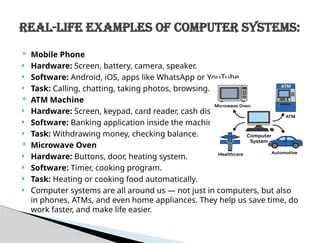
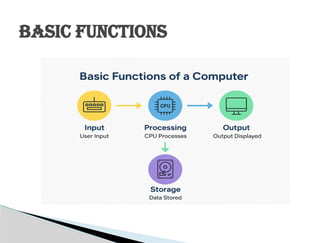
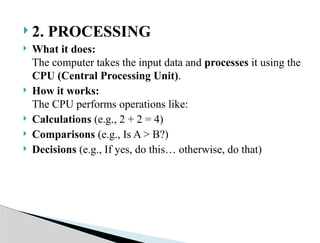
This presentation introduces the concept of computers in a simple and clear manner. It covers the basic definition, essential components, and working of a computer system. Learners will understand how computers receive input, process data, store information, and produce output.
Key topics include:
What is a Computer?
Characteristics and Functions of a Computer