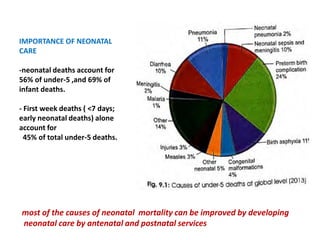
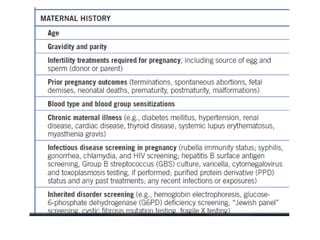
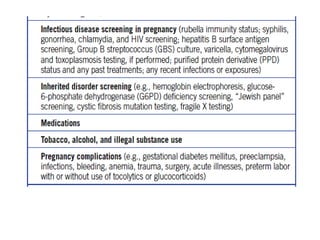
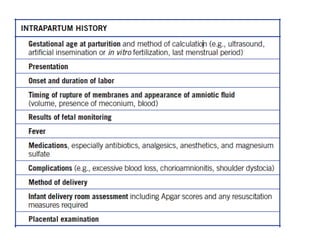
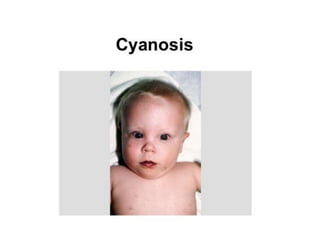
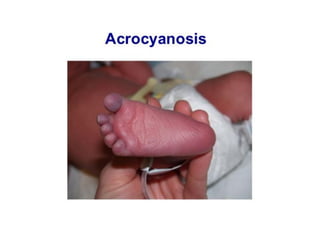
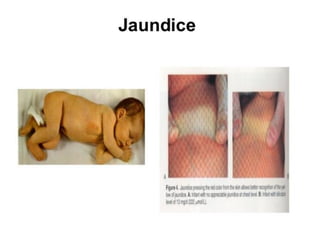
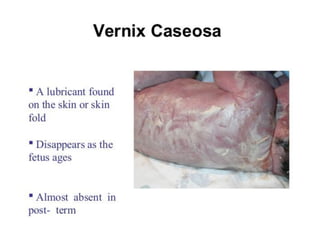
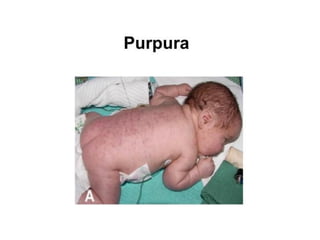
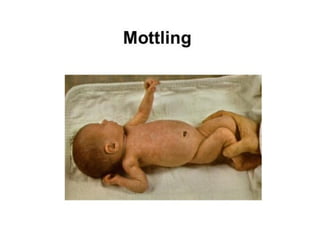
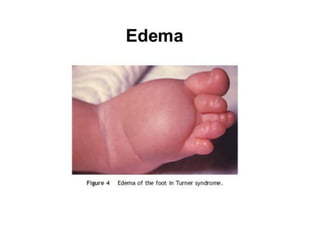
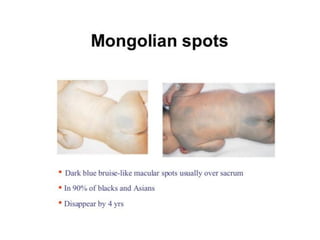
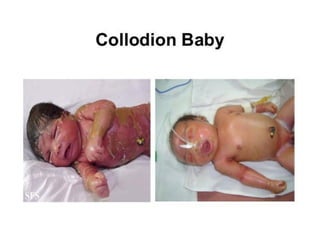
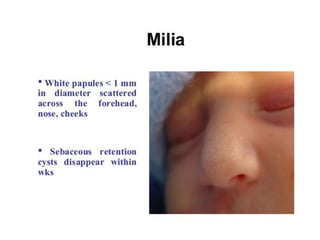
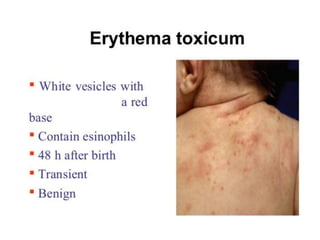
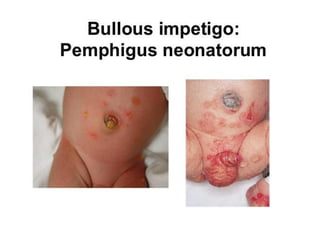
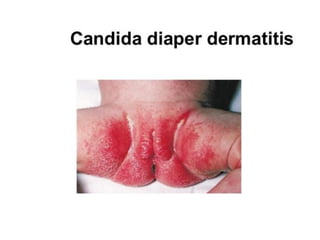
