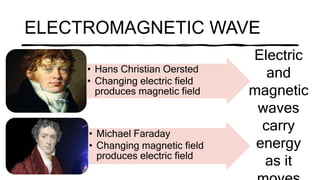
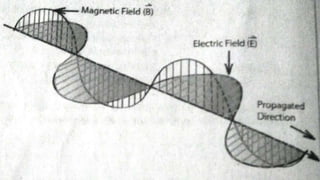
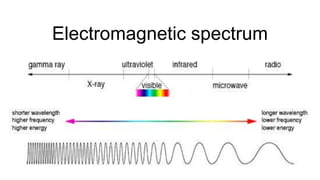
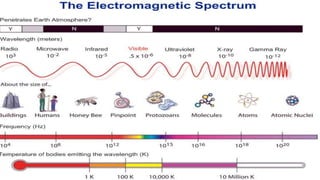
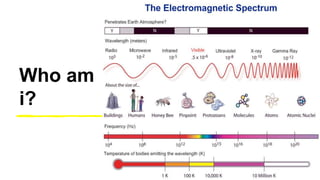
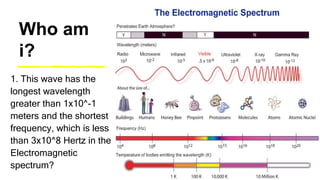
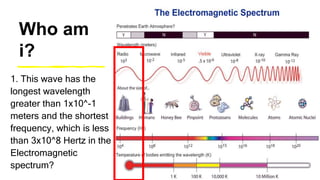
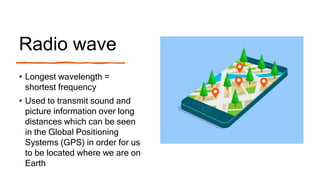
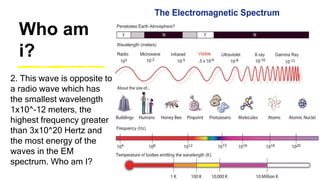
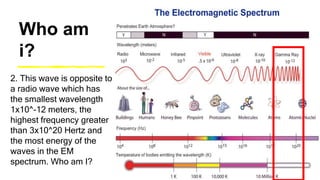
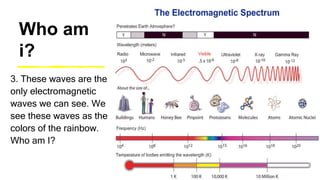
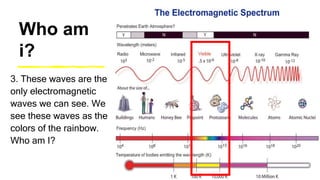
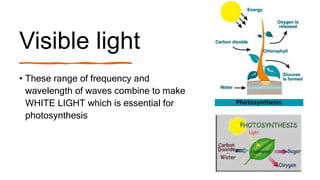
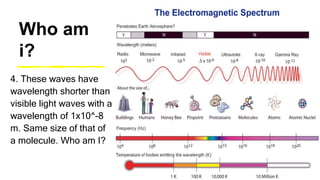
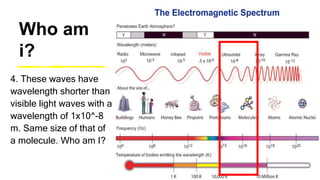
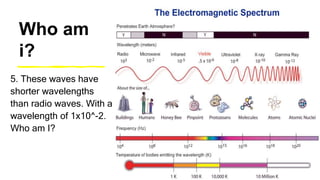
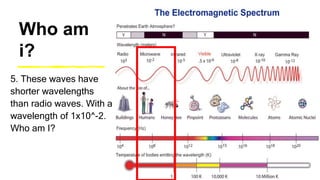
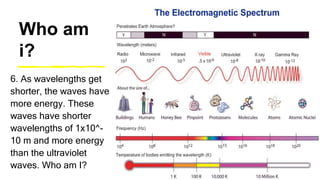
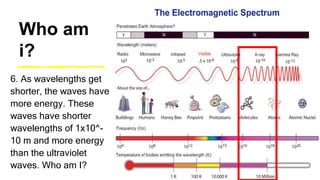
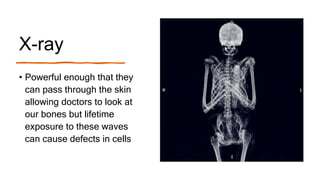
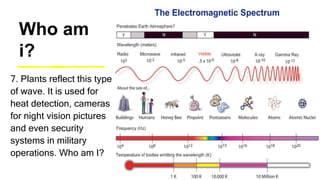
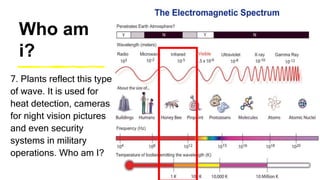
This document provides an introduction to the electromagnetic spectrum. It begins with an activity to introduce key concepts like wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and other wave properties. It then discusses how electromagnetic waves are created by changing electric and magnetic fields. The different types of electromagnetic waves are presented, ranging from radio waves to gamma rays. Key differences in their wavelengths and frequencies are highlighted. The document concludes with activities to review and apply the concepts learned about the electromagnetic spectrum.