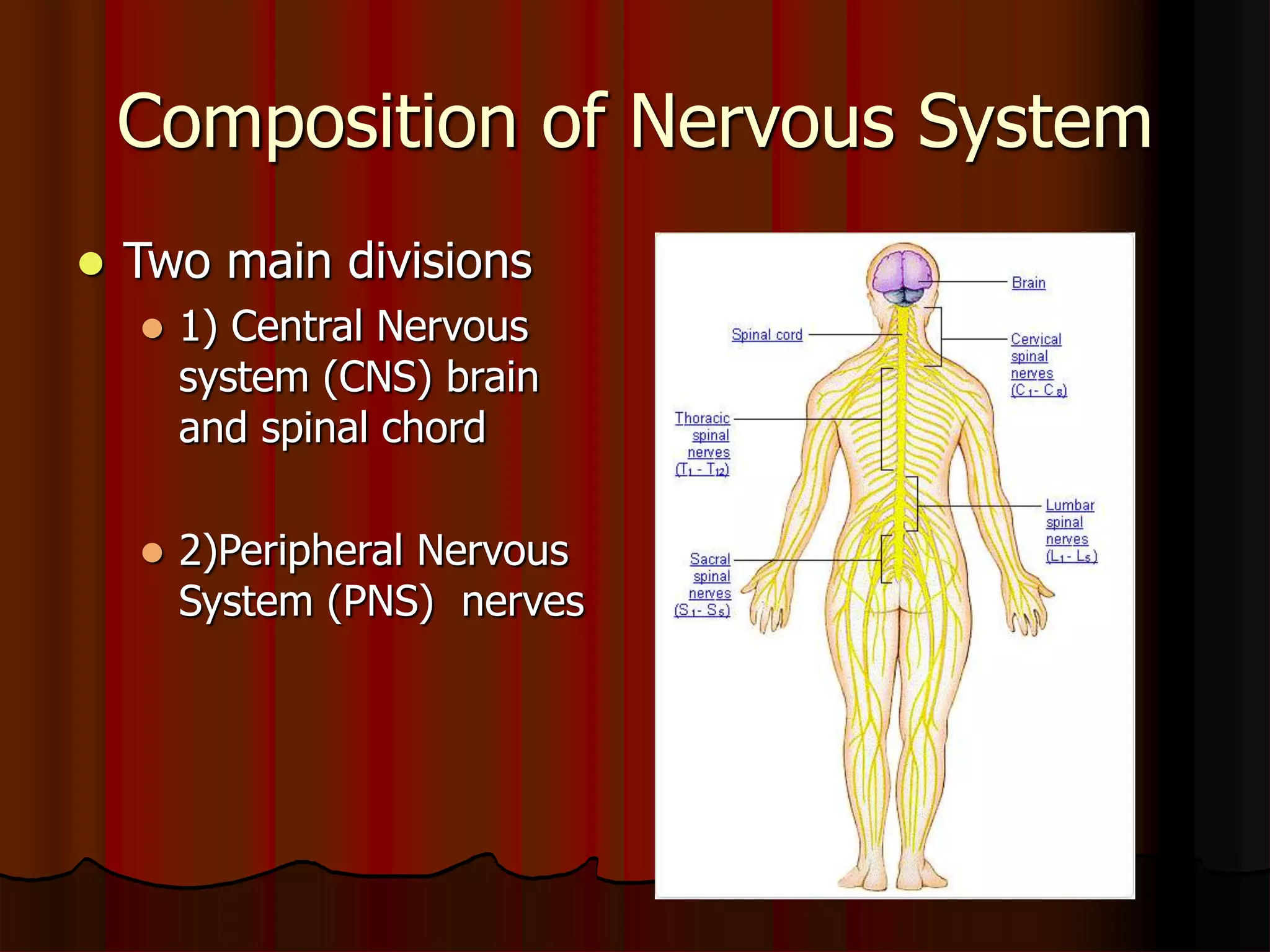
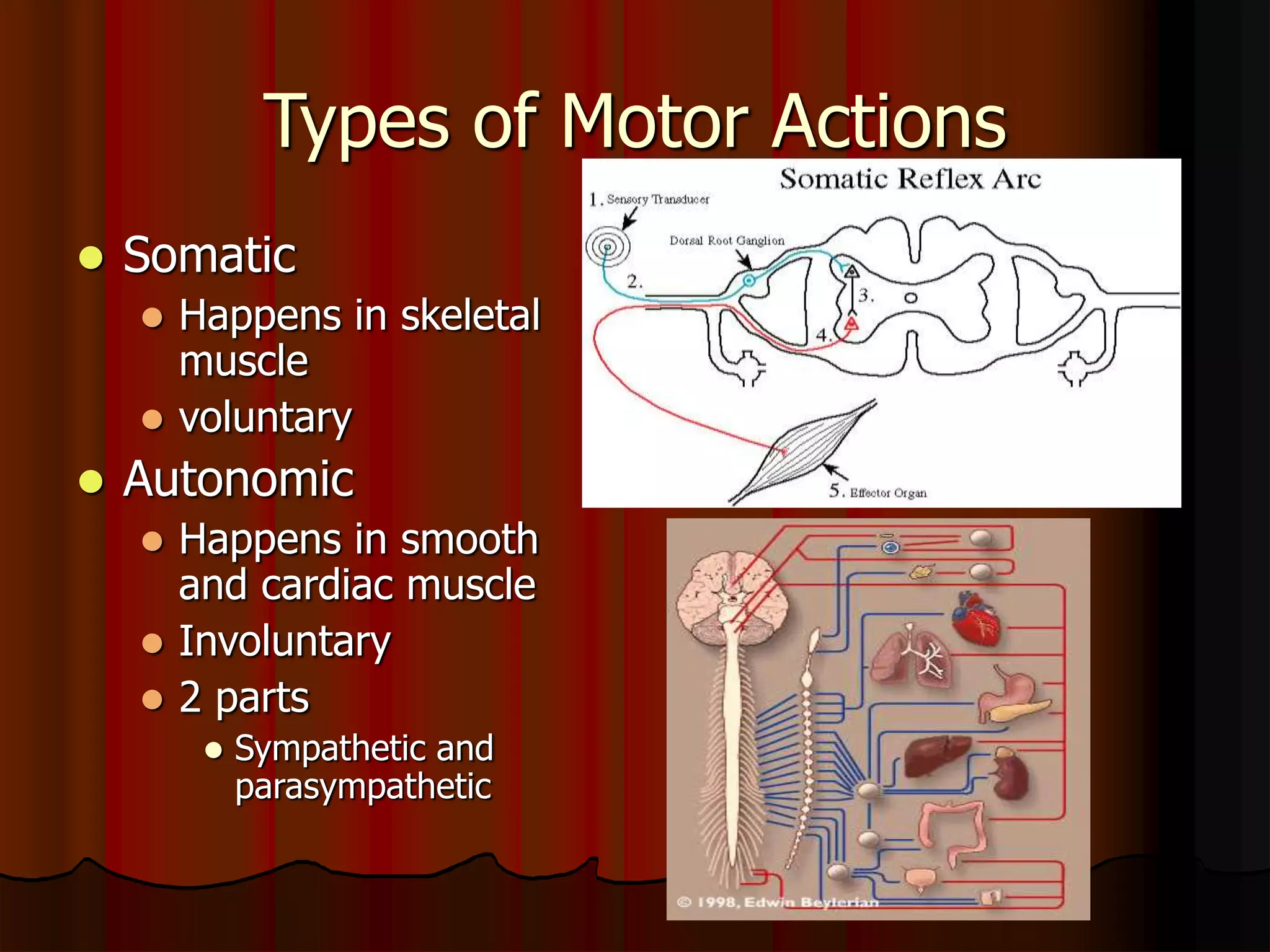
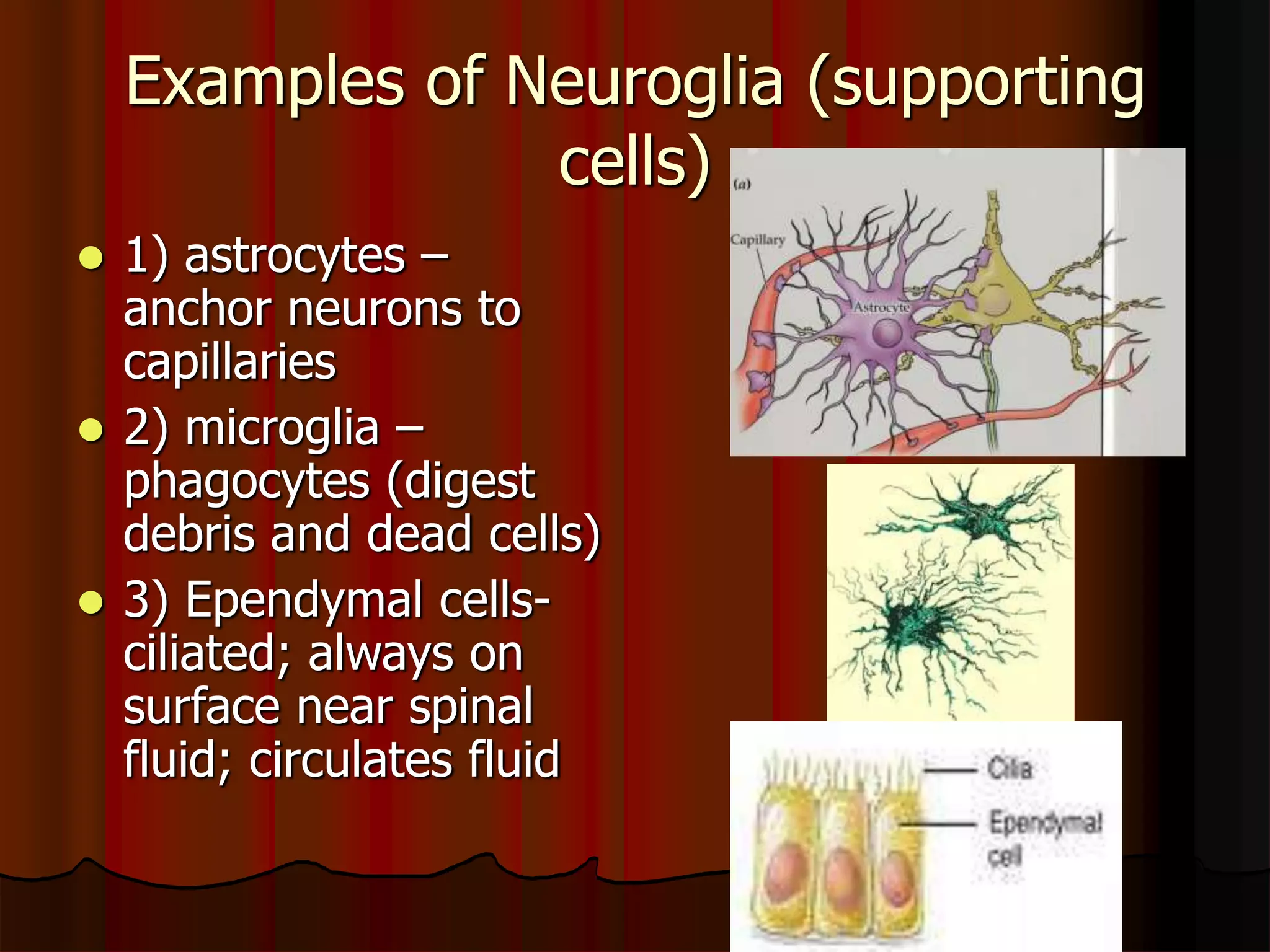
