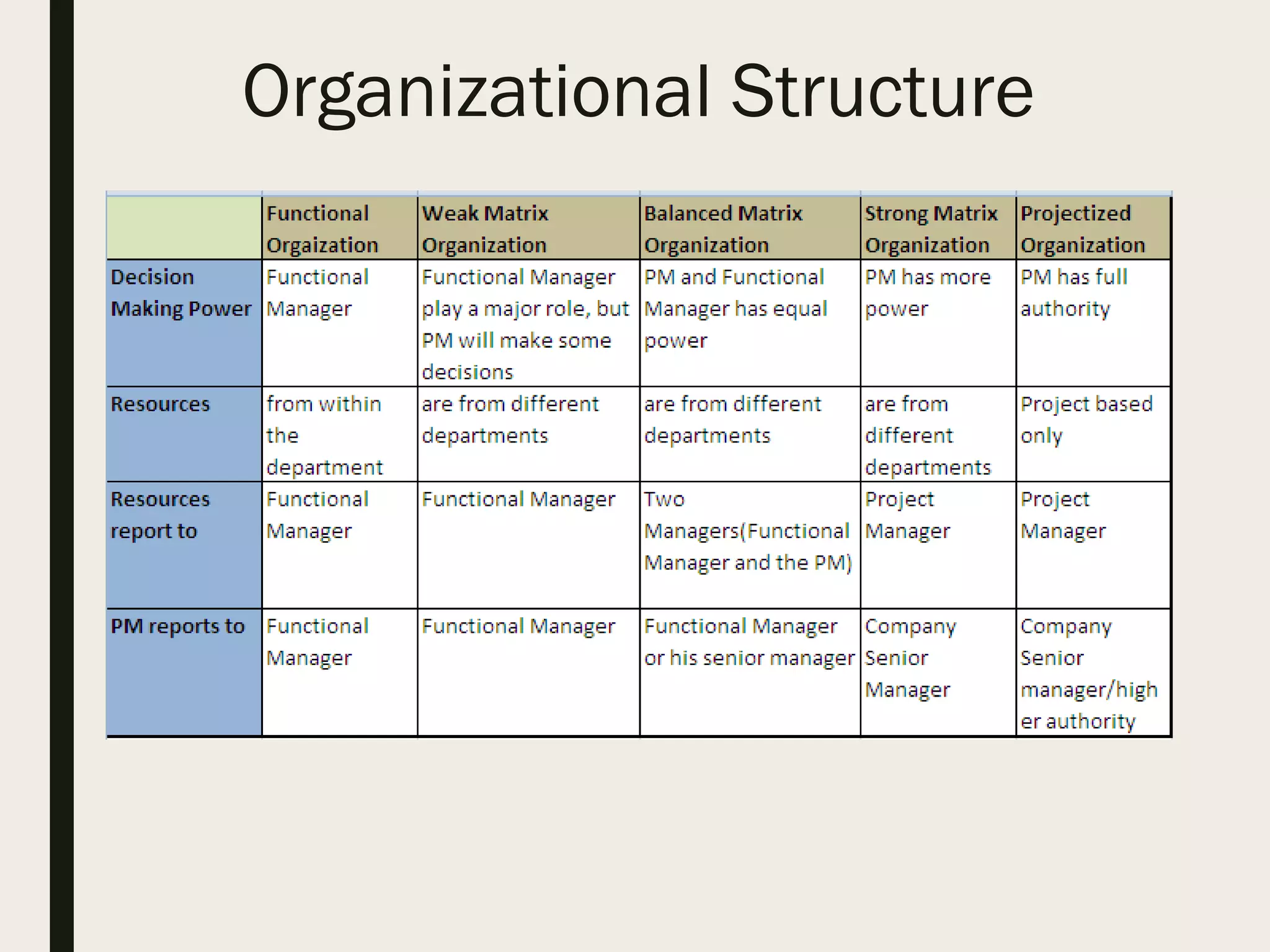
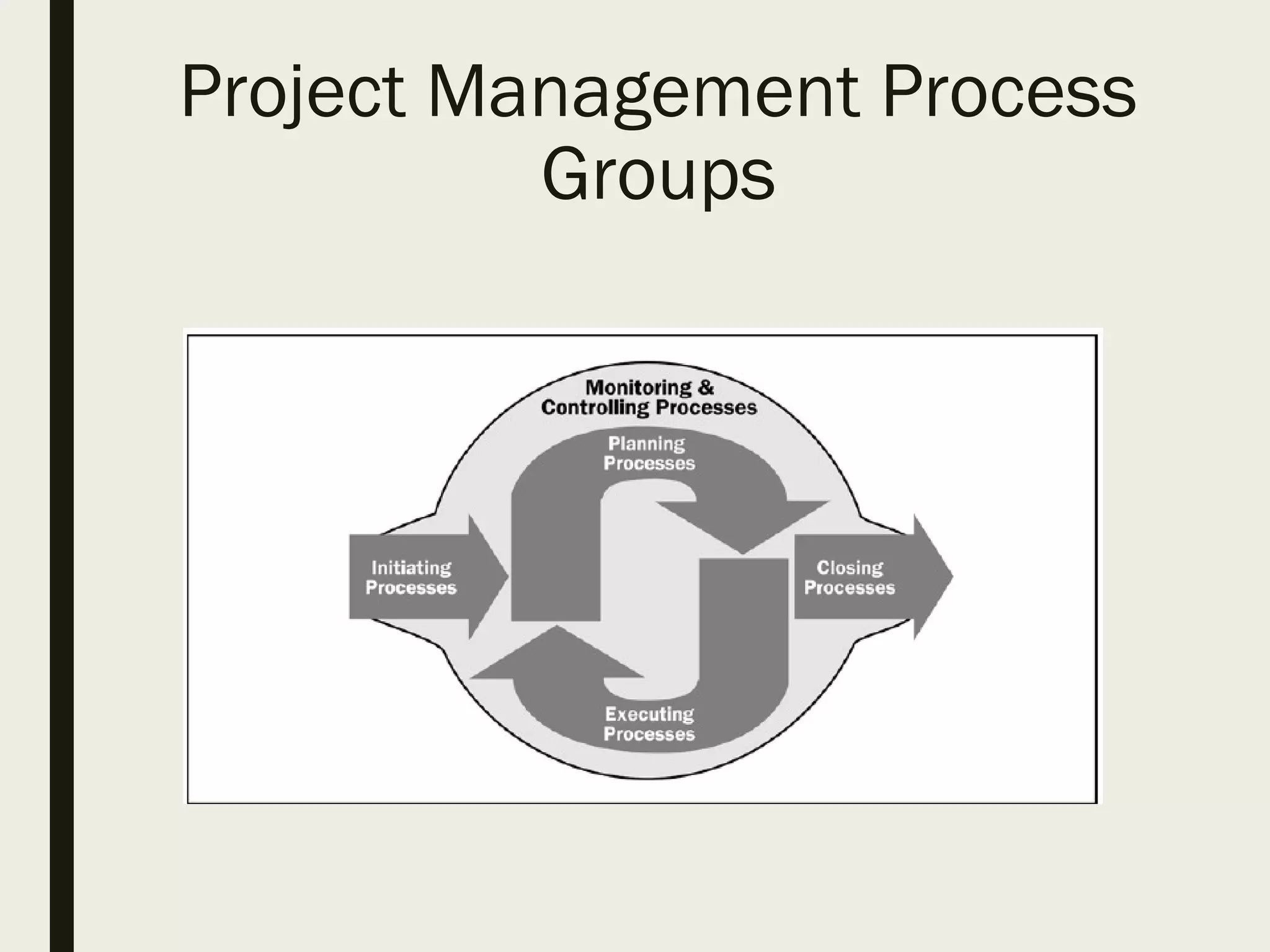
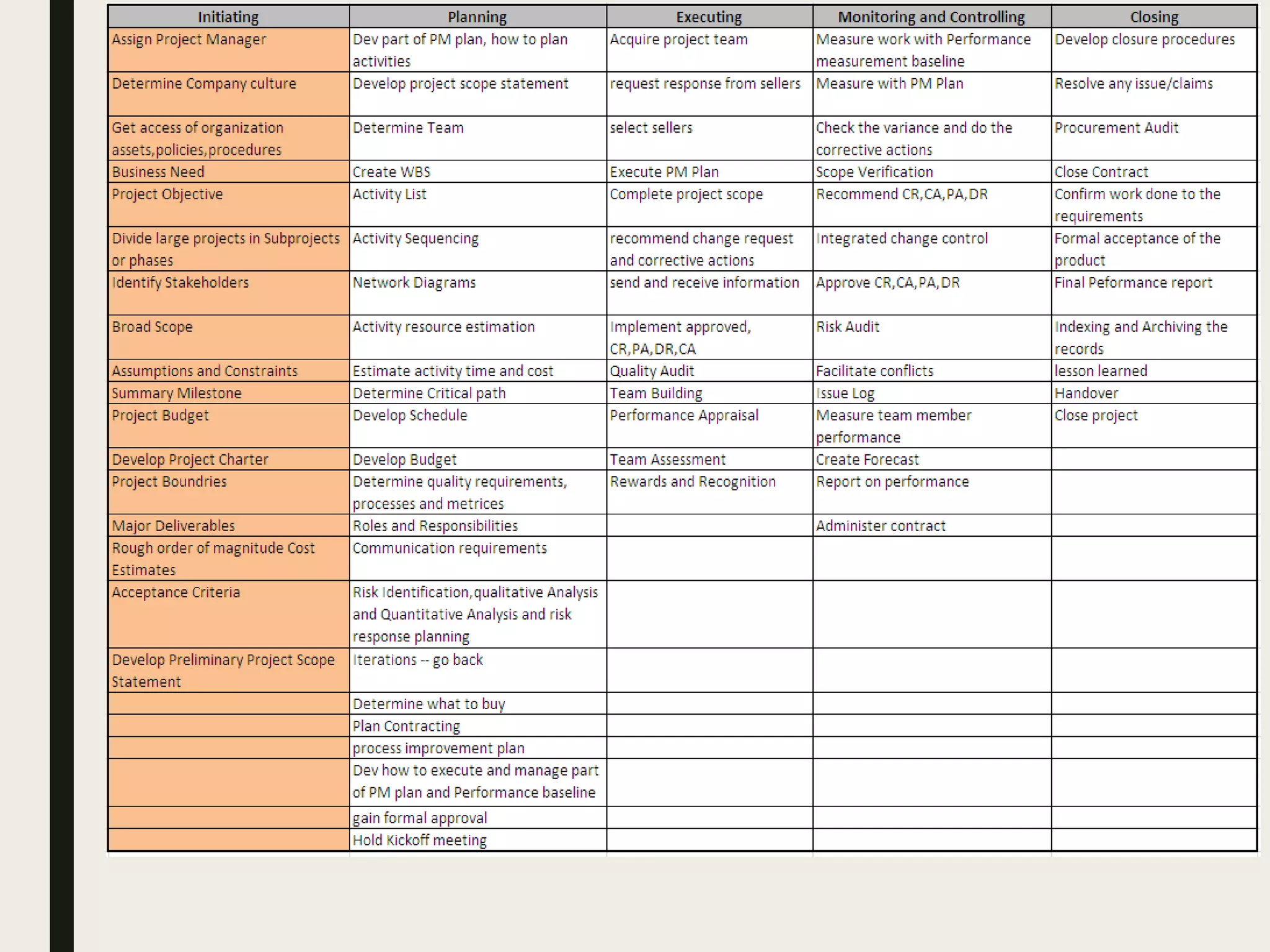
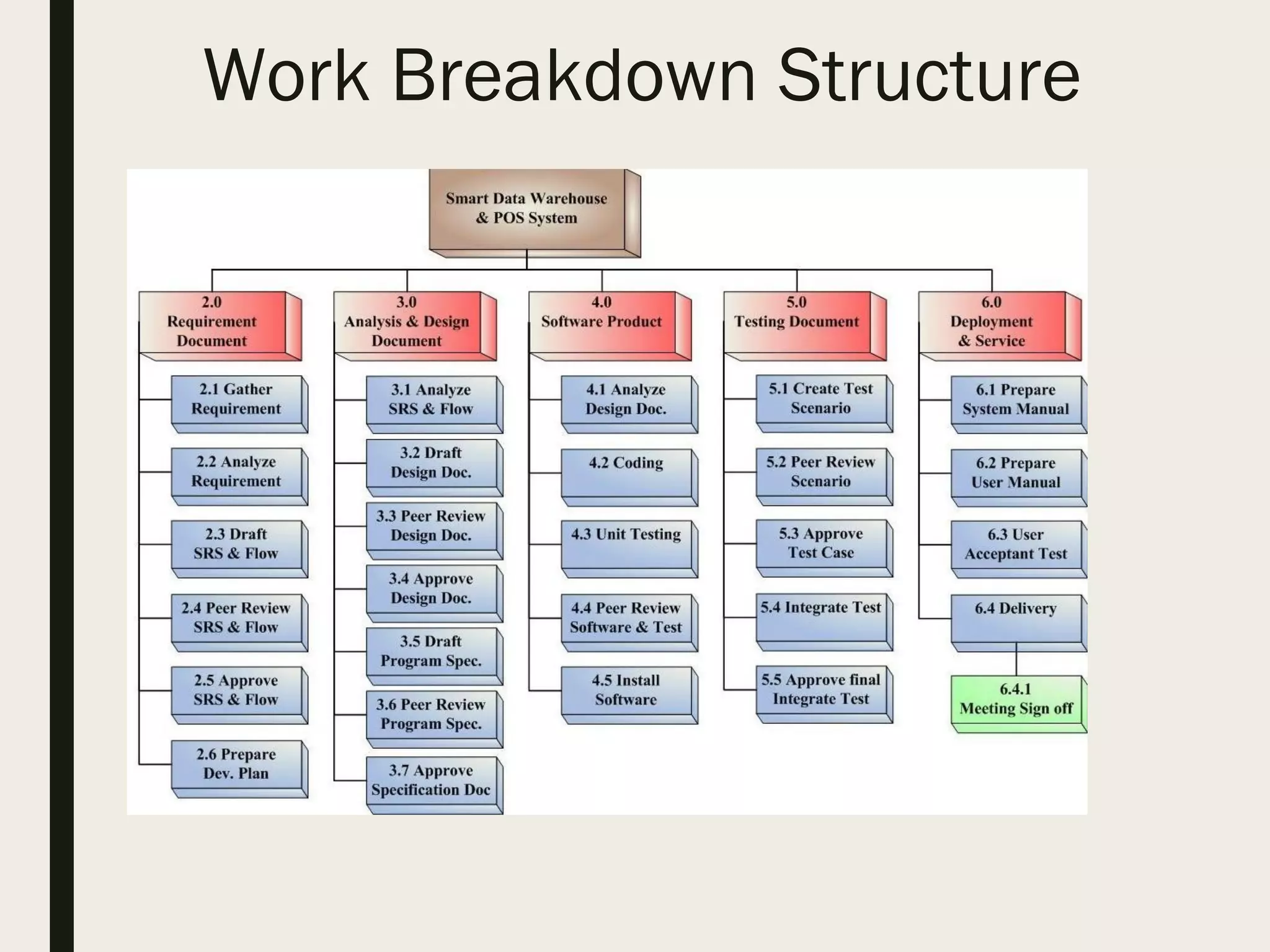
