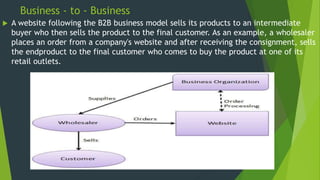
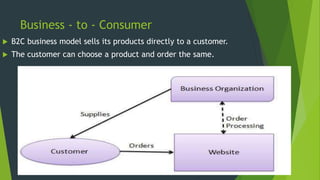
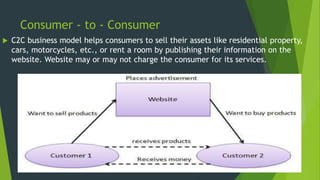
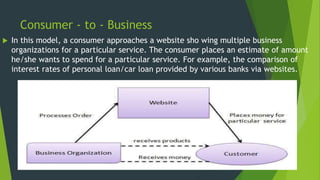
The document discusses e-commerce, providing a brief history from 1994-1999 when early companies like Amazon, eBay, and PayPal launched and pioneered online sales and transactions. It defines e-commerce as buying and selling of goods/services over the internet and outlines several types including business-to-business, business-to-consumer, consumer-to-consumer, and consumer-to-business. Examples are given of direct online sales, online banking, auctions, and media sales. The importance of e-commerce is noted as easier payments, delivery, lower costs, and 24/7 access.