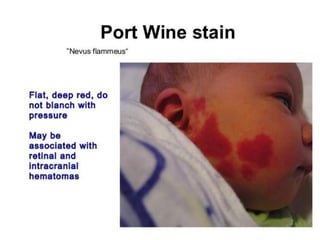
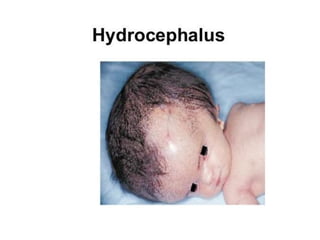
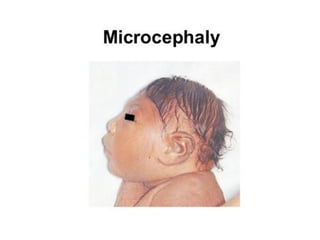
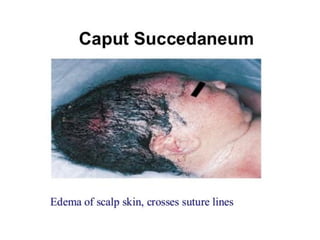
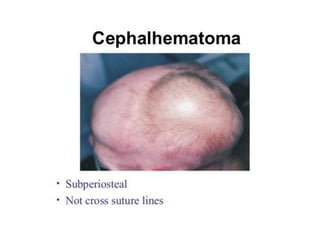
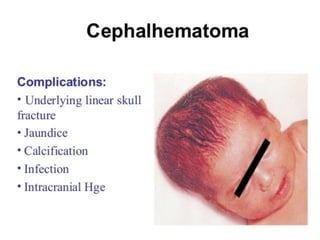
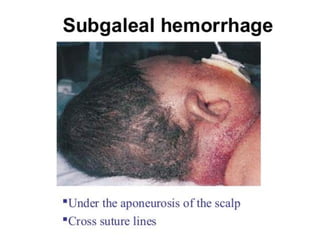
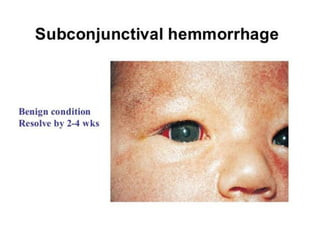
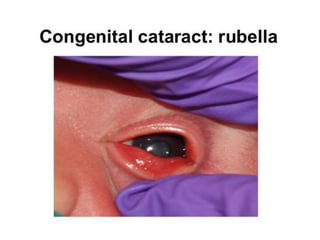
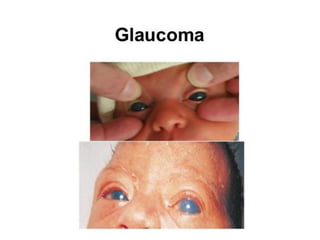
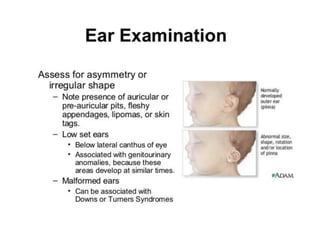
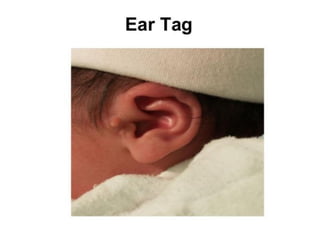
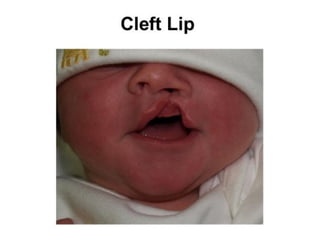
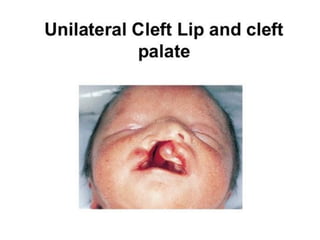
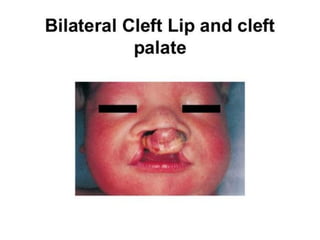
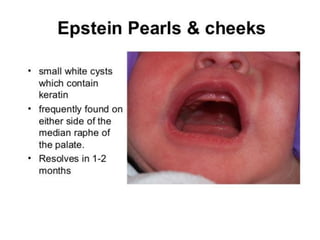
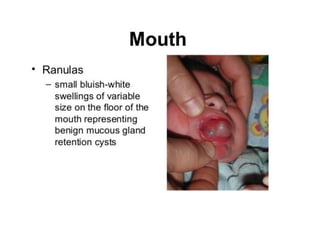
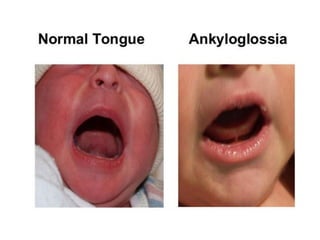