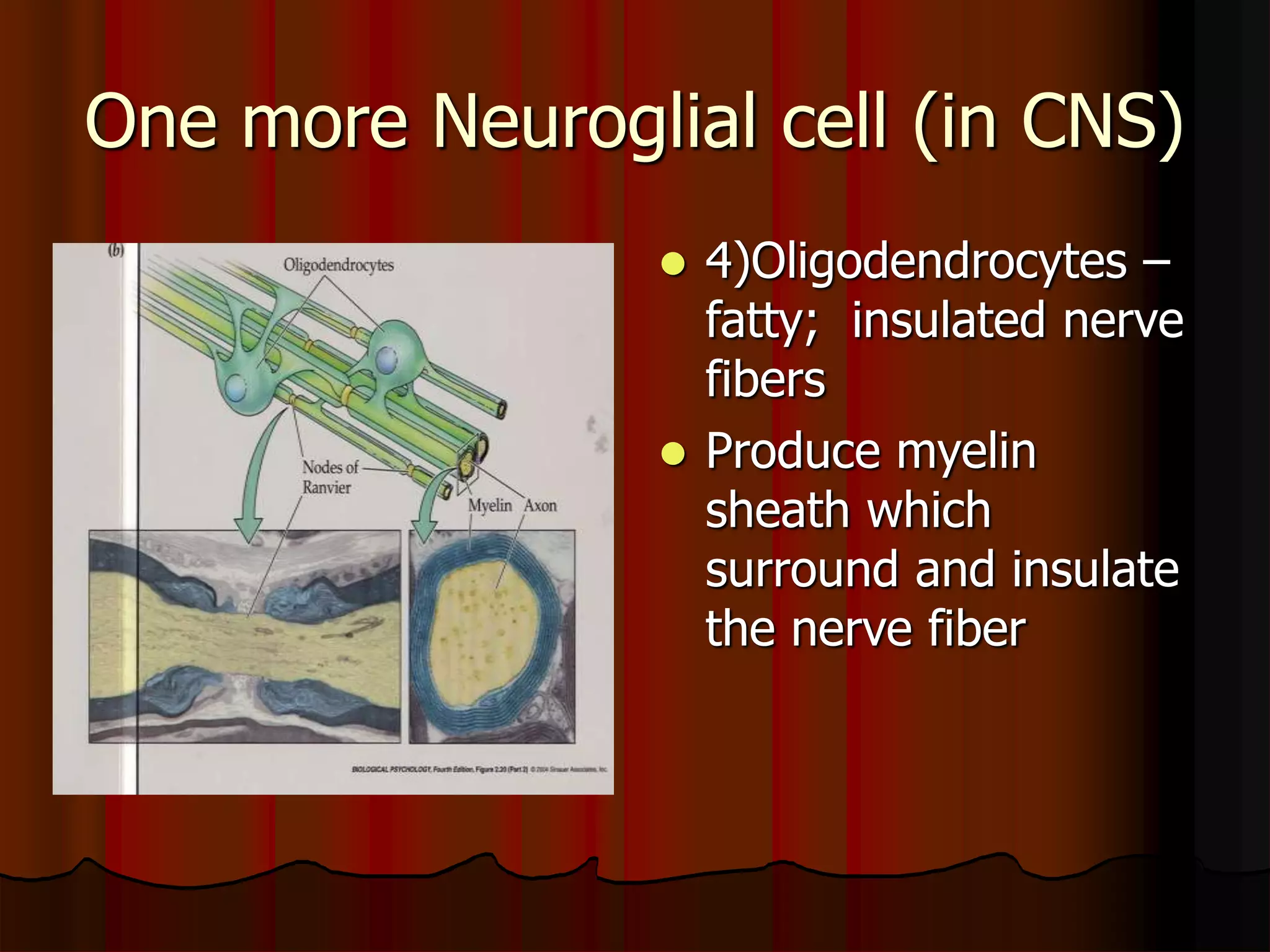
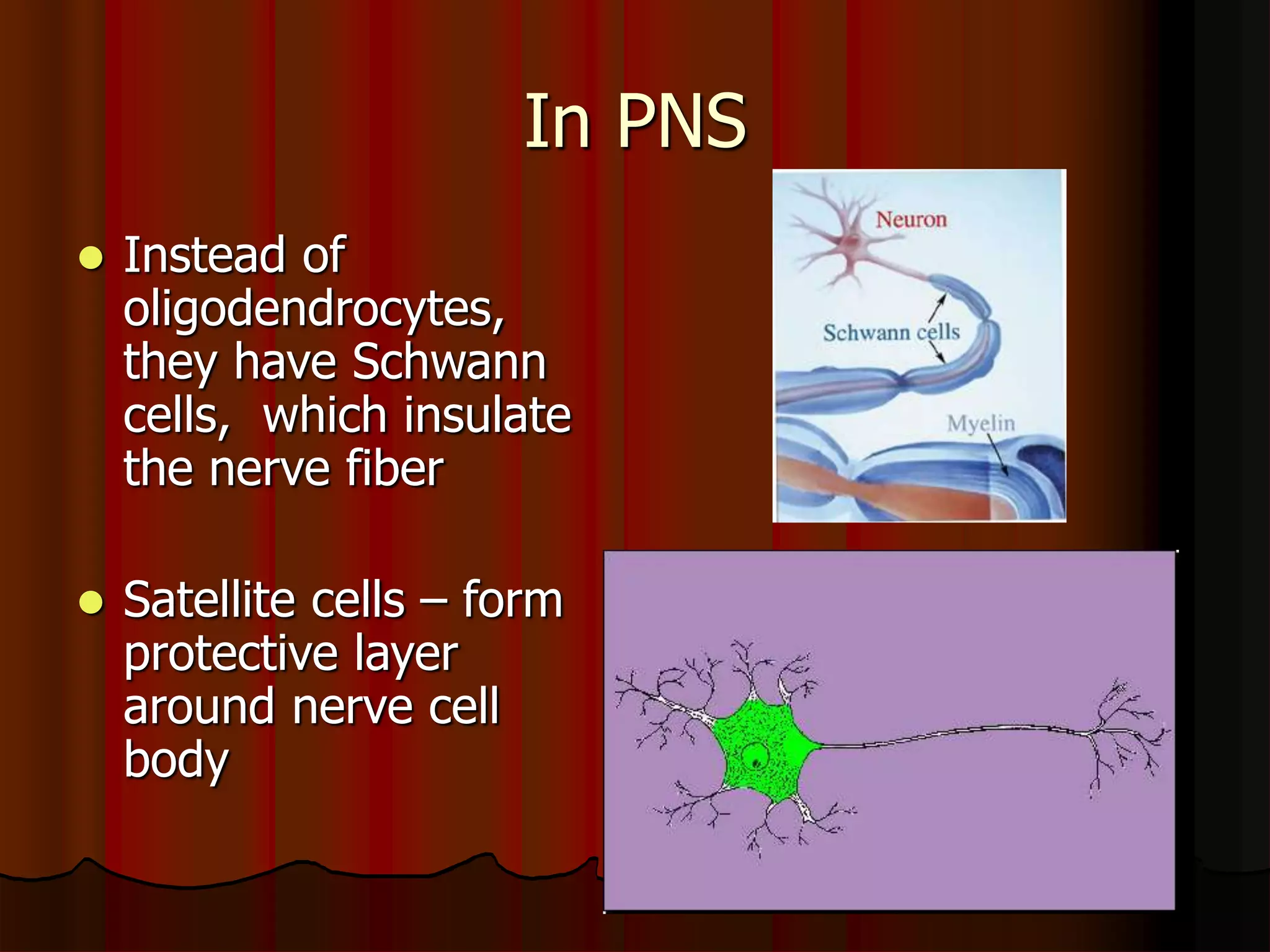
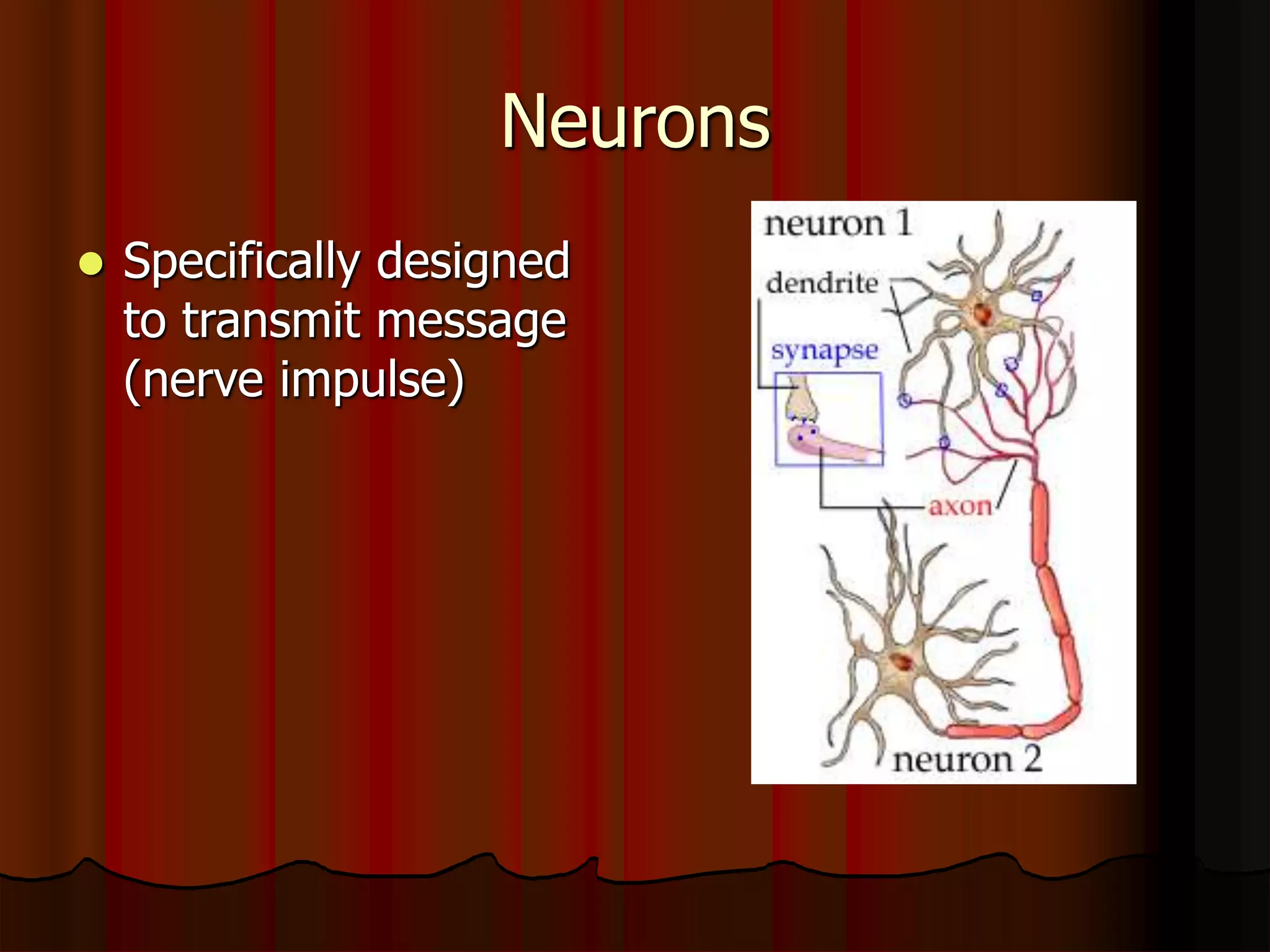
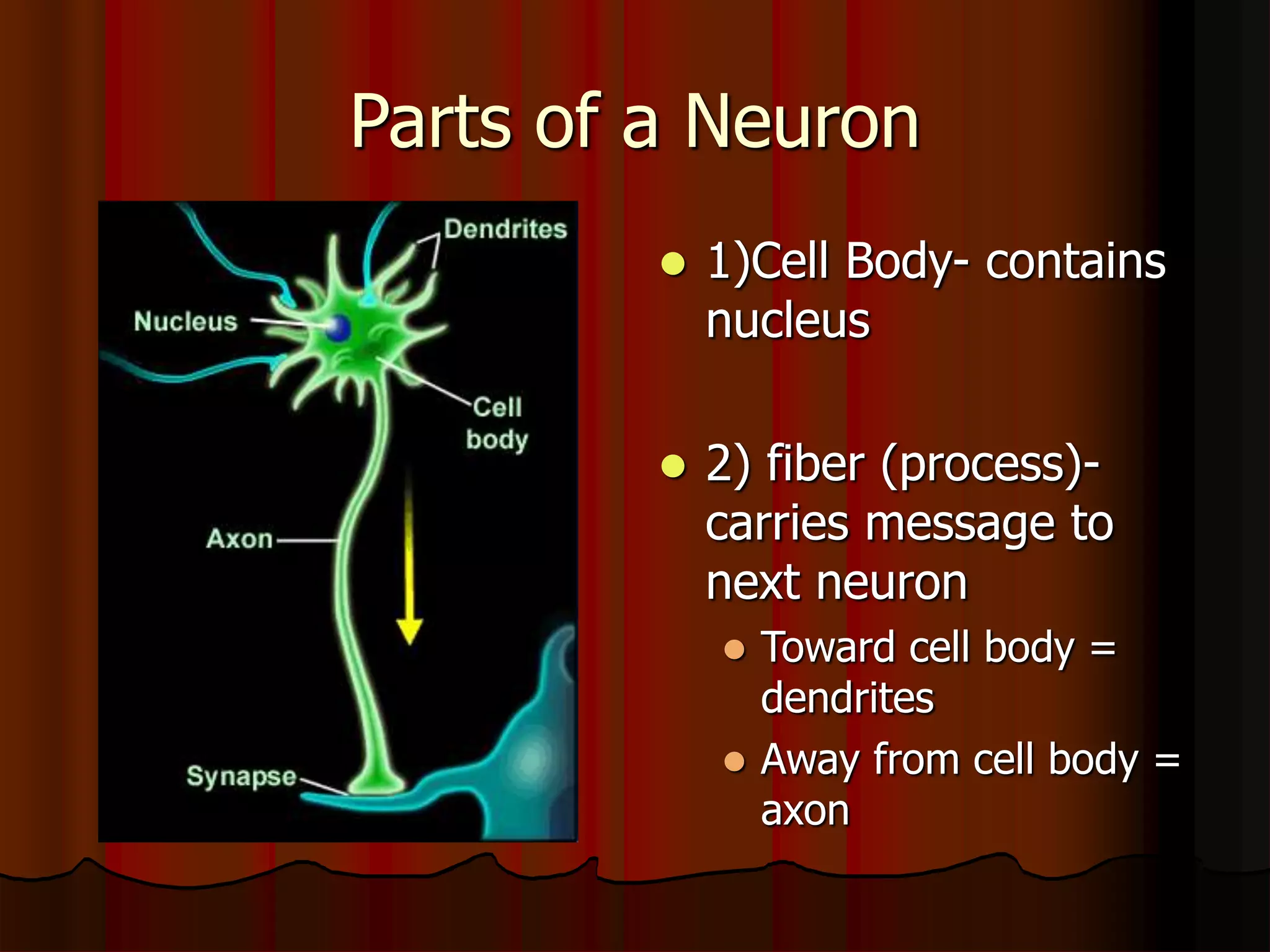
