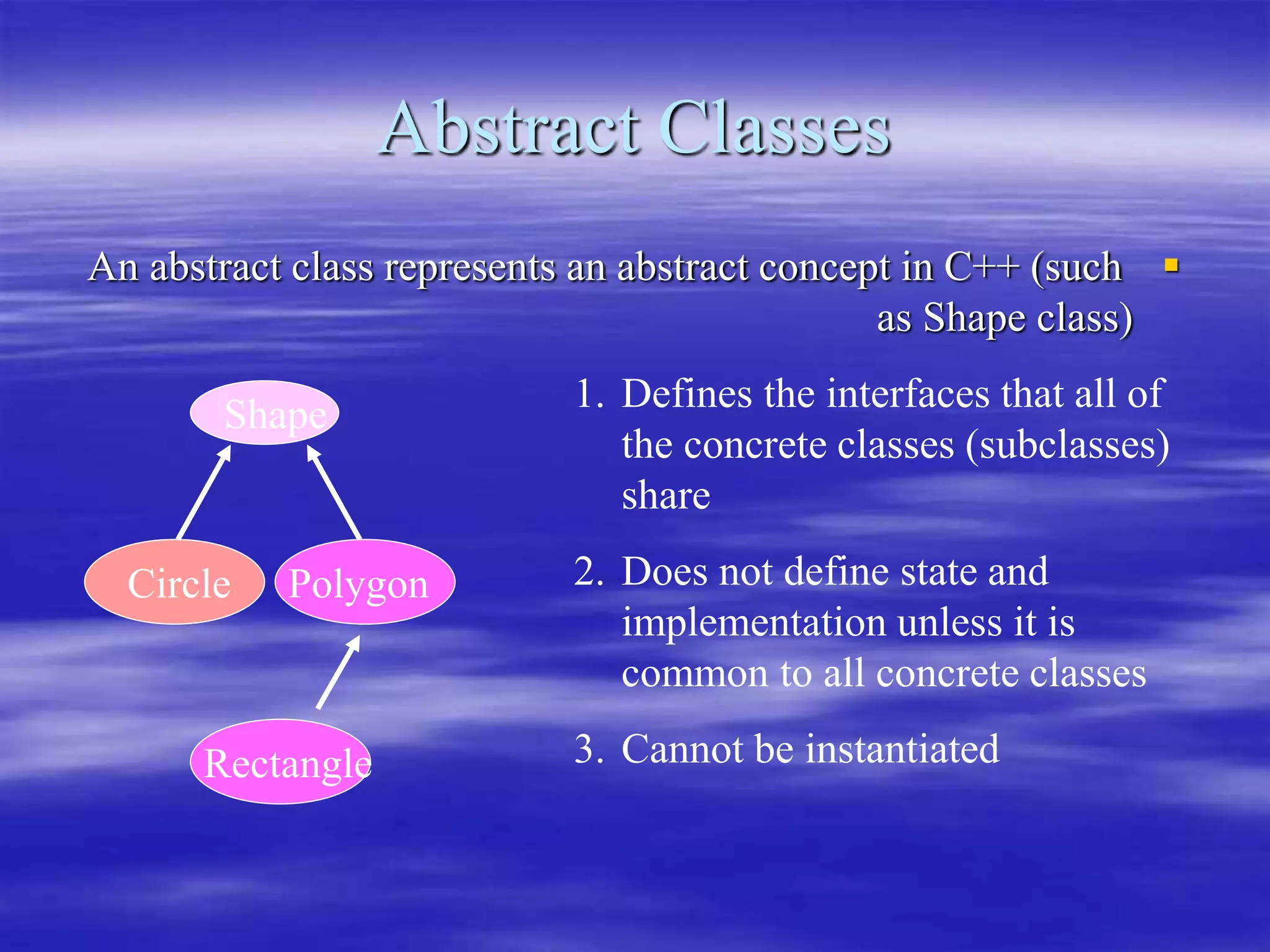
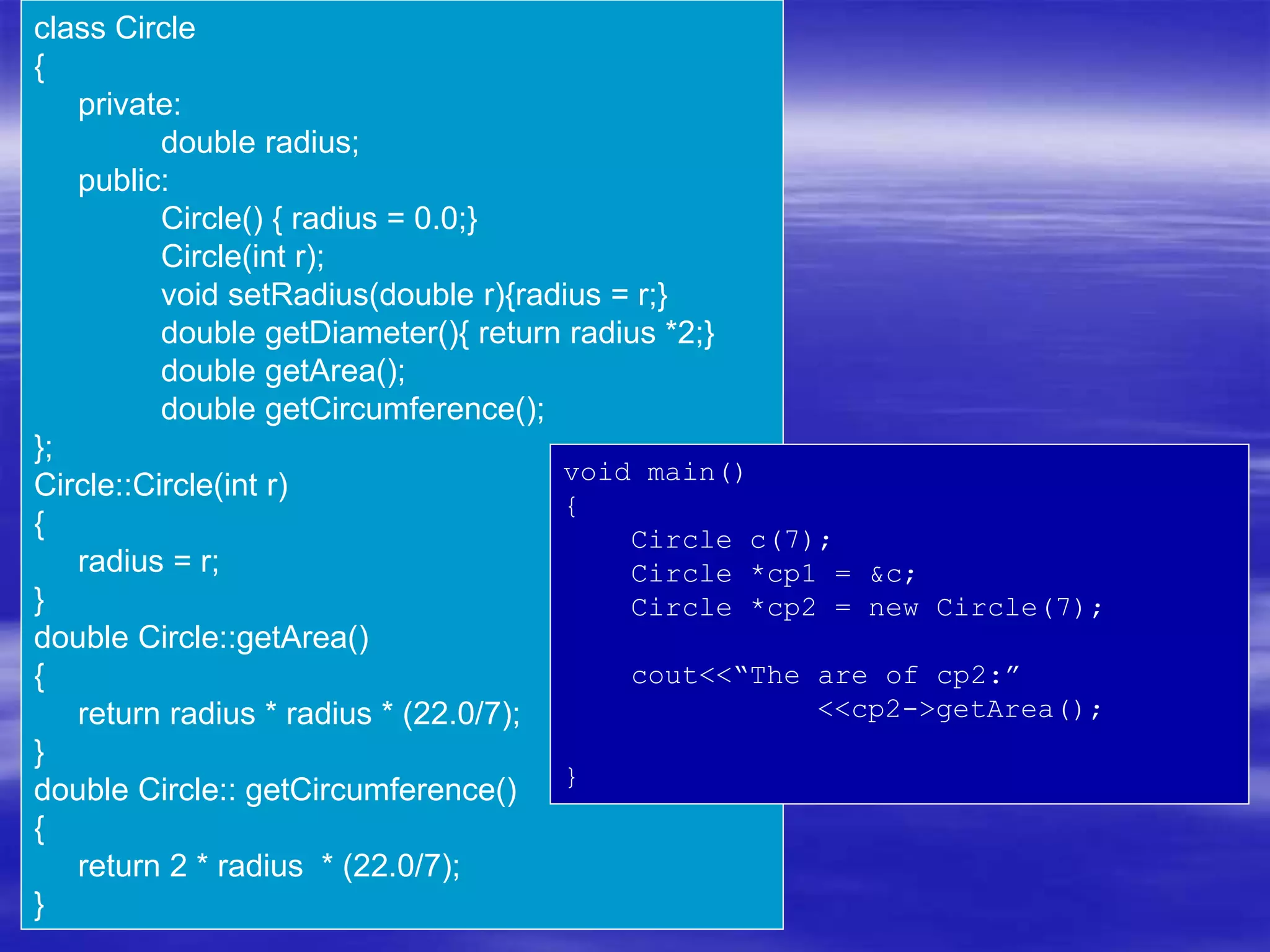
