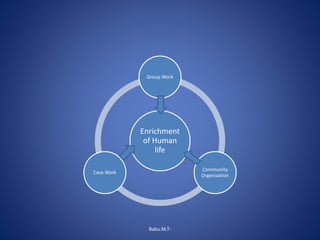
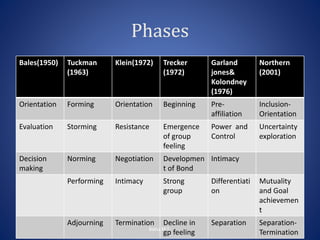
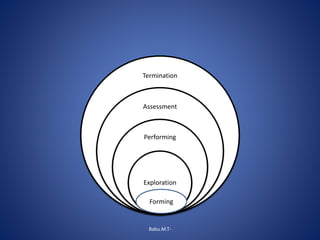
The document discusses the principles and practices of social group work, emphasizing its role in enhancing individual and community welfare through organized group activities. It outlines various models of group work, including social goals, remedial, and reciprocal models, as well as the stages of group development from initial formation to termination. Finally, it highlights the historical context and evolution of group work within social work, particularly in the United States and its adaptation in India.