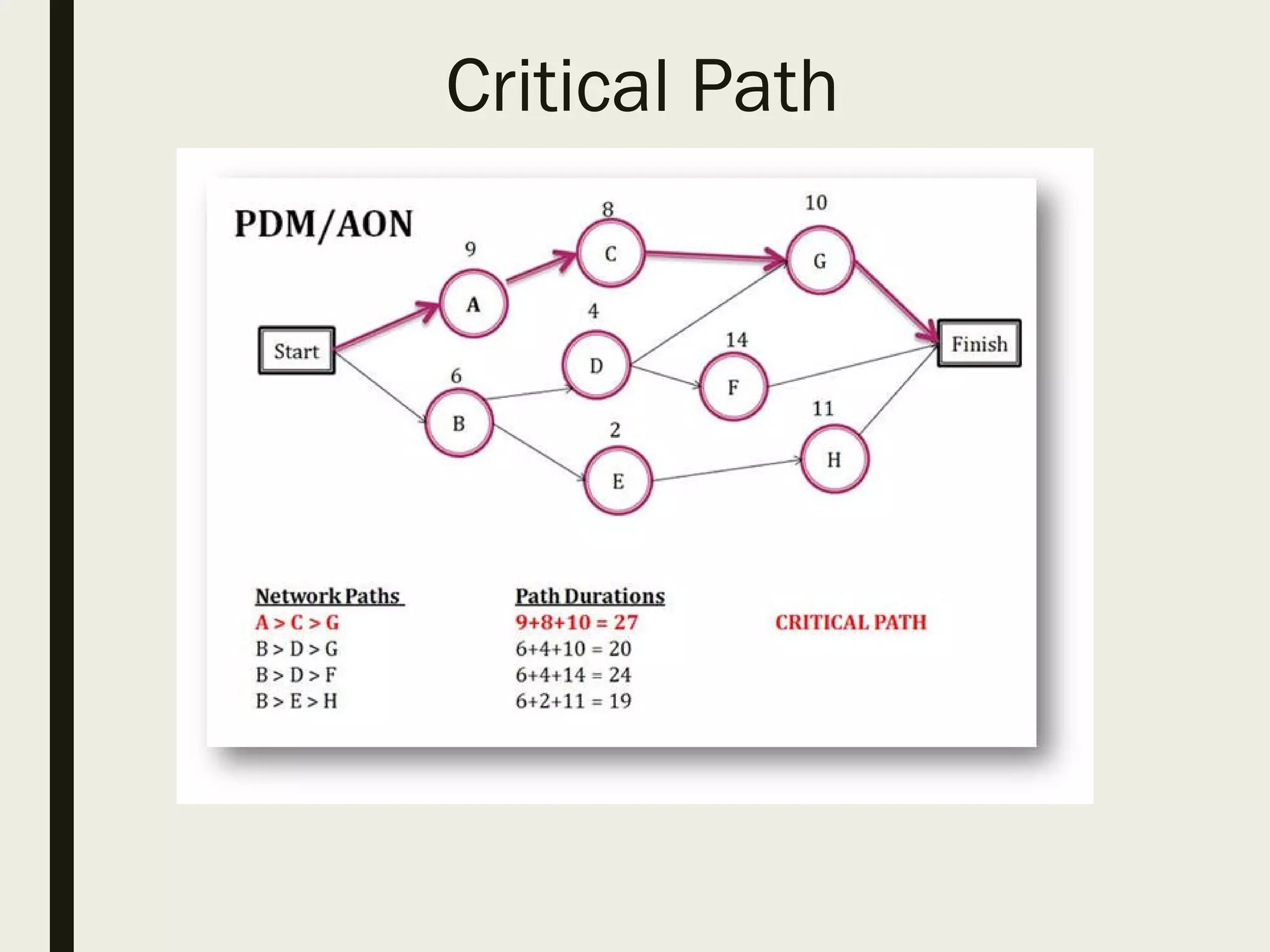
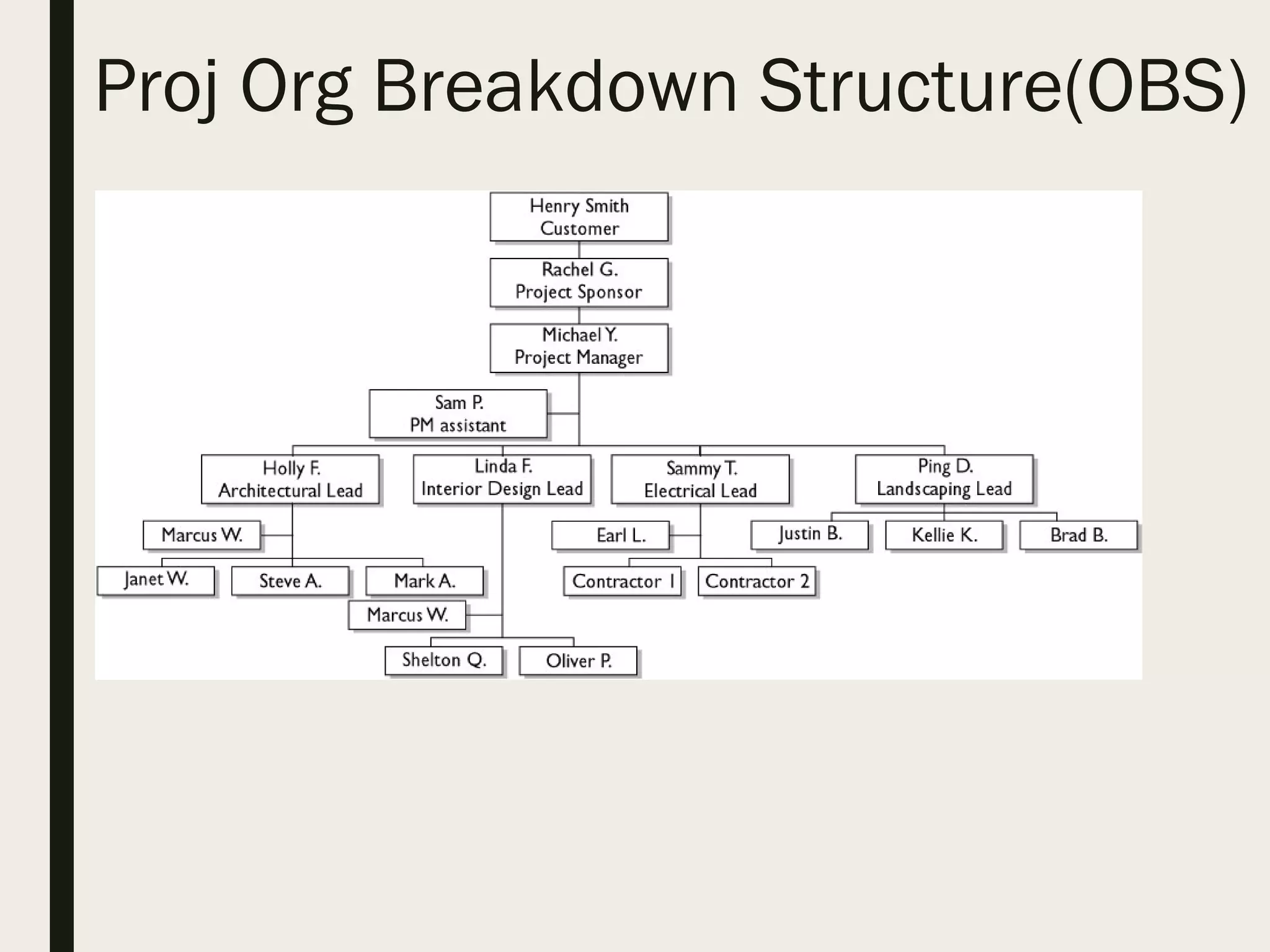
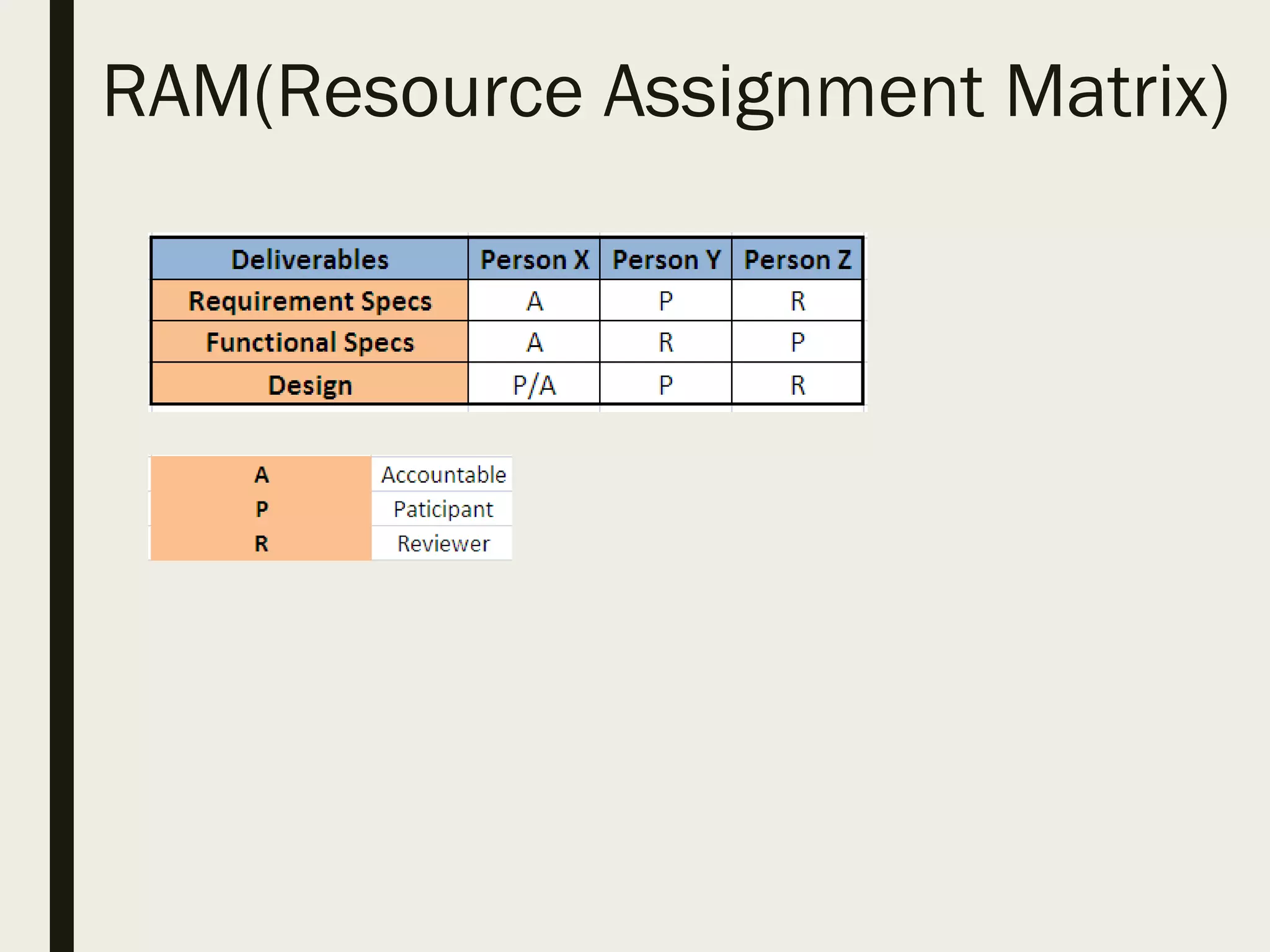