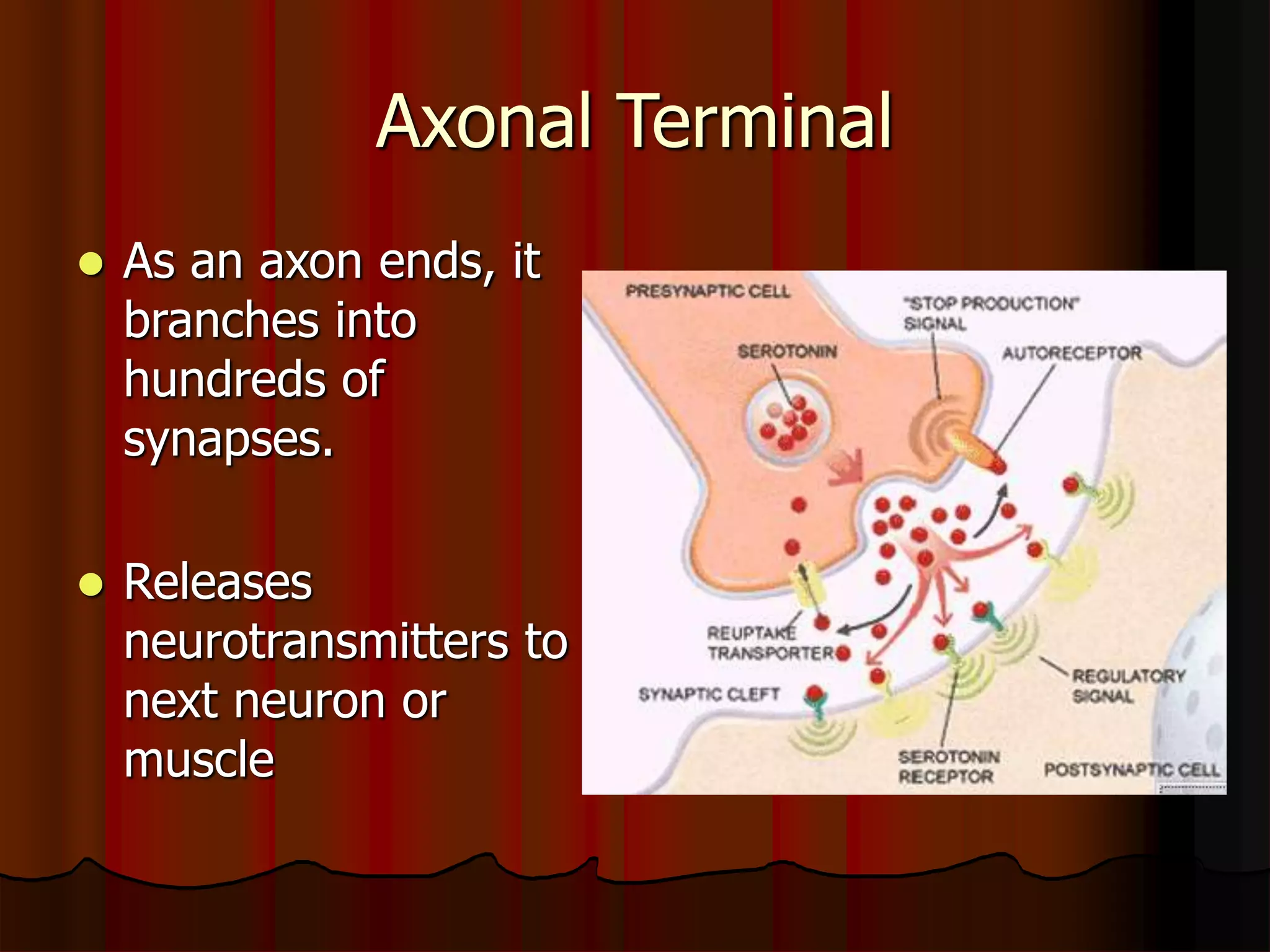
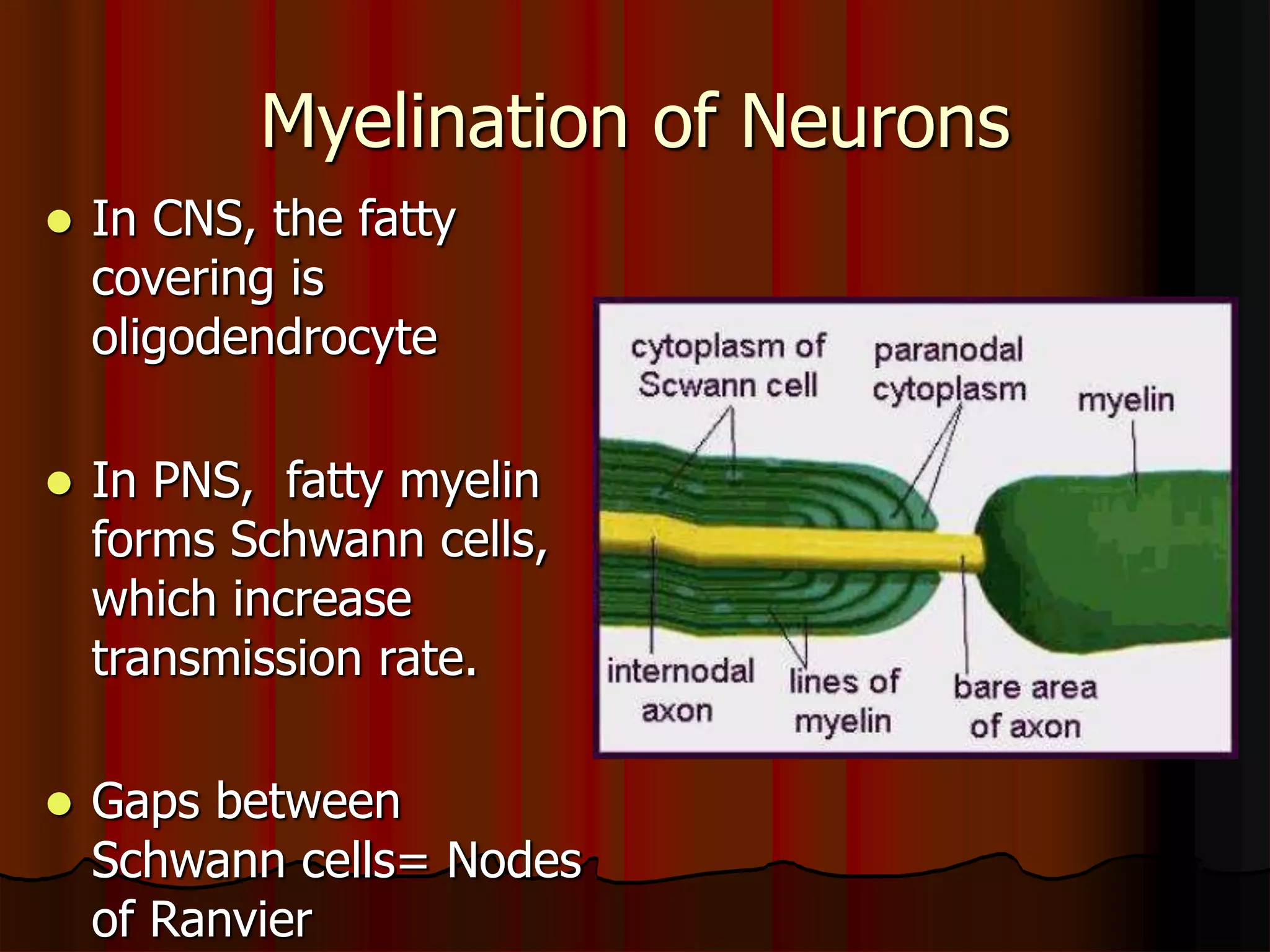
The nervous system is composed of two main divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) containing the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) containing nerves. Sensory neurons carry messages from receptors to the CNS, which then integrates the information and sends motor commands through efferent pathways and motor neurons. Motor actions are either somatic, occurring in skeletal muscle voluntarily, or autonomic, occurring involuntarily in smooth and cardiac muscle. The cells of the nervous system are neurons, which transmit nerve impulses, and neuroglial cells which support neurons. Myelination of neurons by oligodendrocytes in the CNS and Schwann cells in the PNS increases transmission rates.