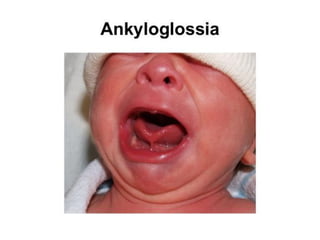
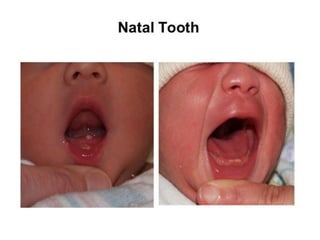
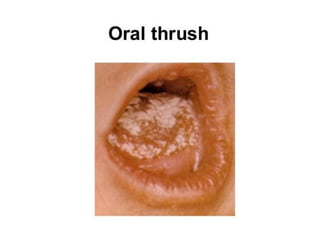
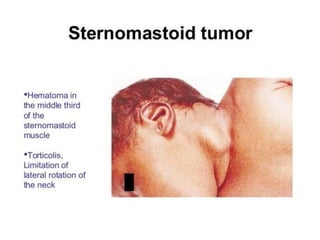
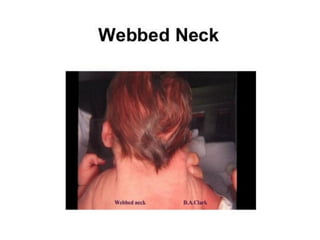
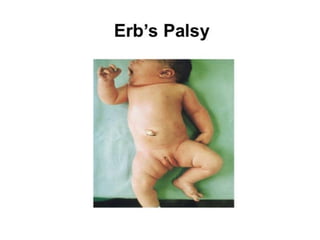
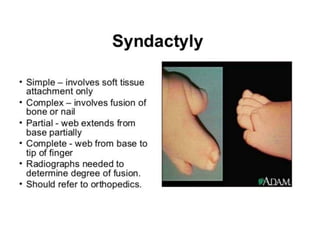
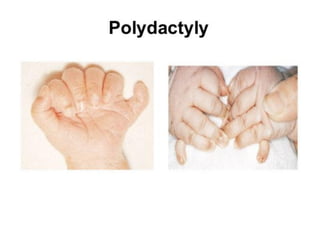
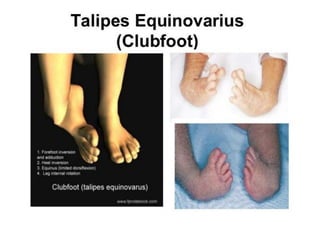
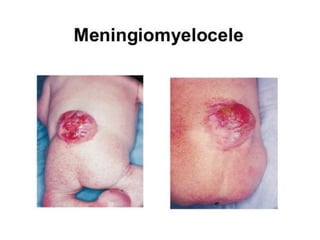
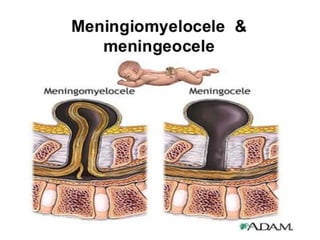
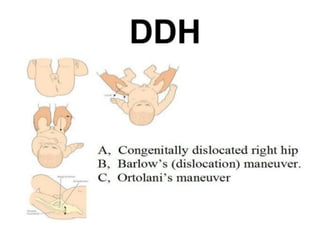
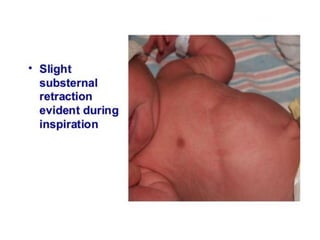
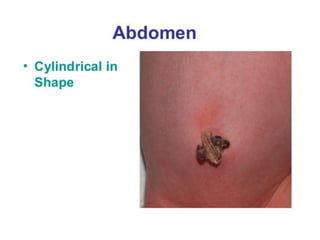
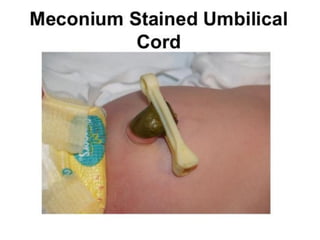
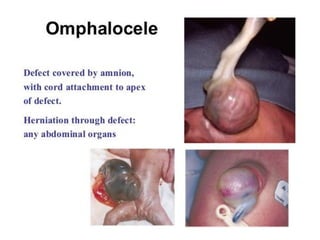
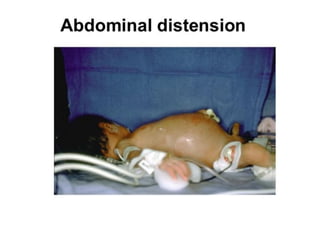