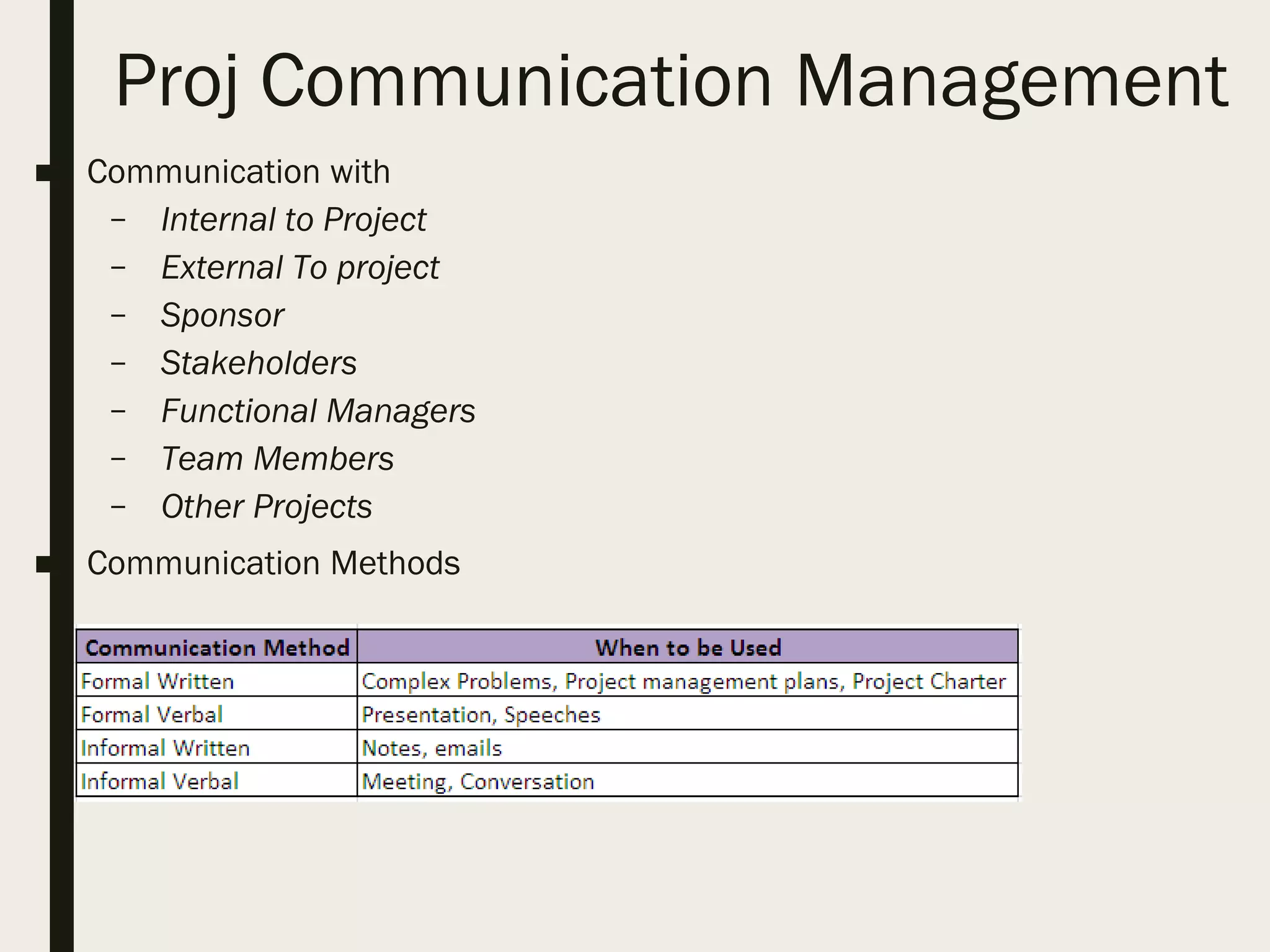
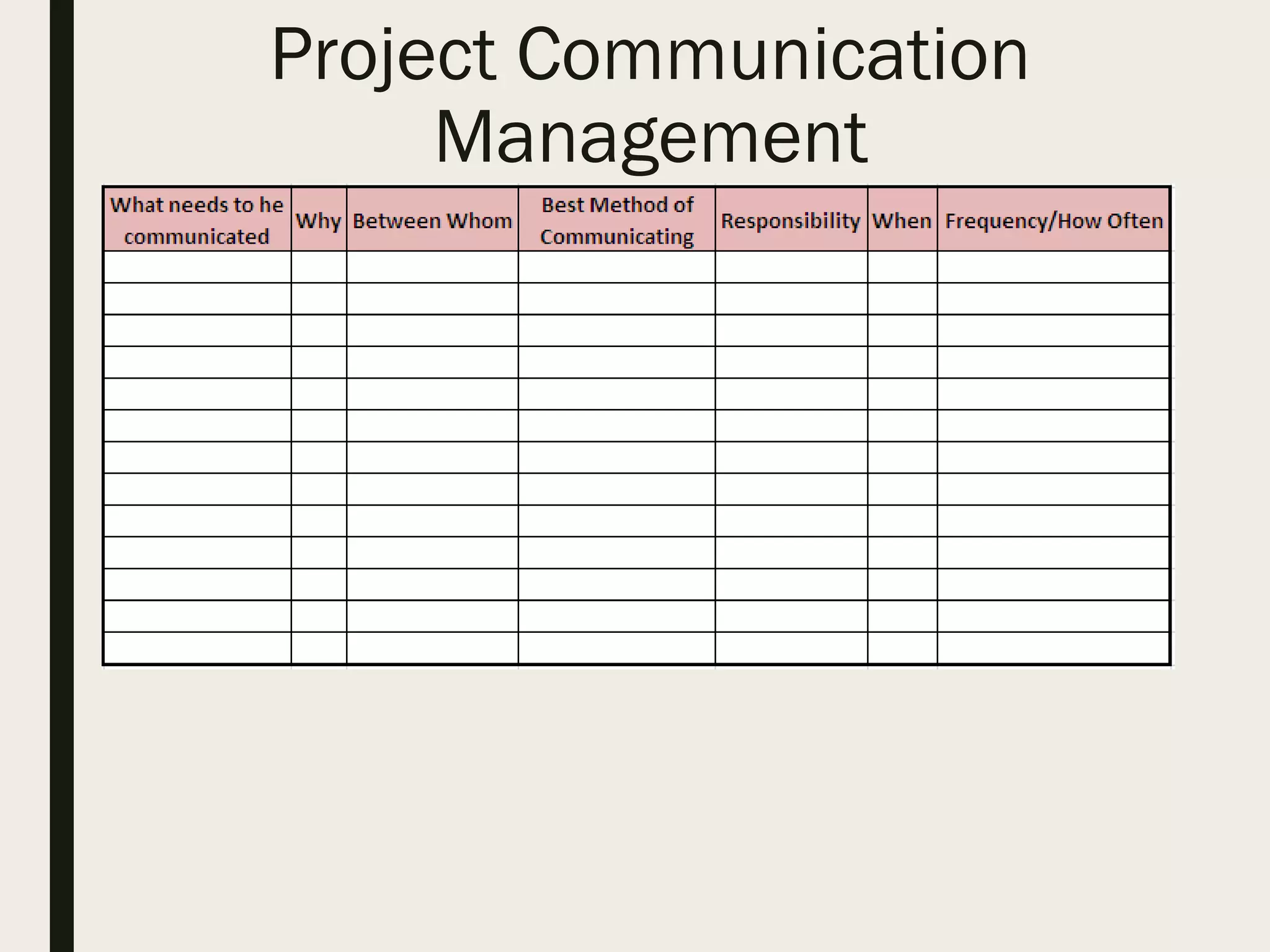
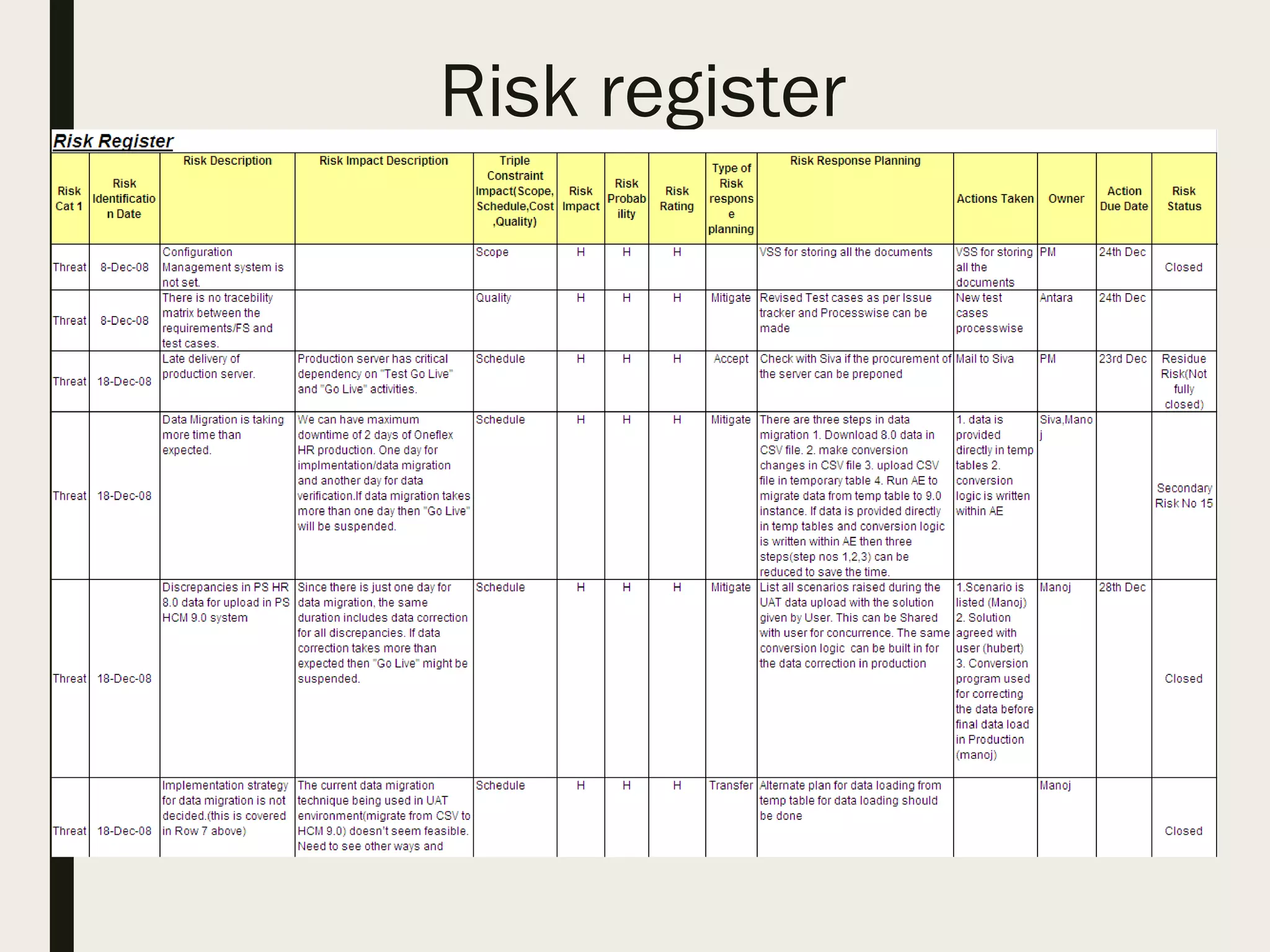
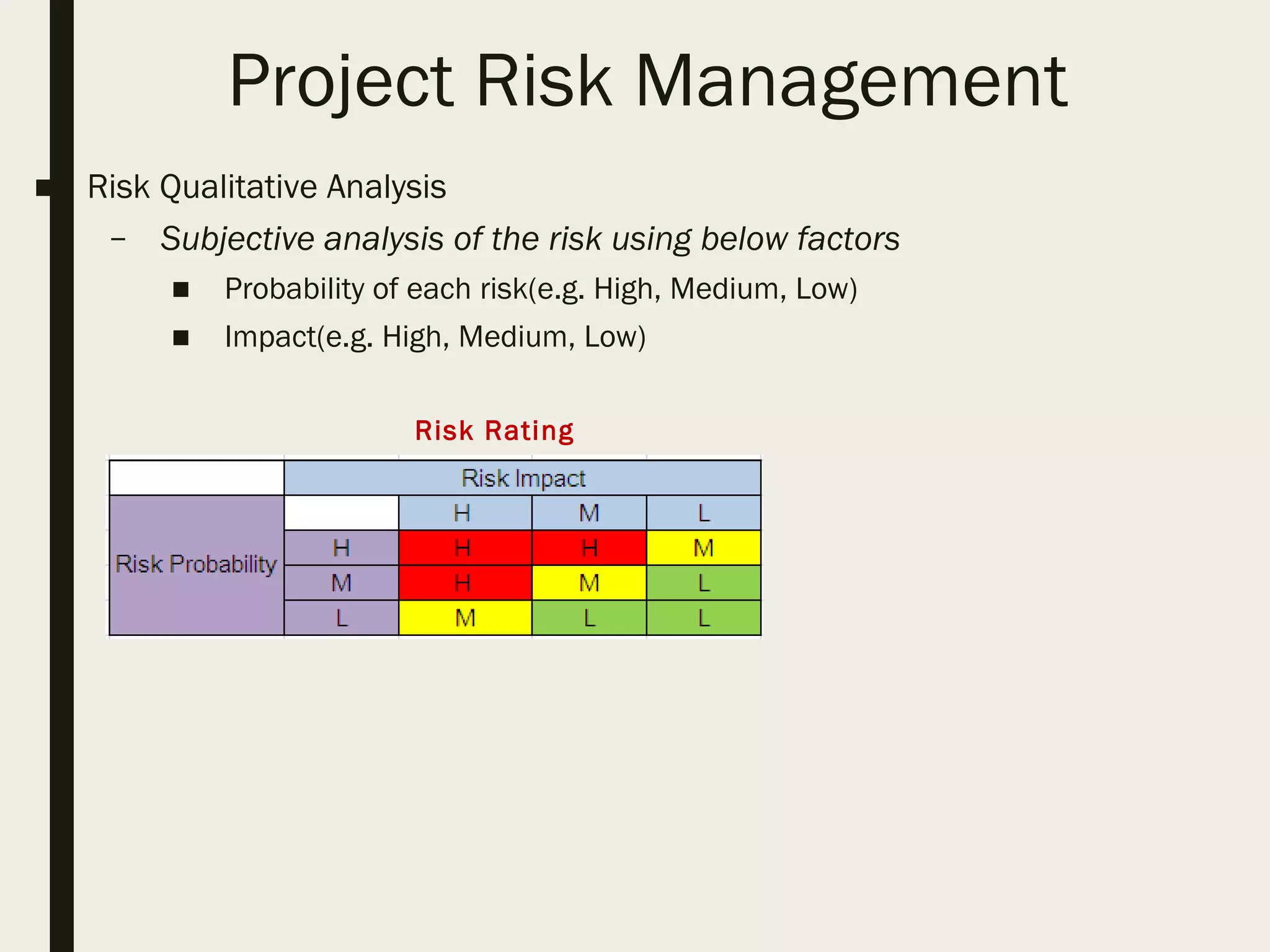