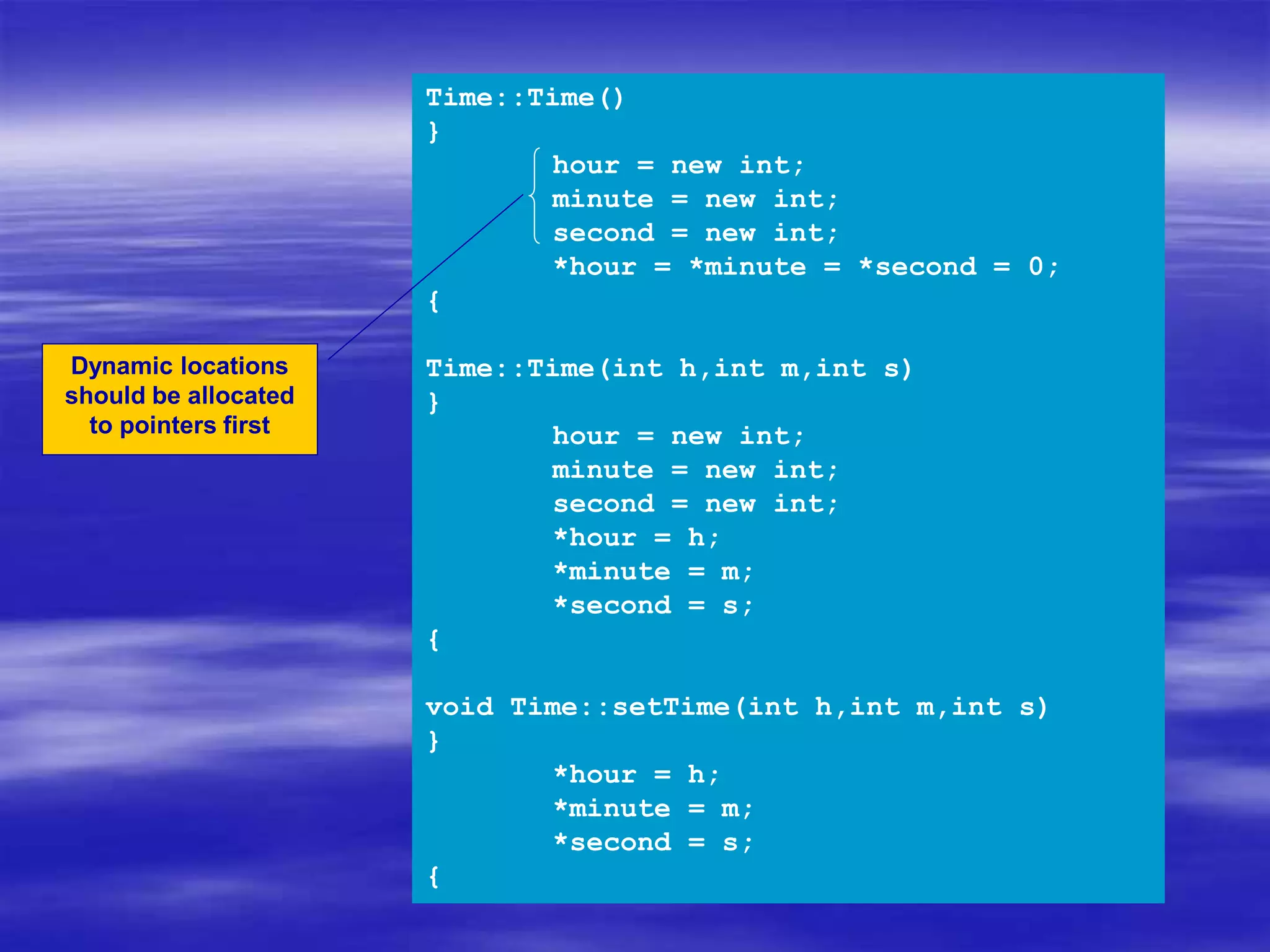
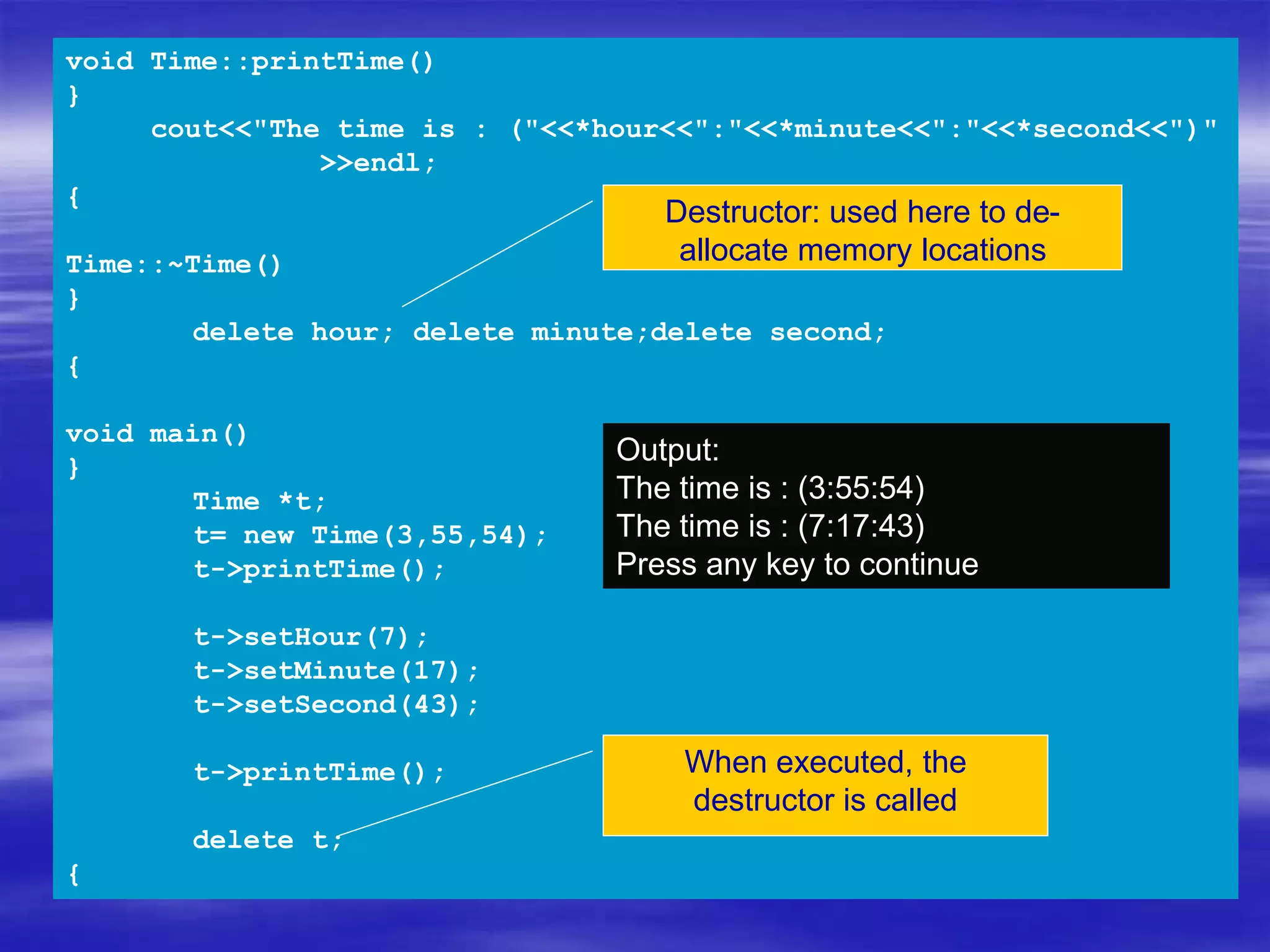
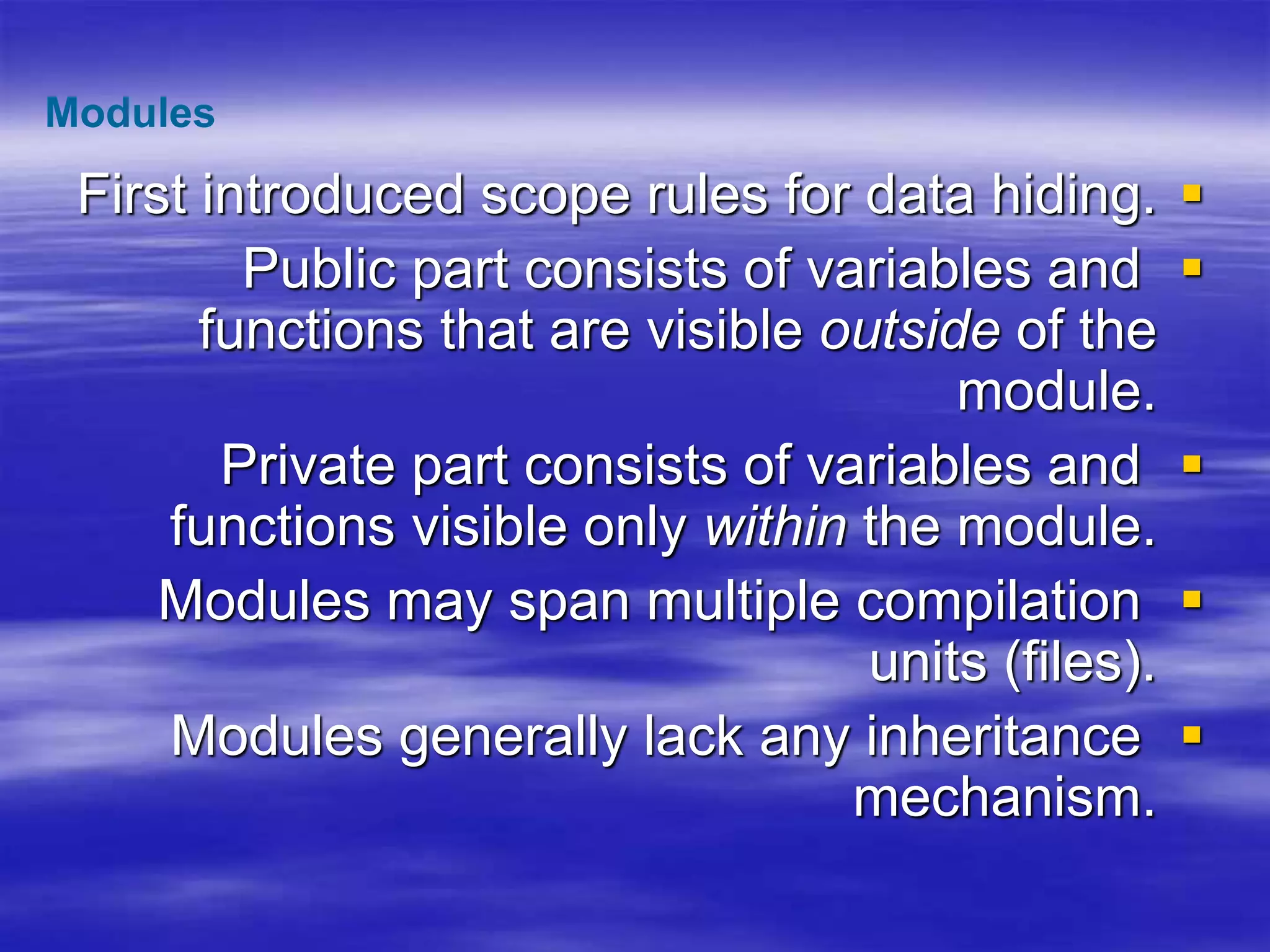