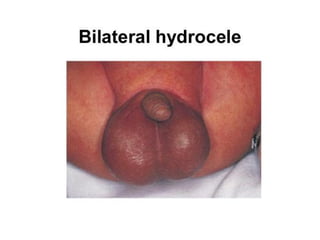
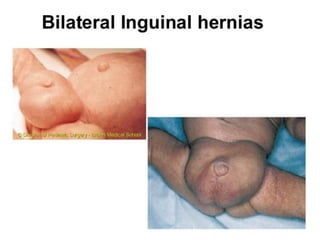
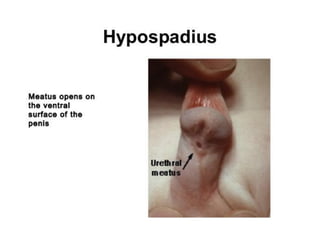
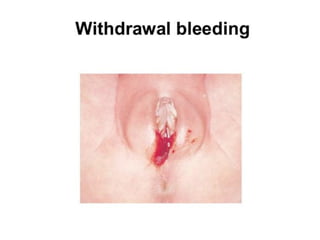
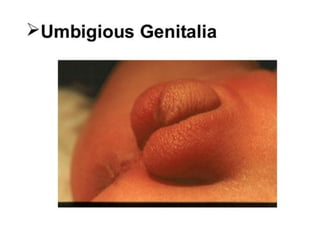
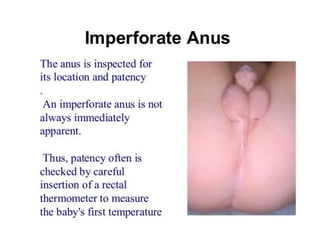
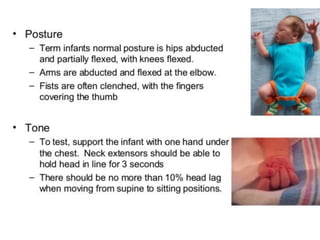
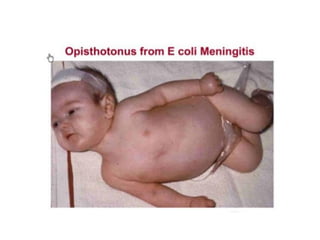
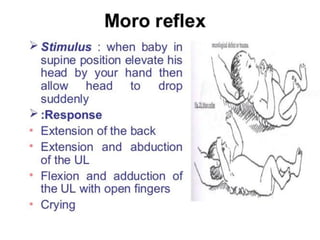
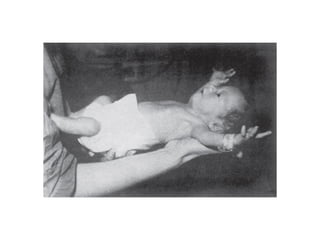
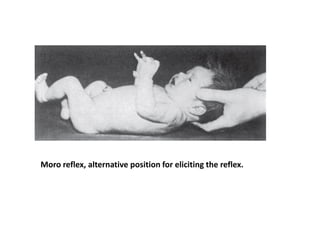
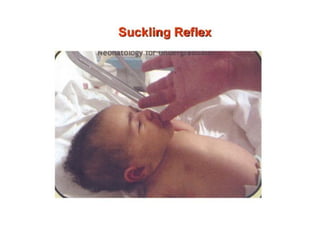
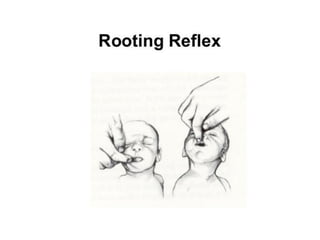
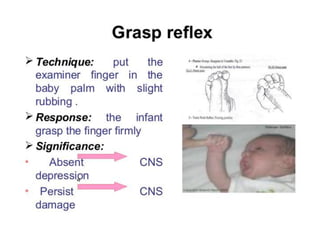
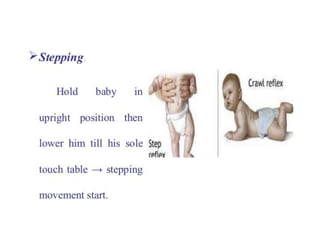
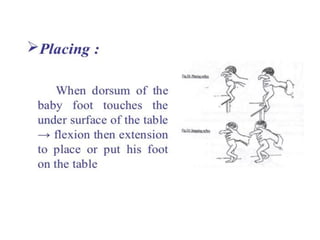
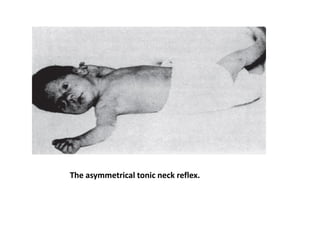