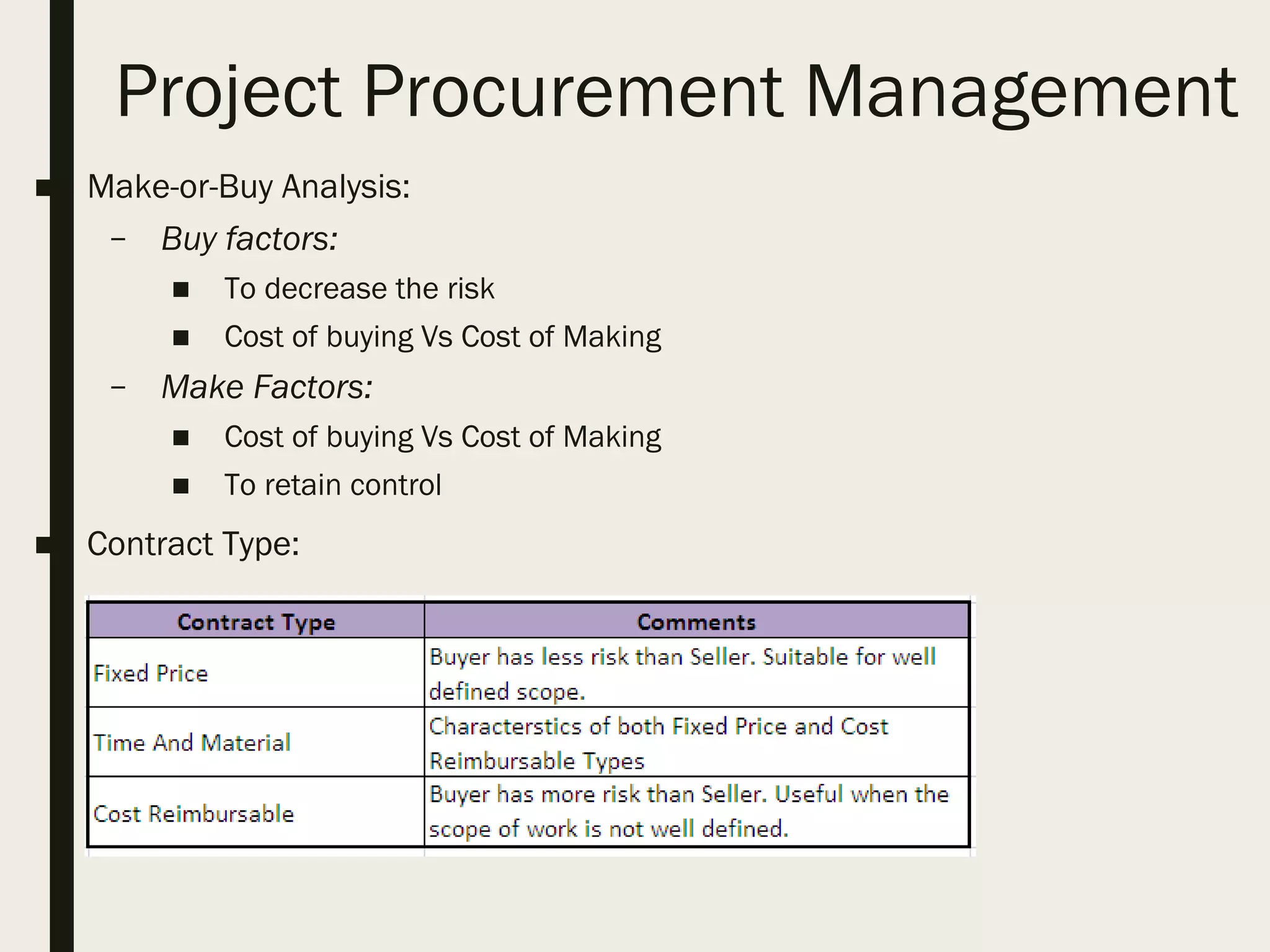
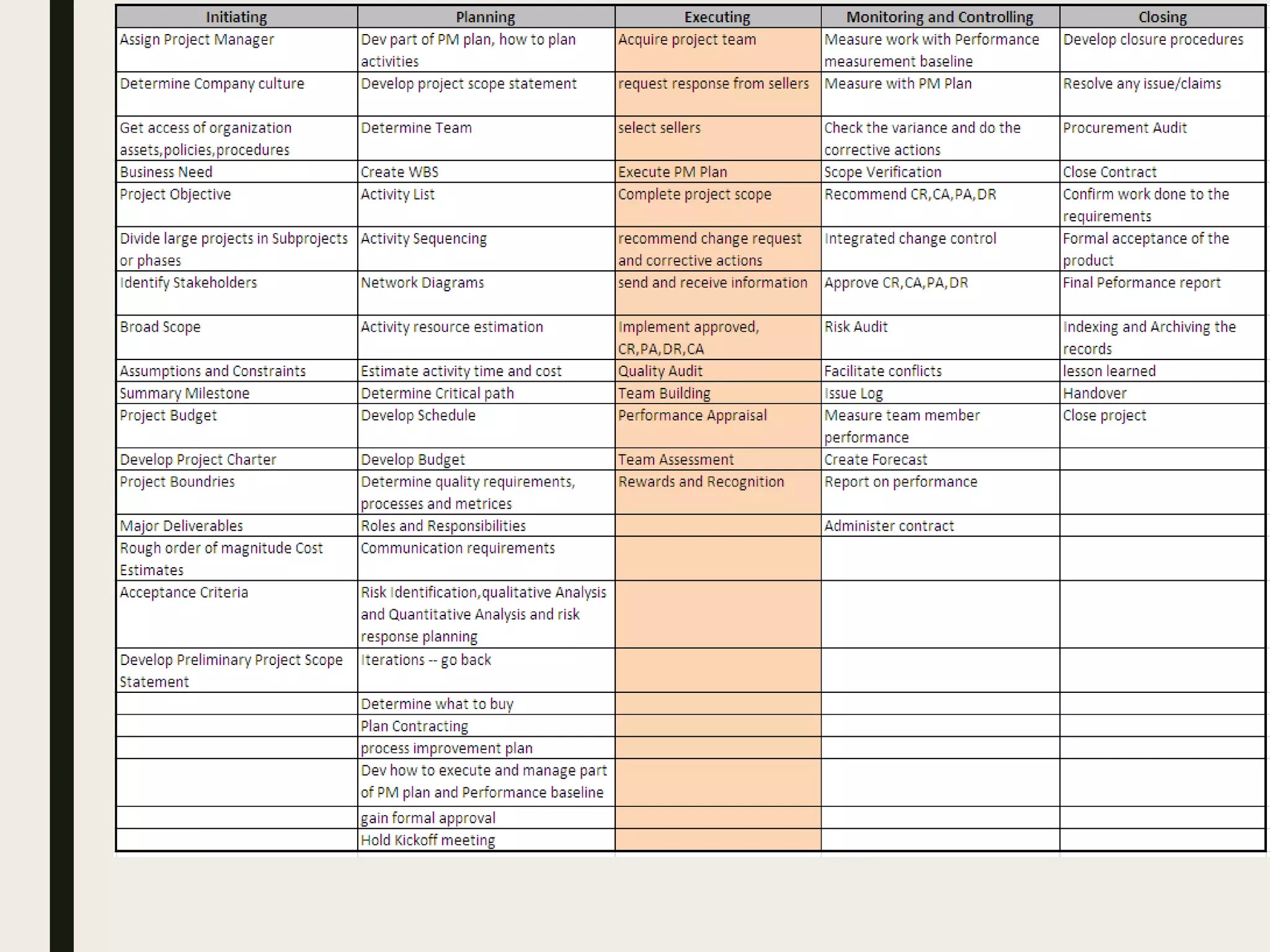
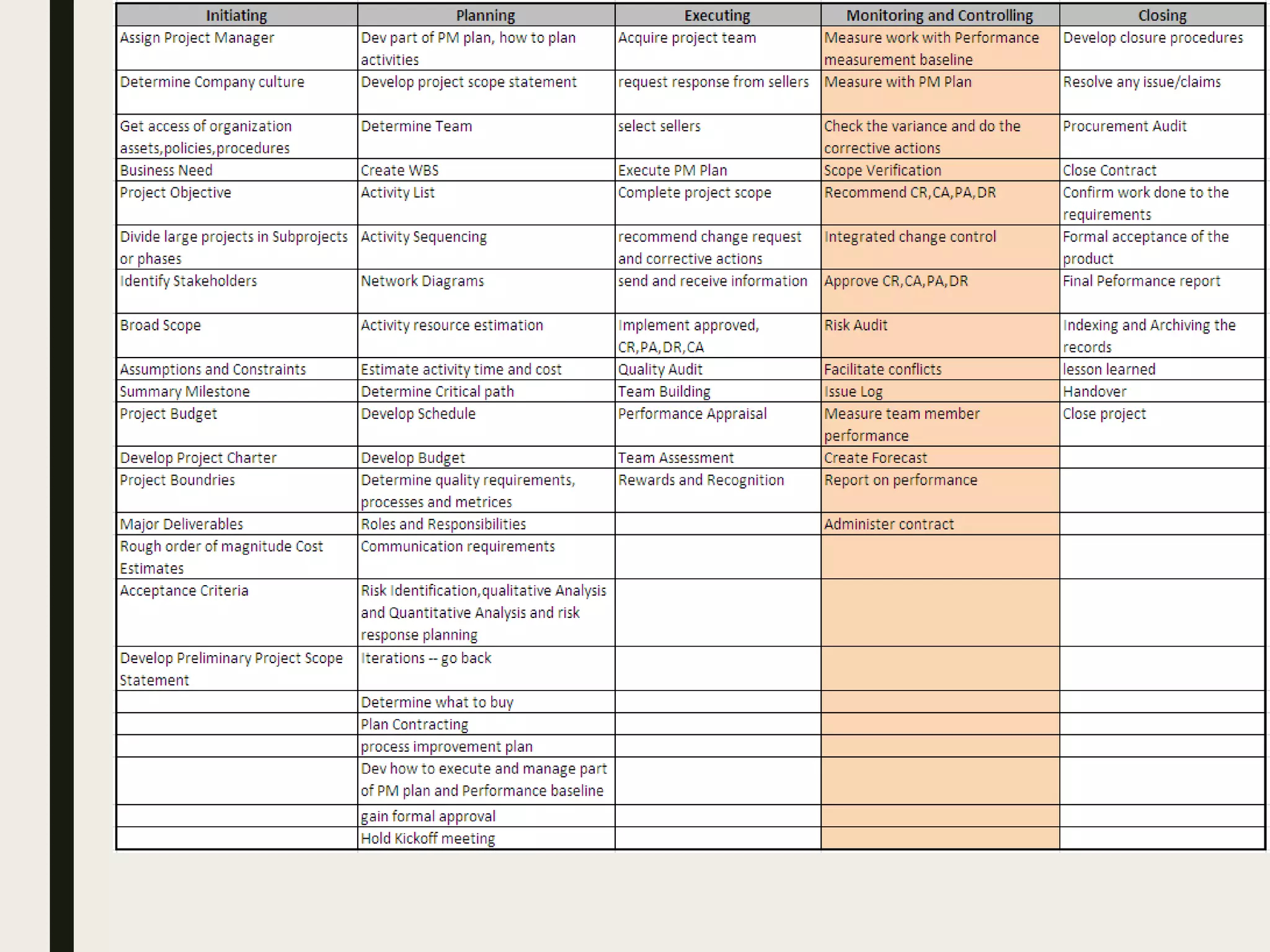
