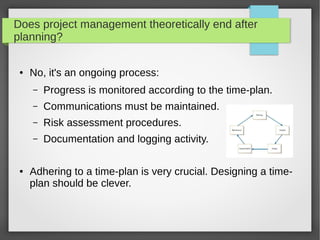
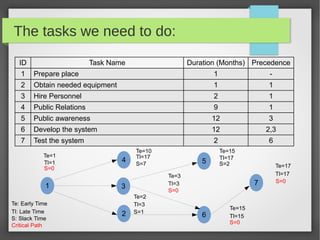
The document provides an introduction to project management, focusing on key concepts such as the stages of a project, including initiation, planning, execution, and closedown. It highlights the importance of a project baseline plan that encompasses problem definition, constraints, schedule, risk assessment, budget, and resources. Additionally, it discusses the significance of designing a professional time-plan and different diagramming methods like Gantt charts for tracking project progress.