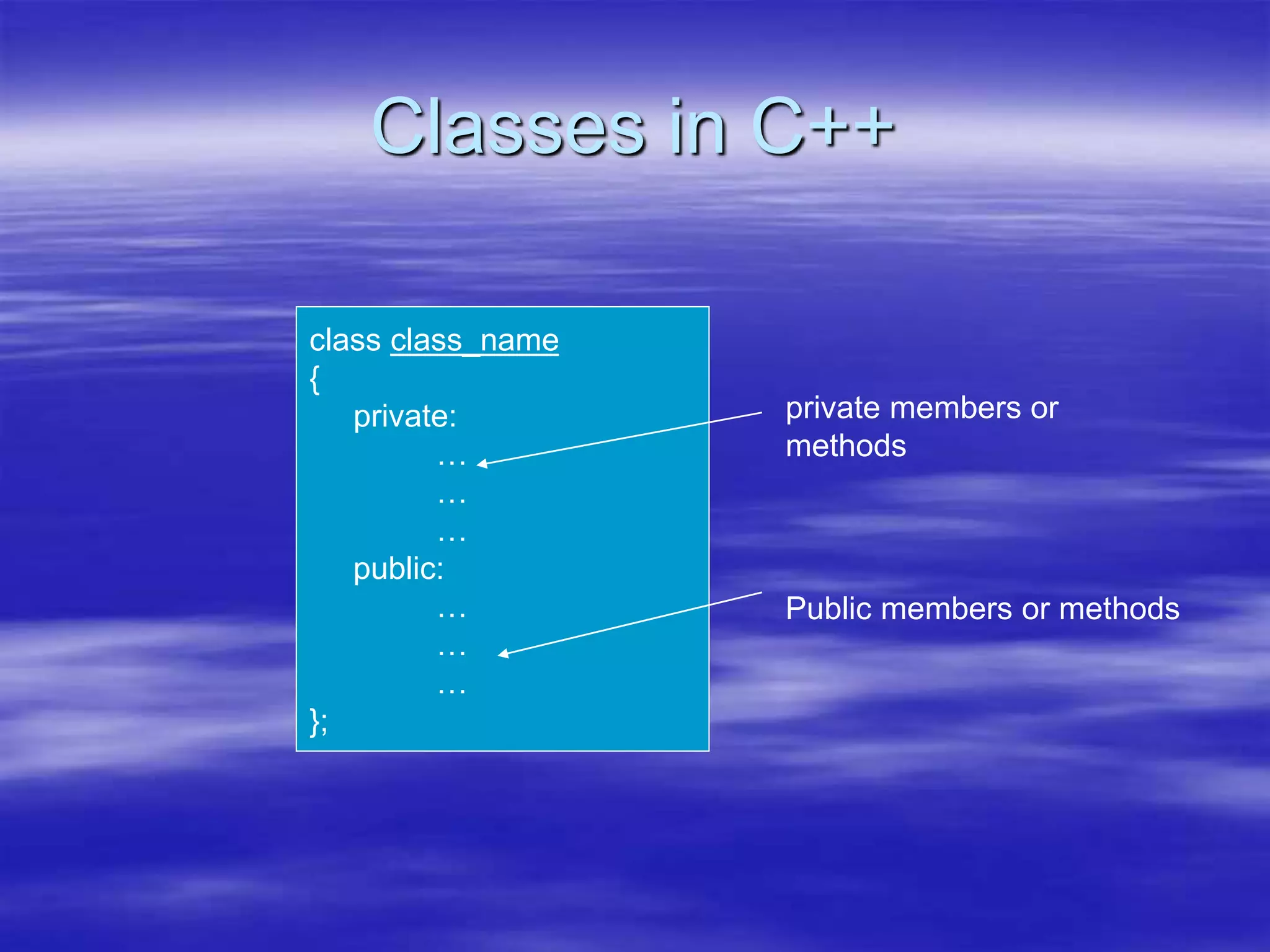
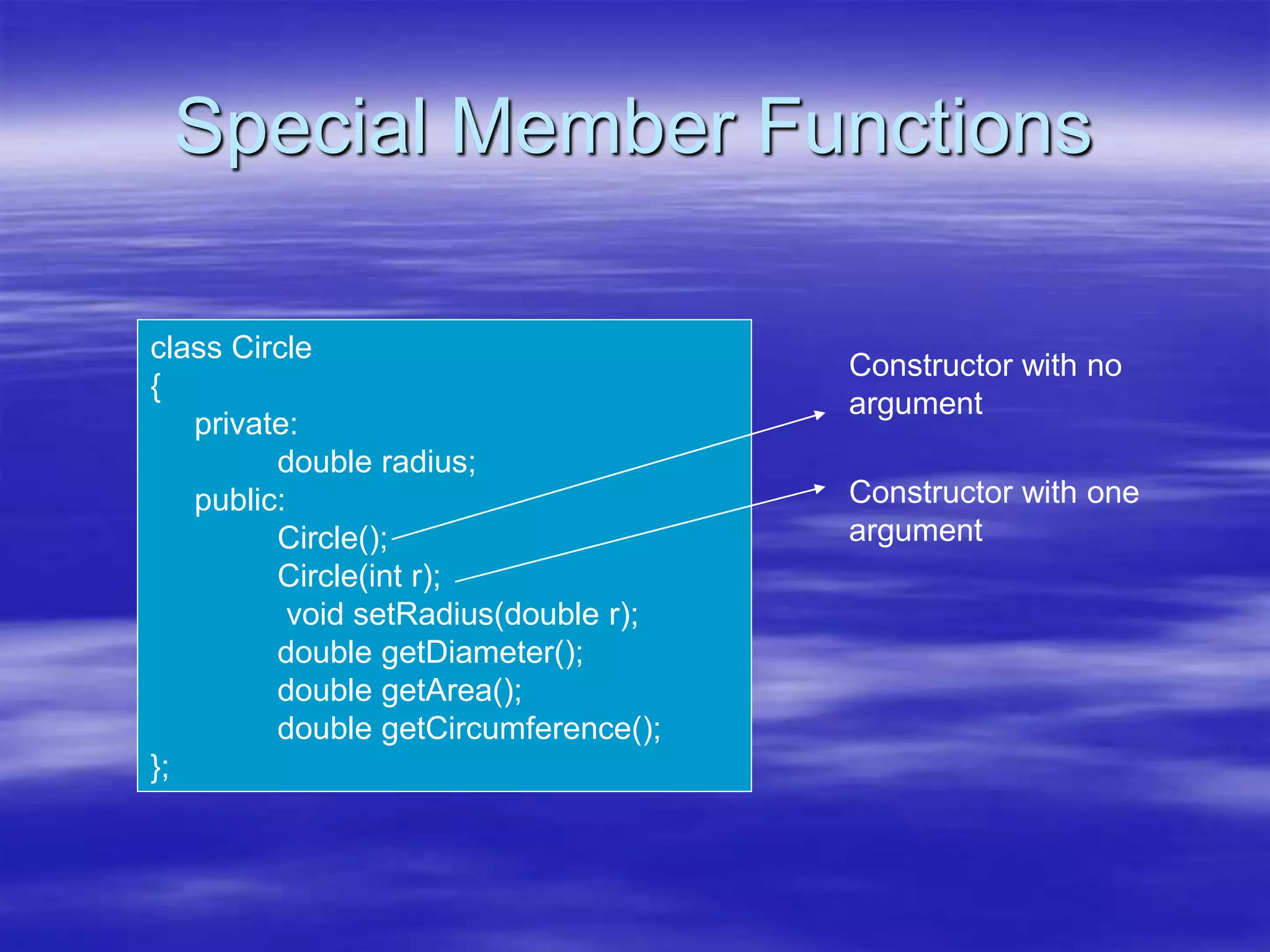