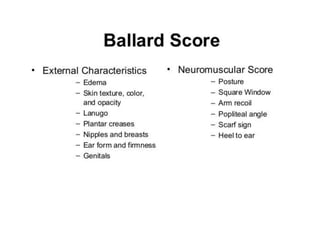
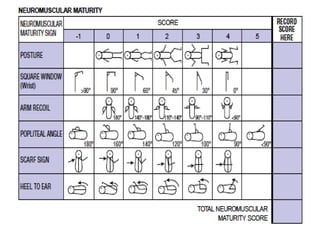
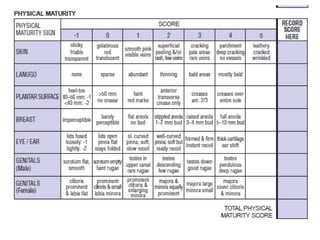
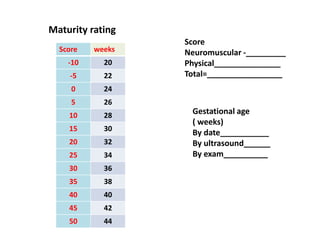
Neonatal care is important as neonatal deaths account for over half of under-5 mortality. The document defines various neonatal periods and terms like low birth weight. It provides guidance on care of normal newborns, including clean delivery practices to prevent sepsis, maintaining temperature, delayed cord clamping, cleaning and examination of the baby. It discusses transitional care in the first few hours and routine care like keeping the baby with the mother and early breastfeeding initiation. Physical assessments of the newborn are also described.