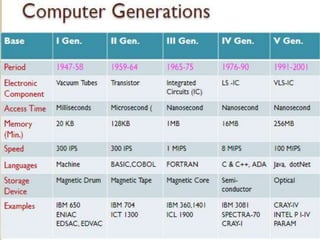
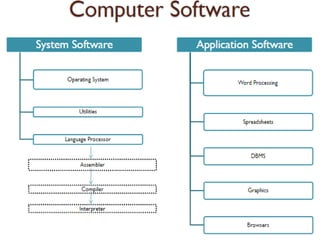
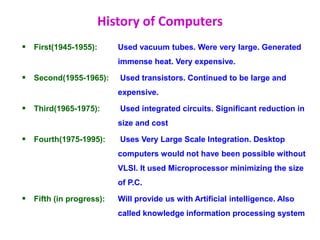
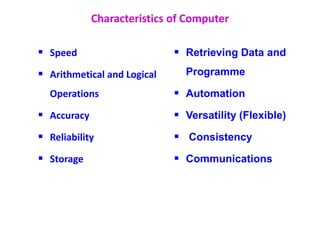
The document provides an overview of computers, including their definition, history, characteristics, hardware, software, types, and applications. It explains the internet, its uses, important concepts like networks, clients, servers, and protocols, as well as problem-solving techniques in computer programming, including algorithms. Key features of algorithms are also outlined, emphasizing their role in systematic problem-solving.