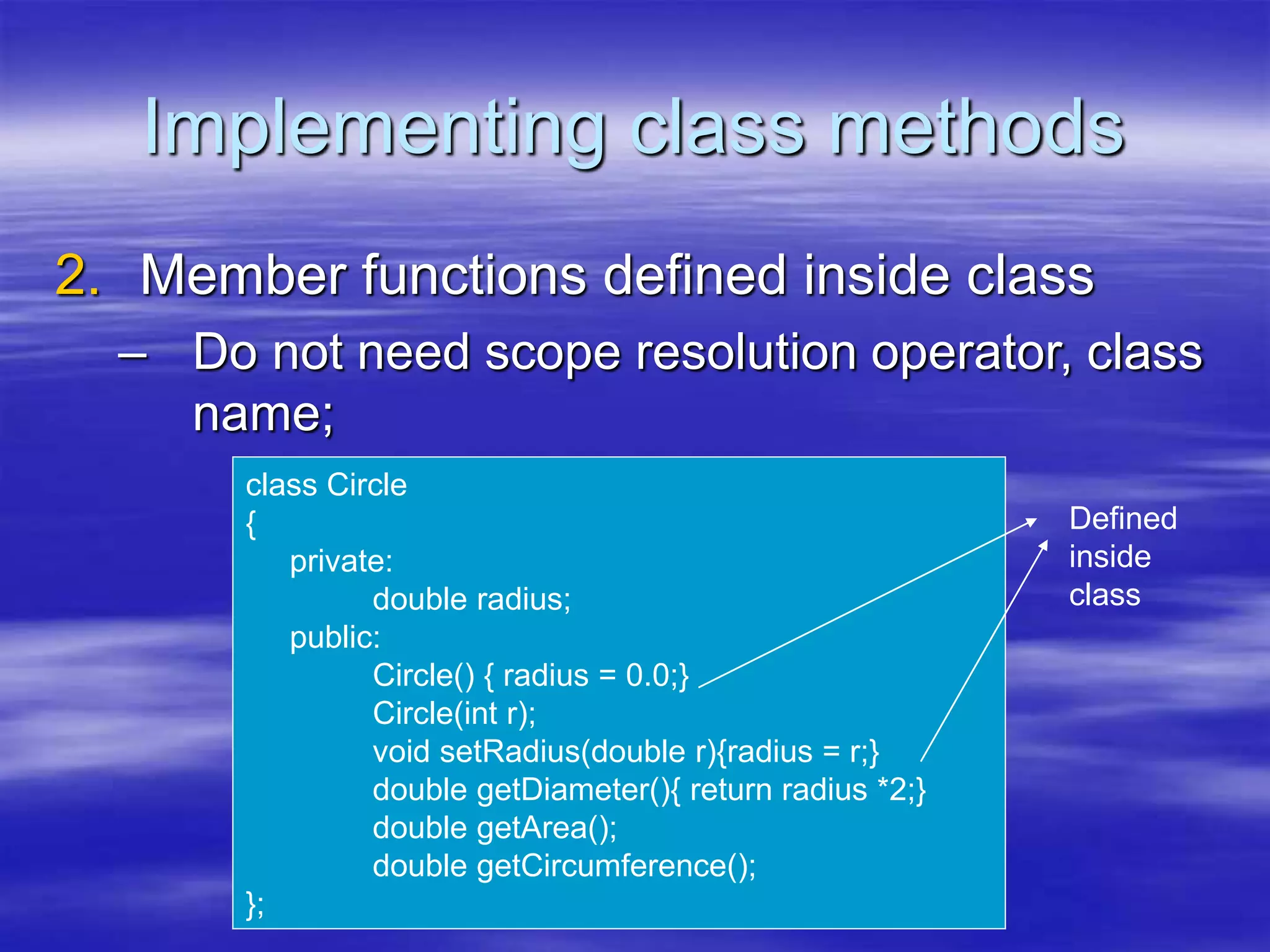
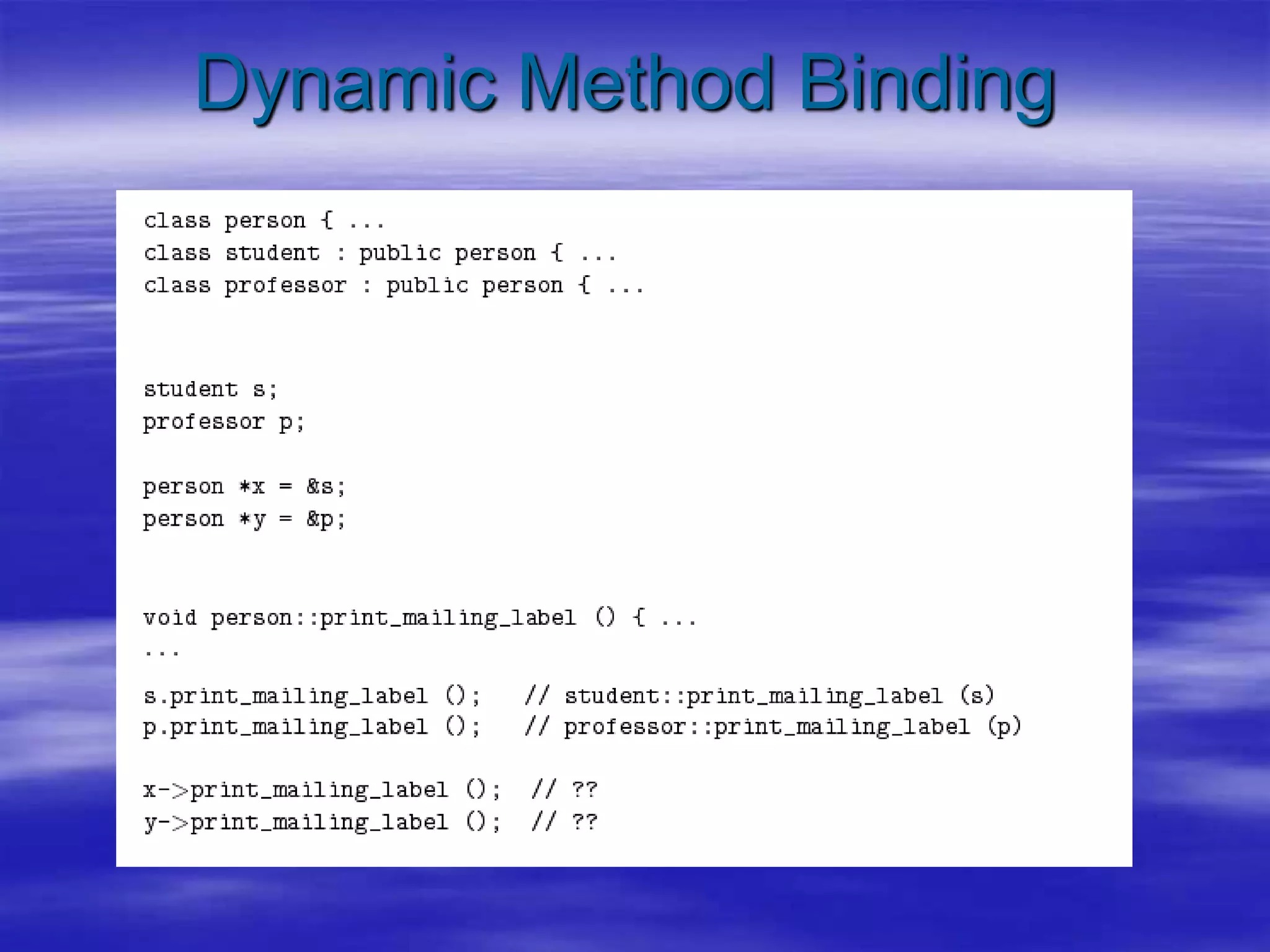
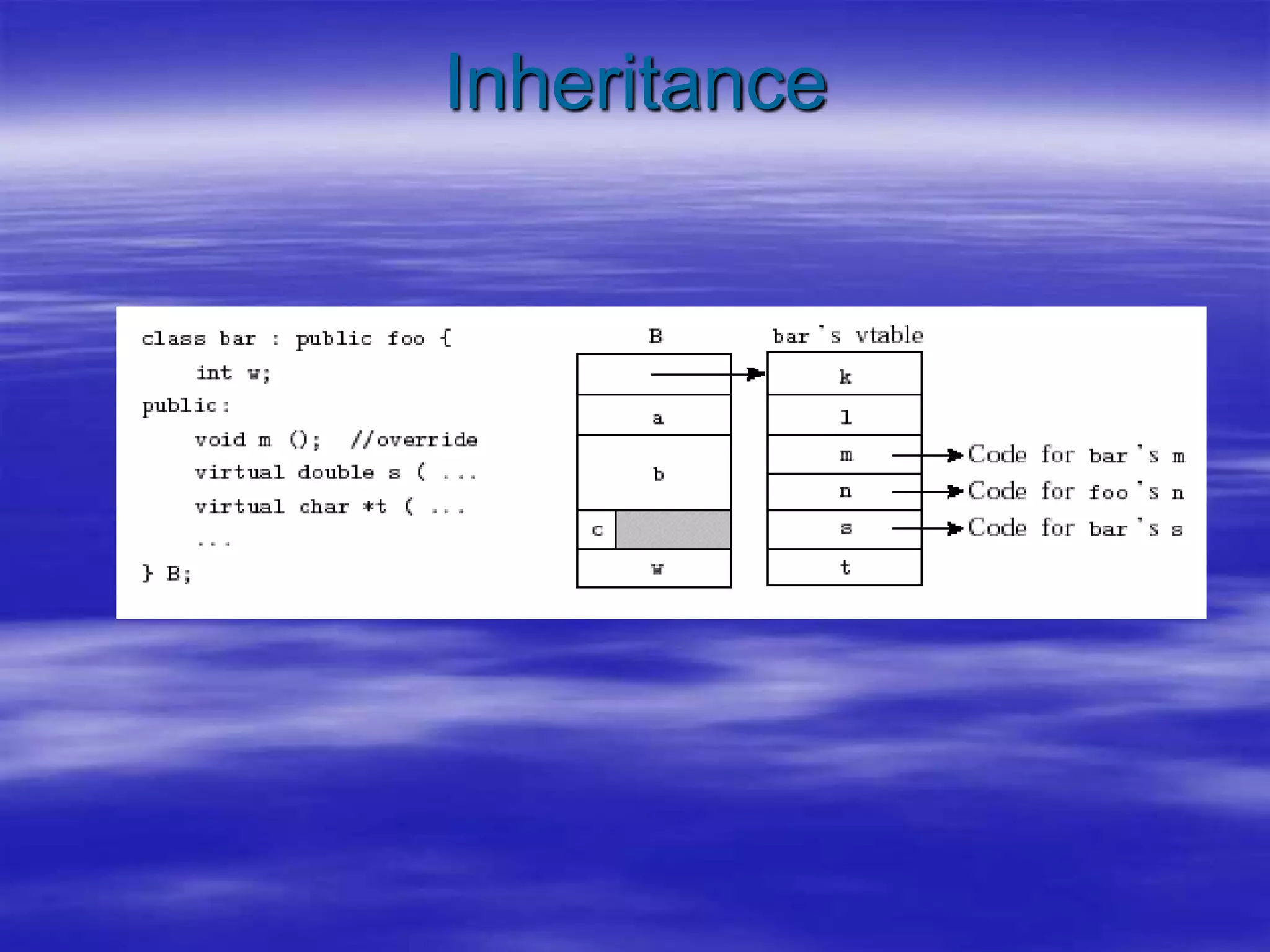
