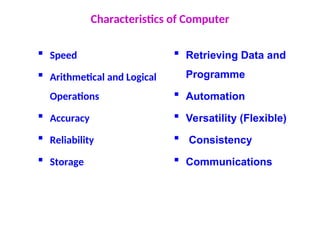
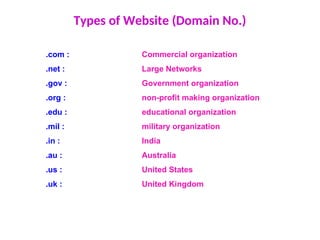
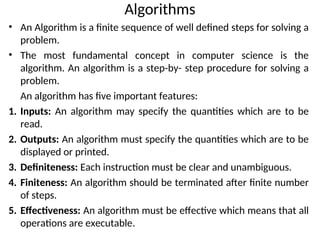
The document provides an overview of procedural programming, emphasizing its structure of organizing code into reusable procedures and its importance in programming education and critical systems. It also explains the basic concepts of computer hardware and software, detailing types of computers, applications, internet basics, and problem-solving methodologies using algorithms. Additionally, it includes a sample C program that calculates the factorial of a number, demonstrating the structure of a C program.