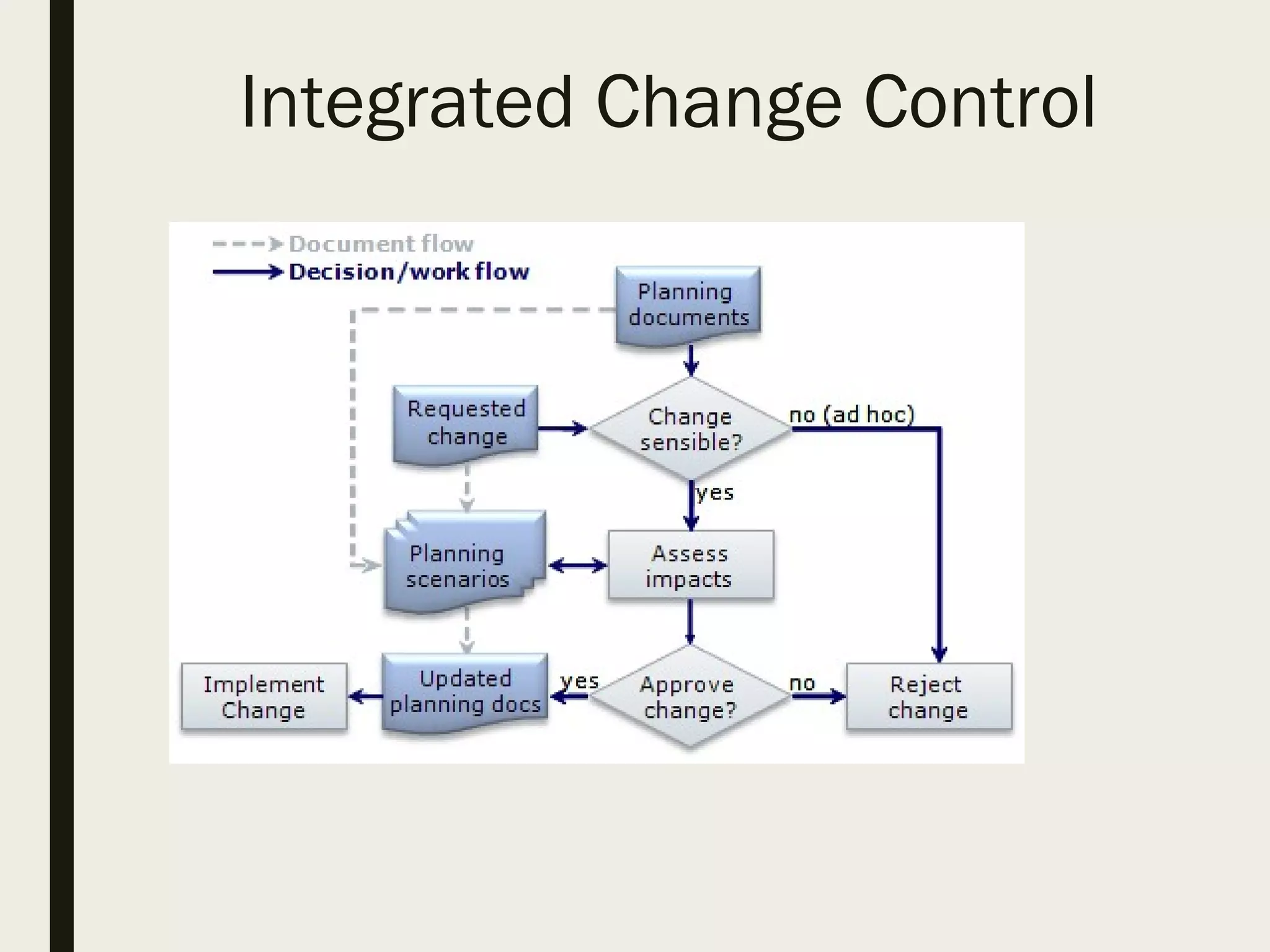
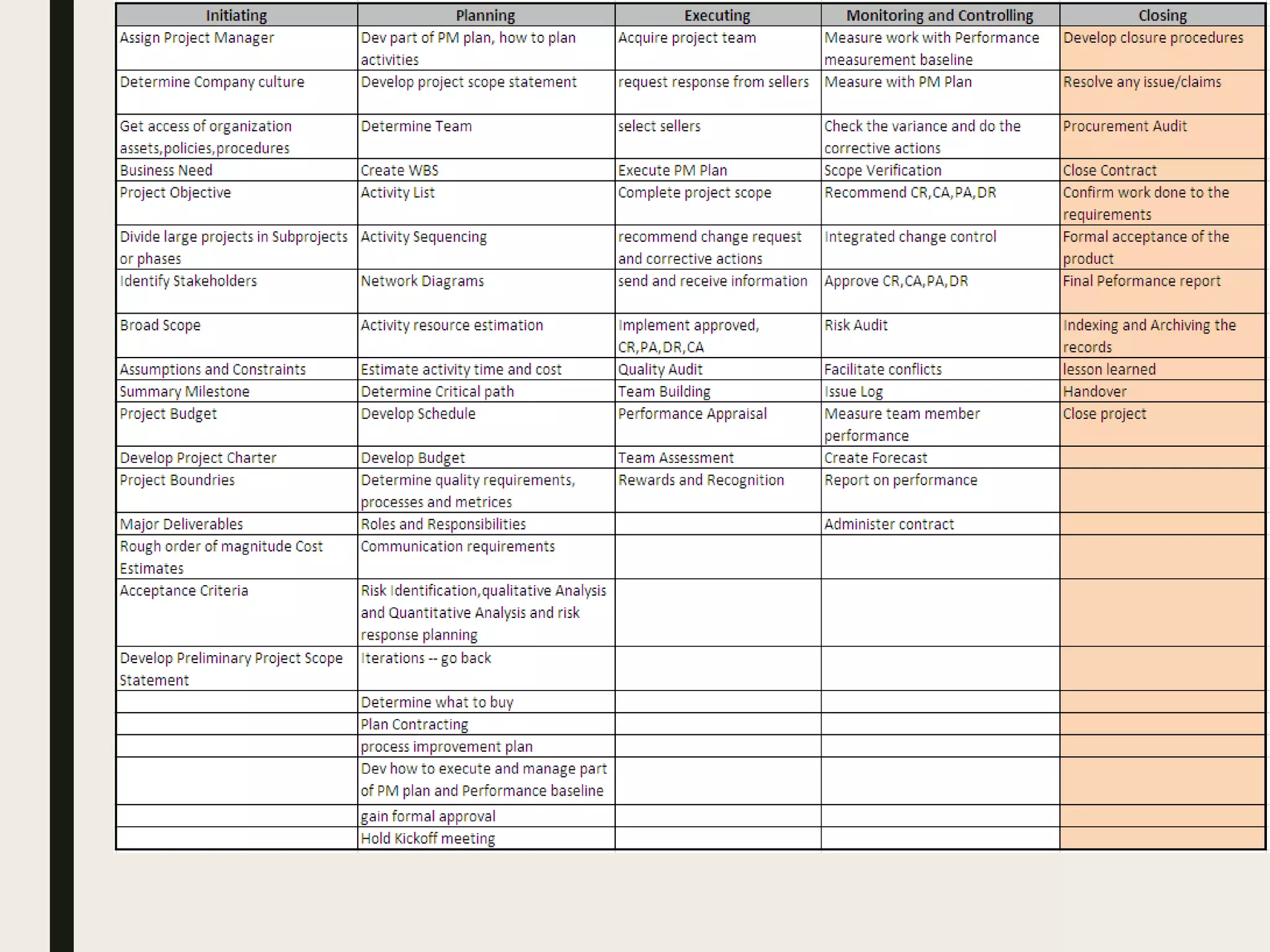
This document provides a comprehensive overview of project management, detailing the definition of a project, the project management framework, and key roles and responsibilities within project management. It covers essential components such as project phases, stakeholder identification, project planning documents, risk management strategies, and quality assurance processes. The document also outlines the processes involved in initiating, executing, monitoring, controlling, and closing projects.