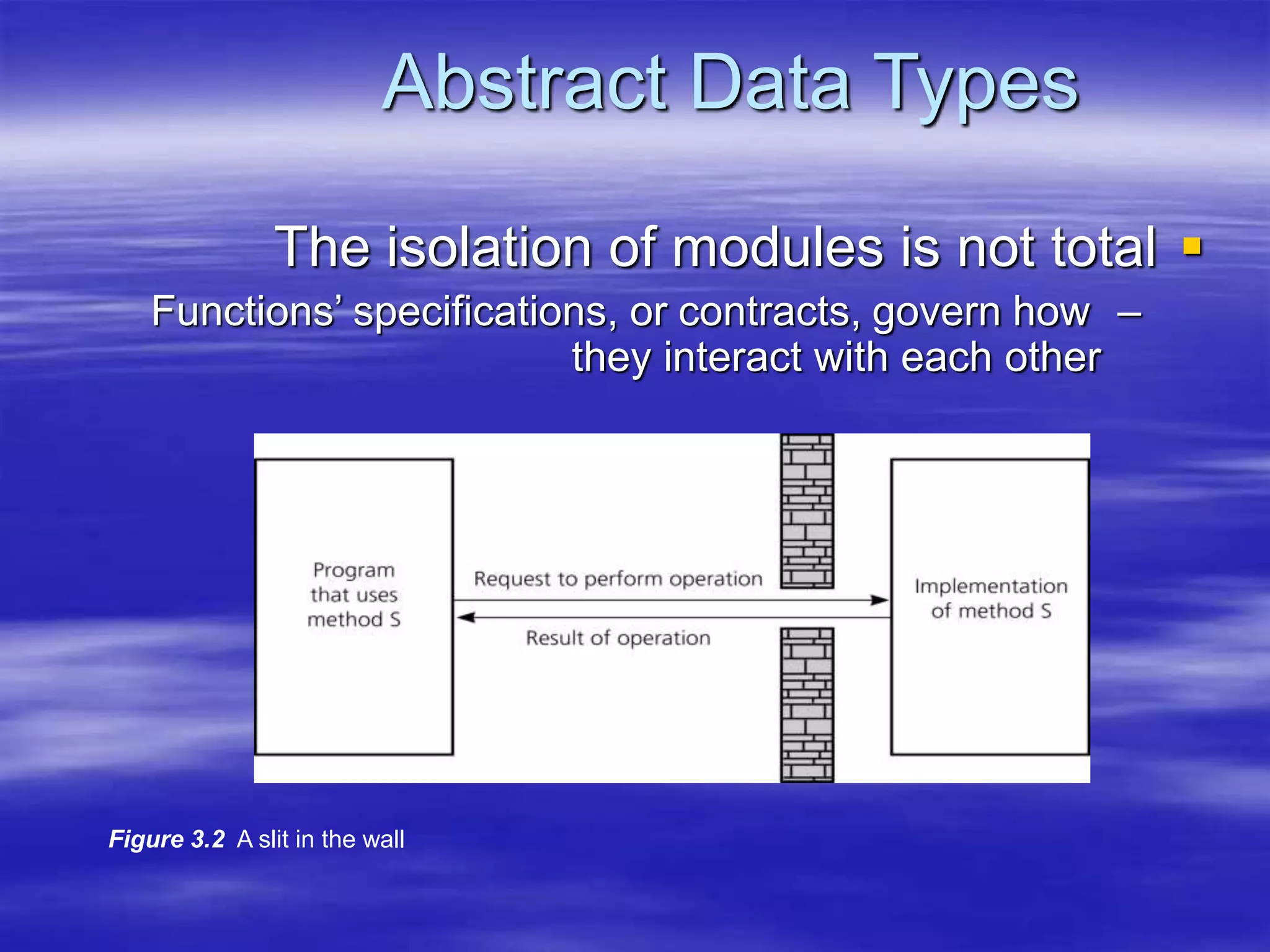
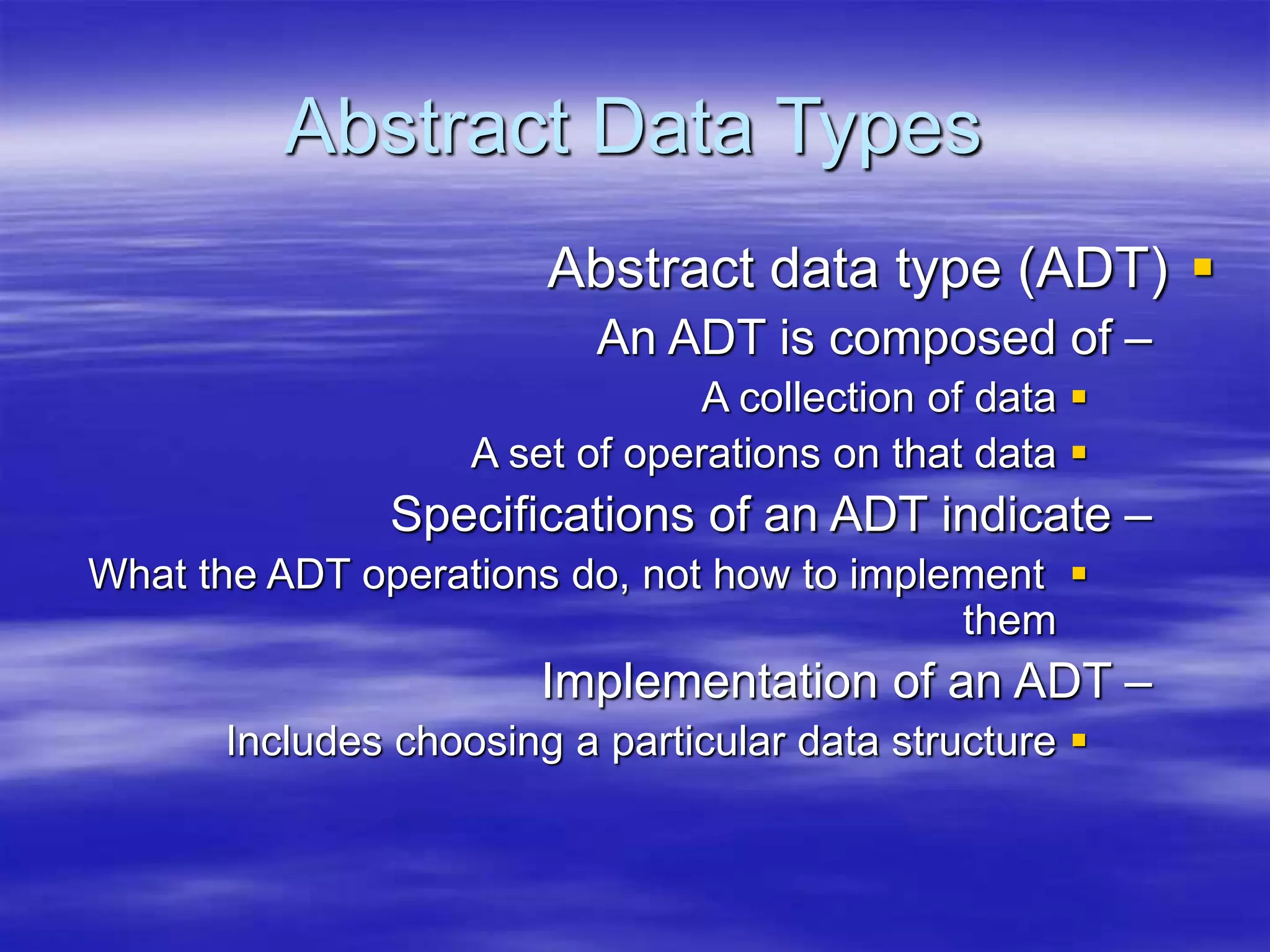
