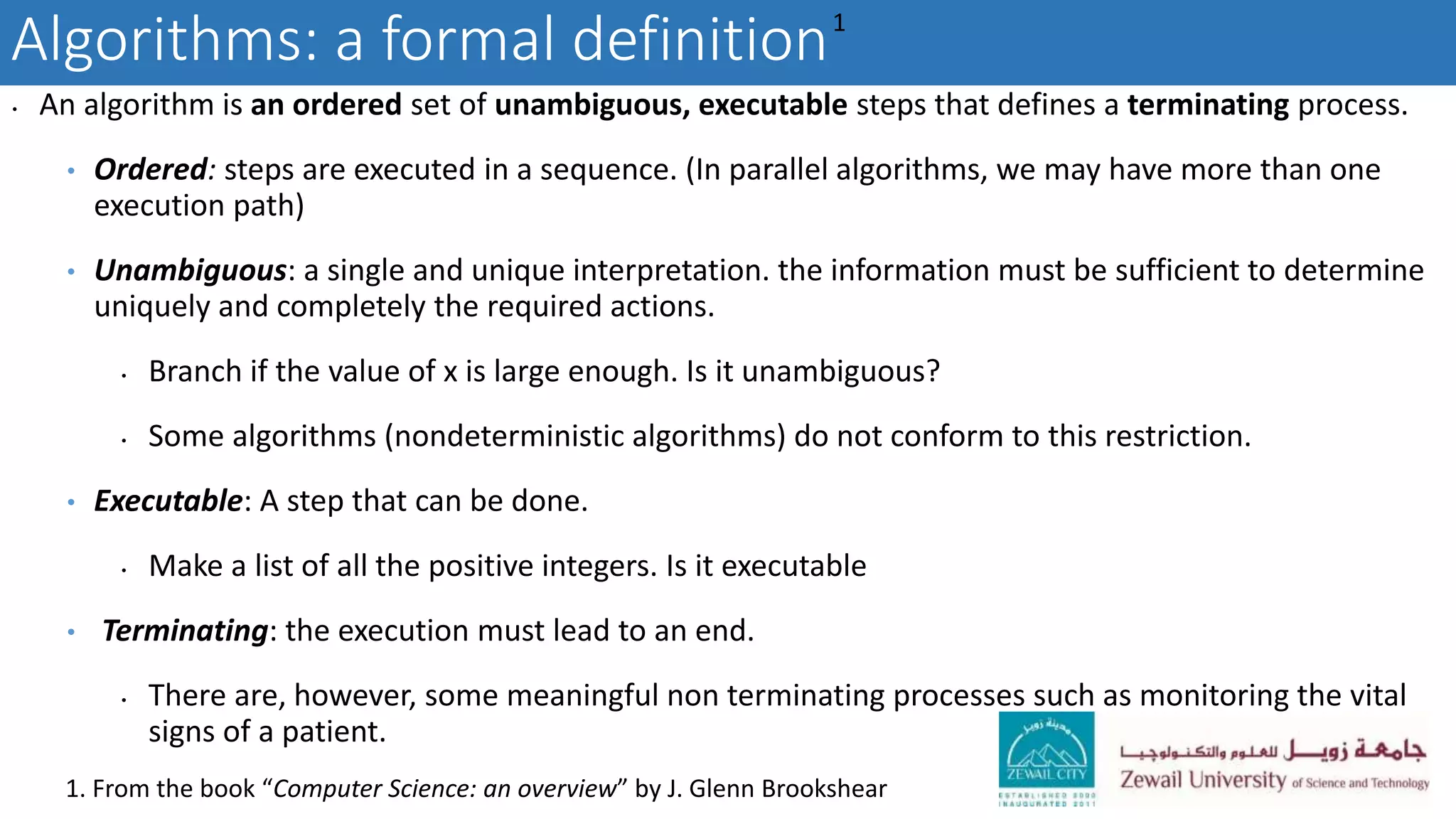
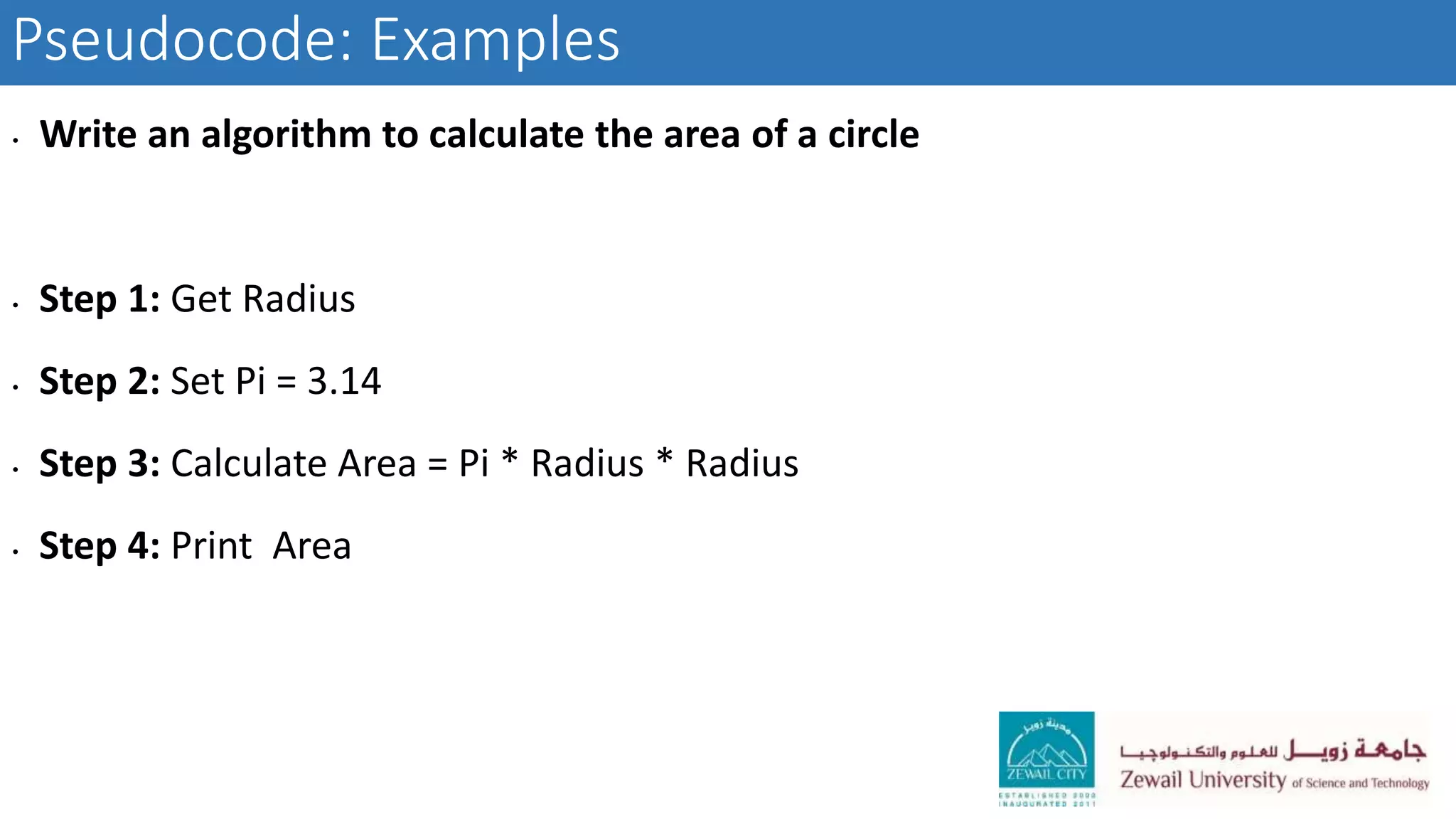
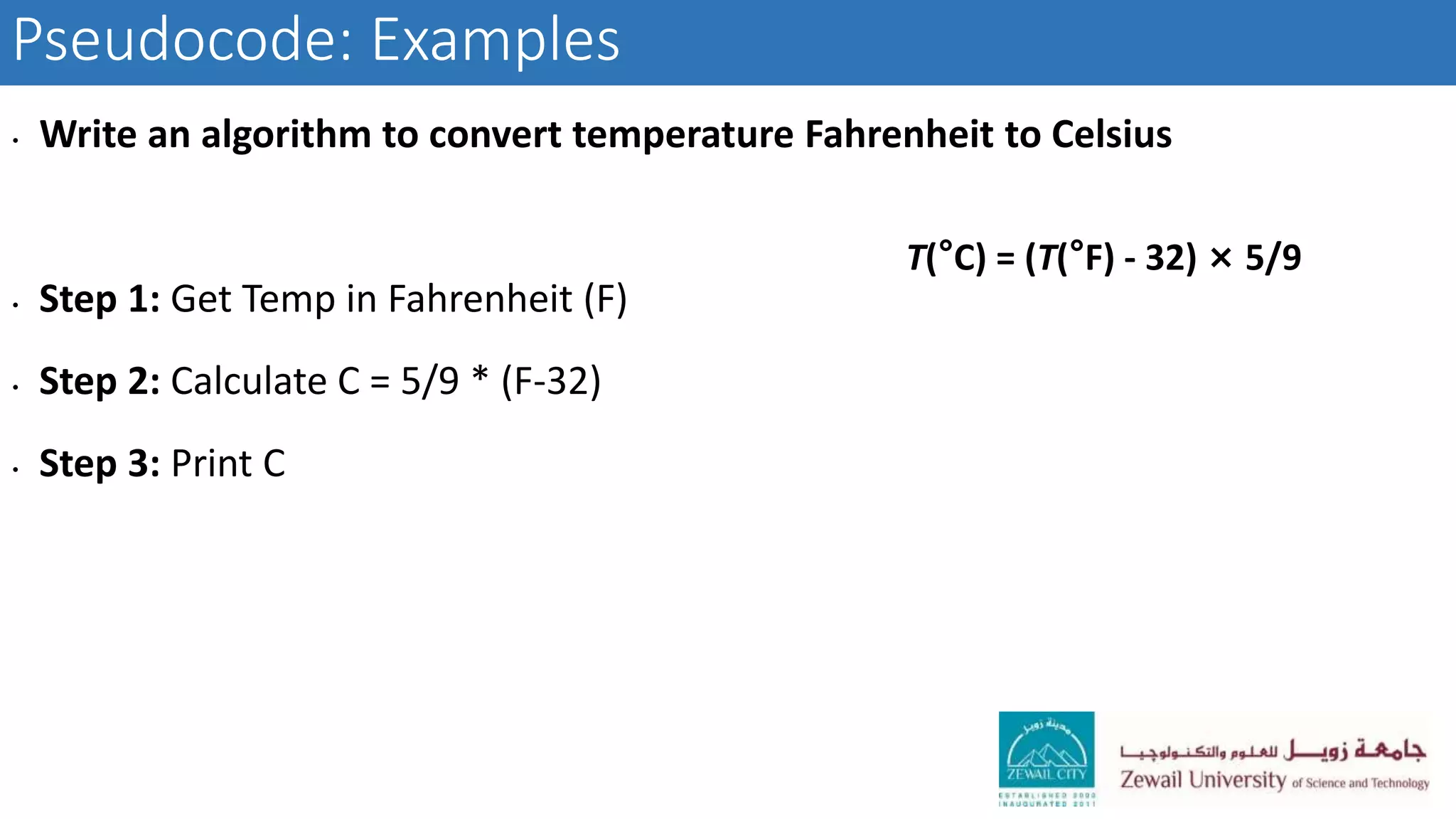
The document describes CSCI 101, an introductory computer science course that covers basic computer hardware and software concepts, algorithms, programming with MATLAB, and problem solving techniques to help students develop logical thinking skills. The course objectives are for students to learn programming, algorithm design, data structures, and how to apply computational methods to solve scientific problems. Requirements include exams, projects, labs, and attendance.








![1. Read the problem statement, and identify
– The input and its range
– The output
– The relationship between the input and the output (how to compute the
output) [Comprehend]
2. Write your thoughts as a sequence of steps. [Algorithm]
3. Convert these steps to Code. [Program]
4. Test your code and compare your program result against a human result.
[Testing]
How to write a software program?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csci101lect00introduction-200319121822/75/Csci101-lect00-introduction-14-2048.jpg)