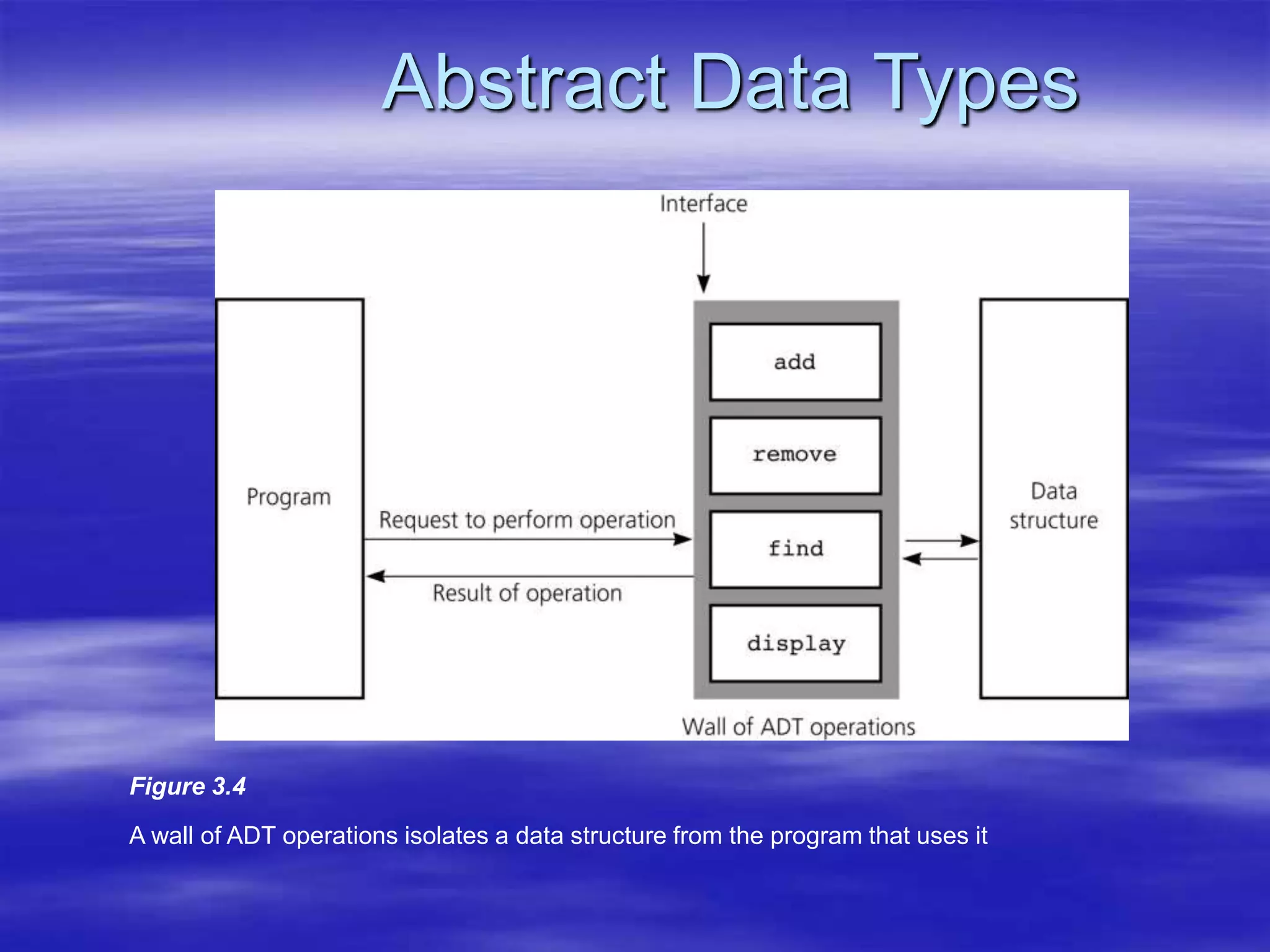
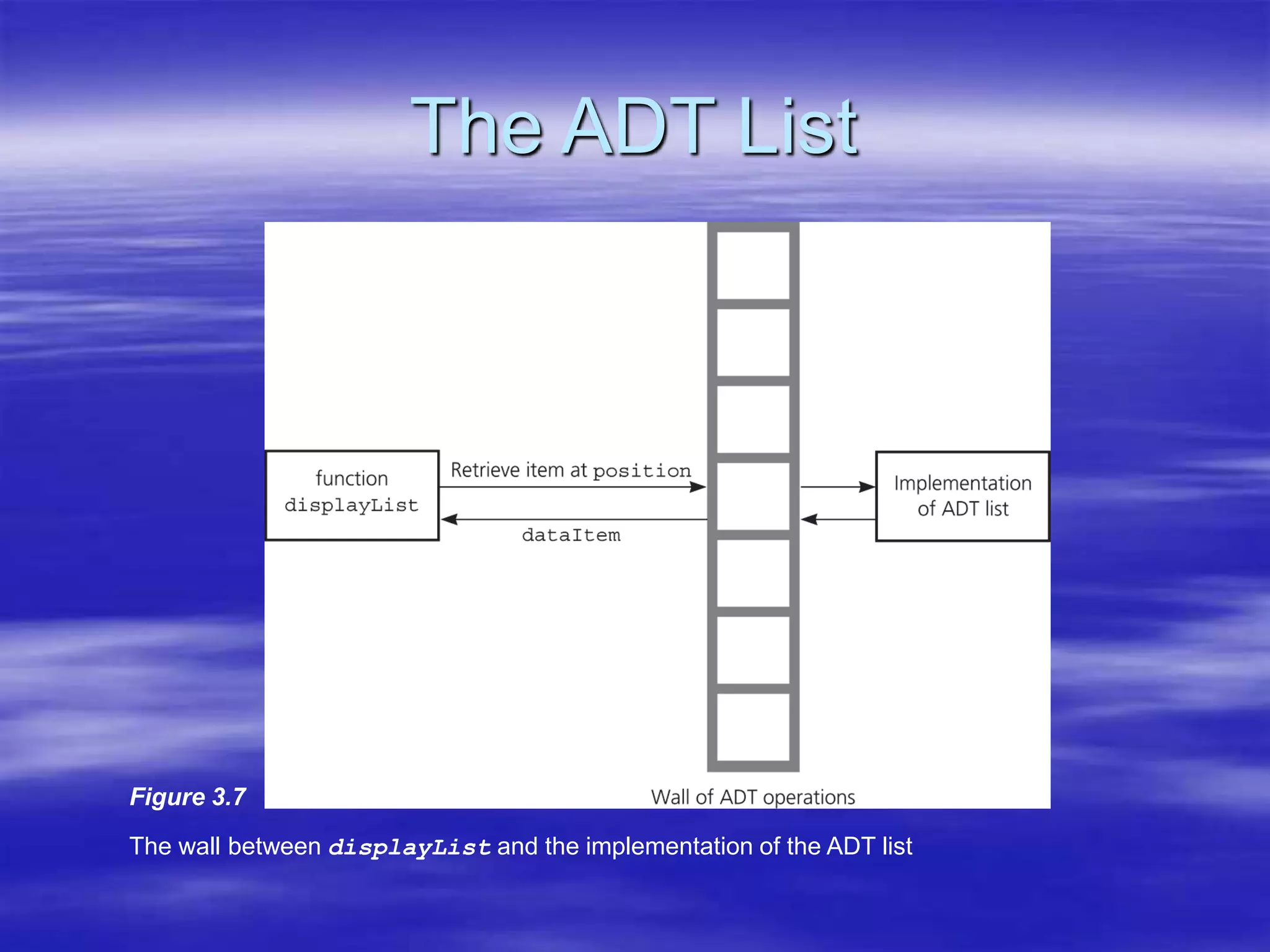
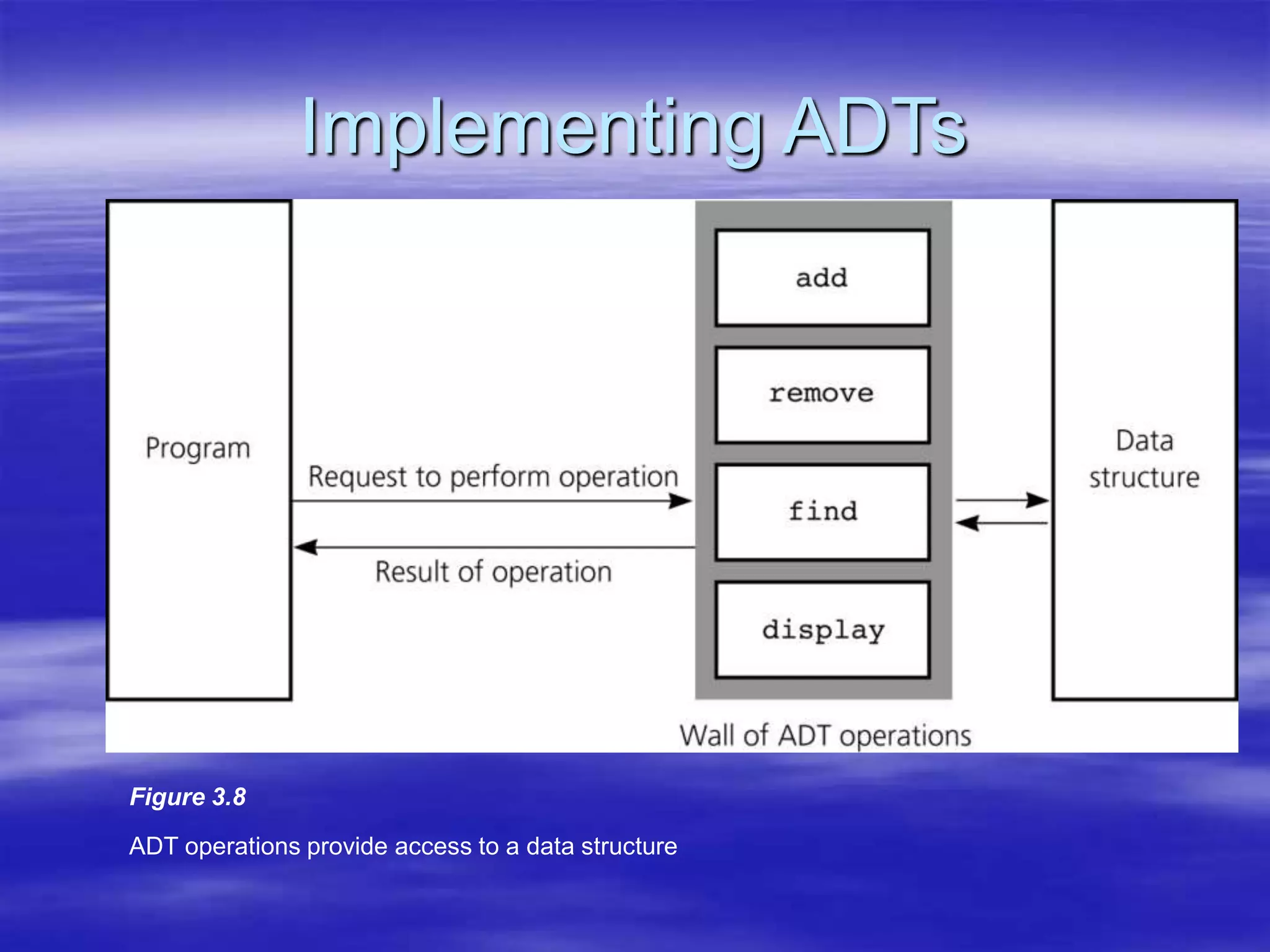
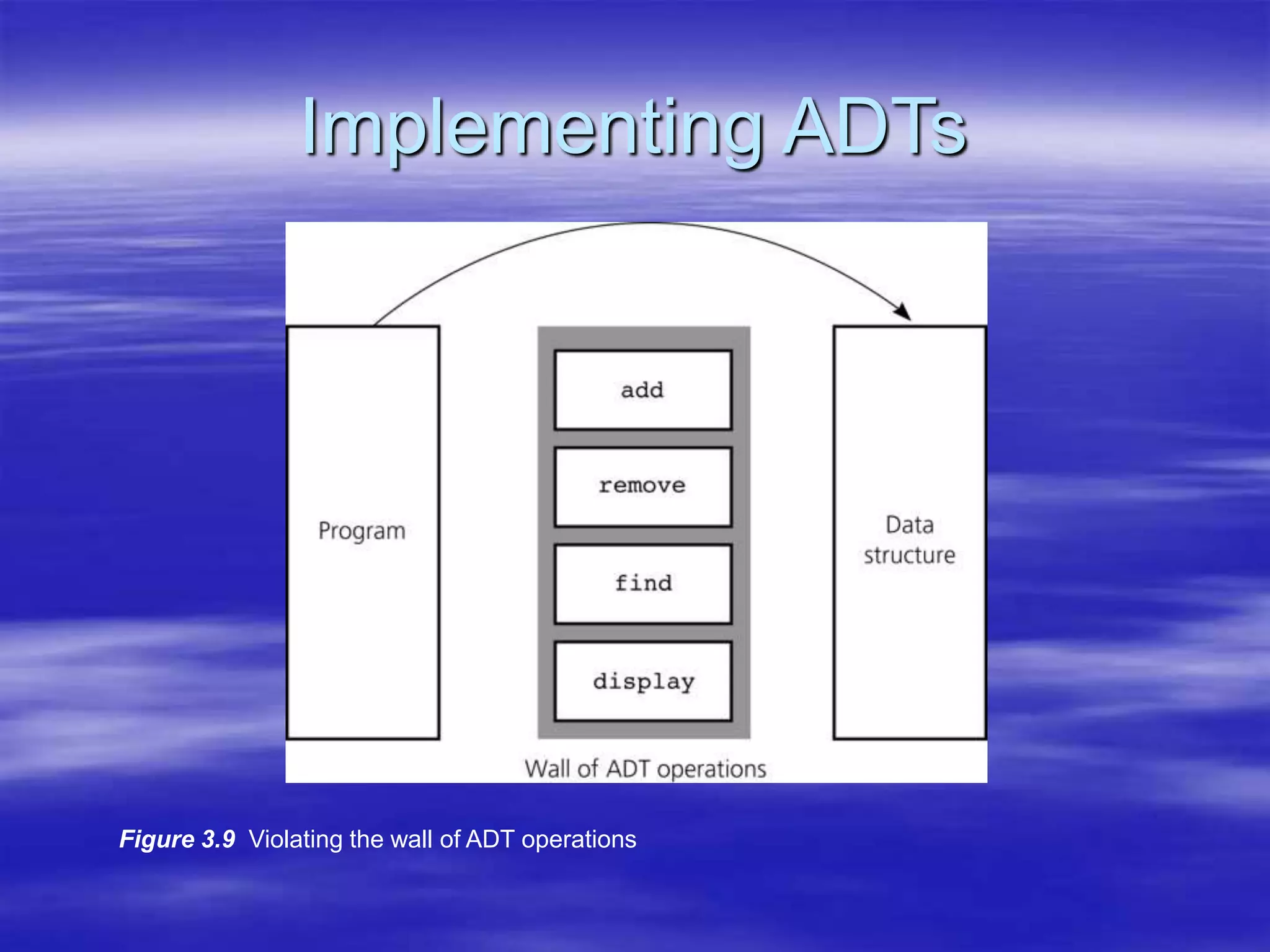
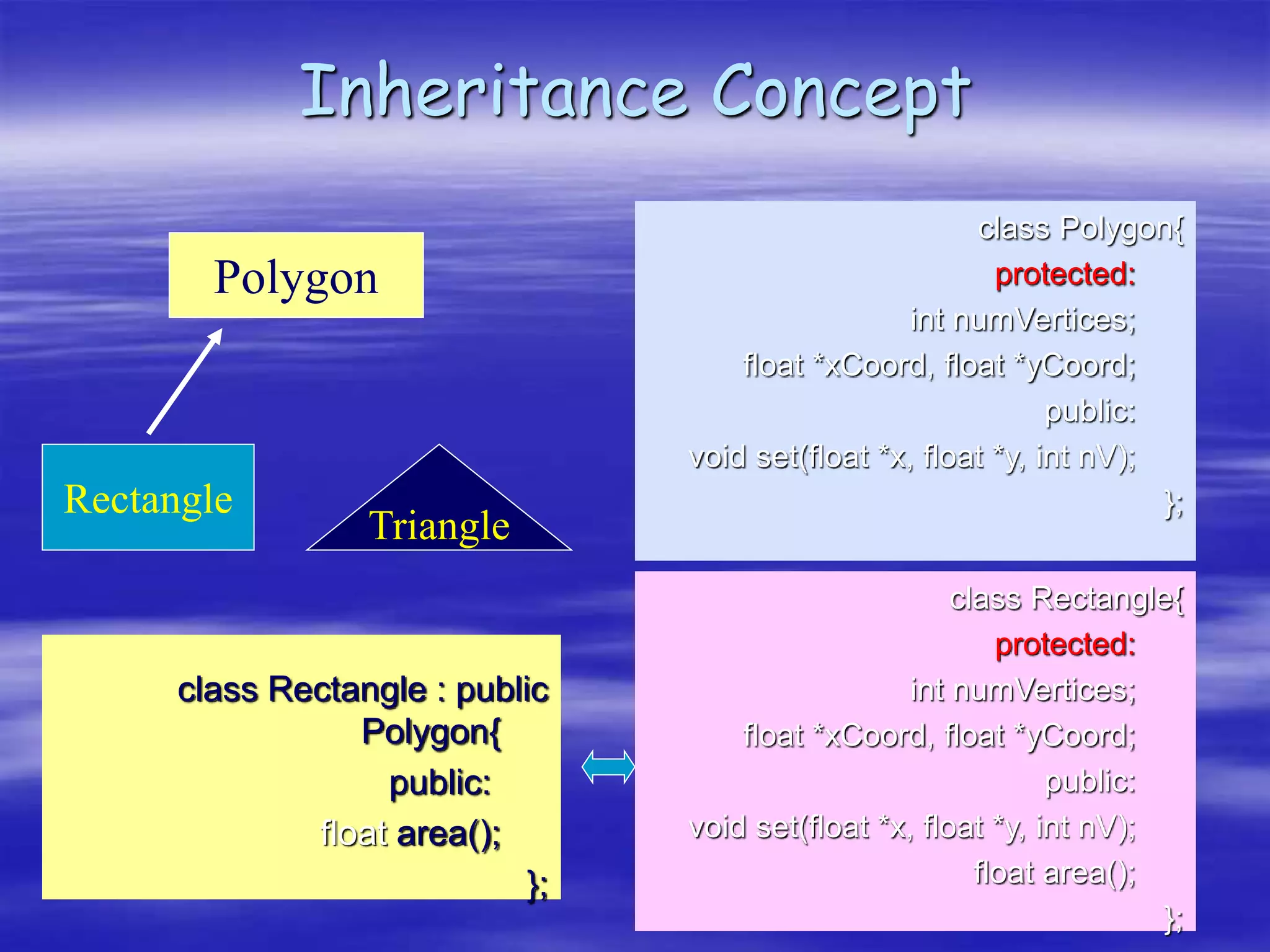
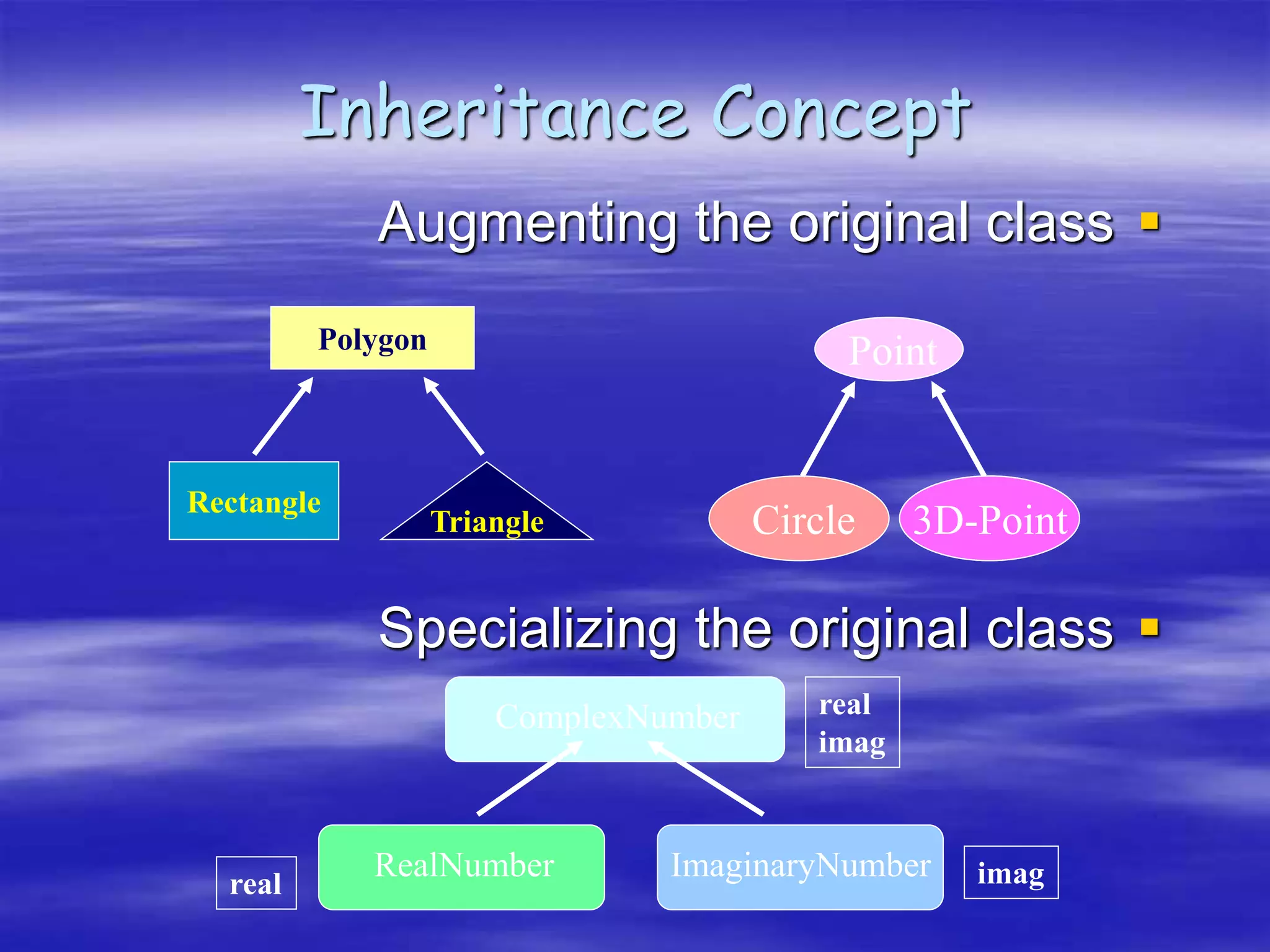
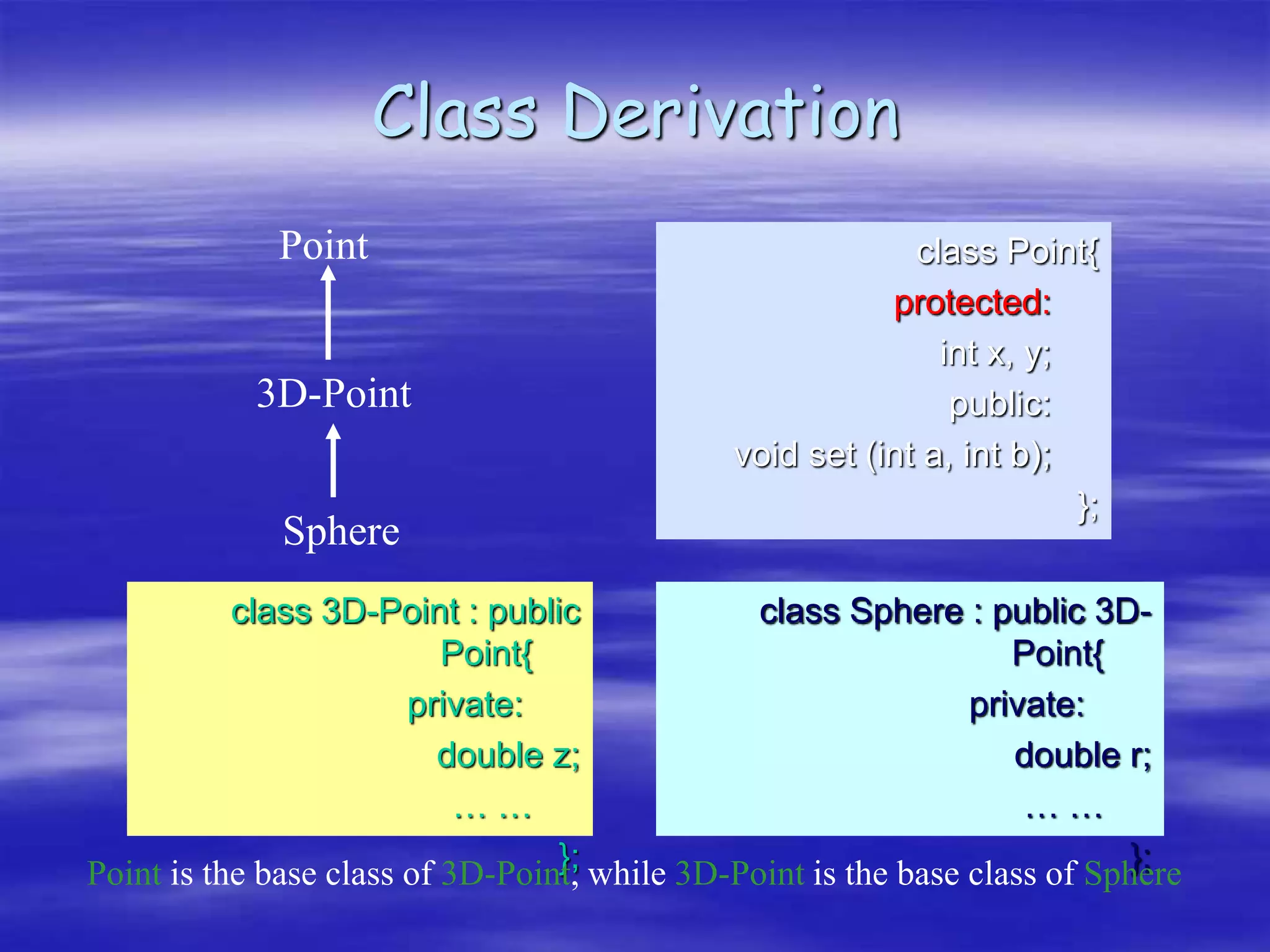
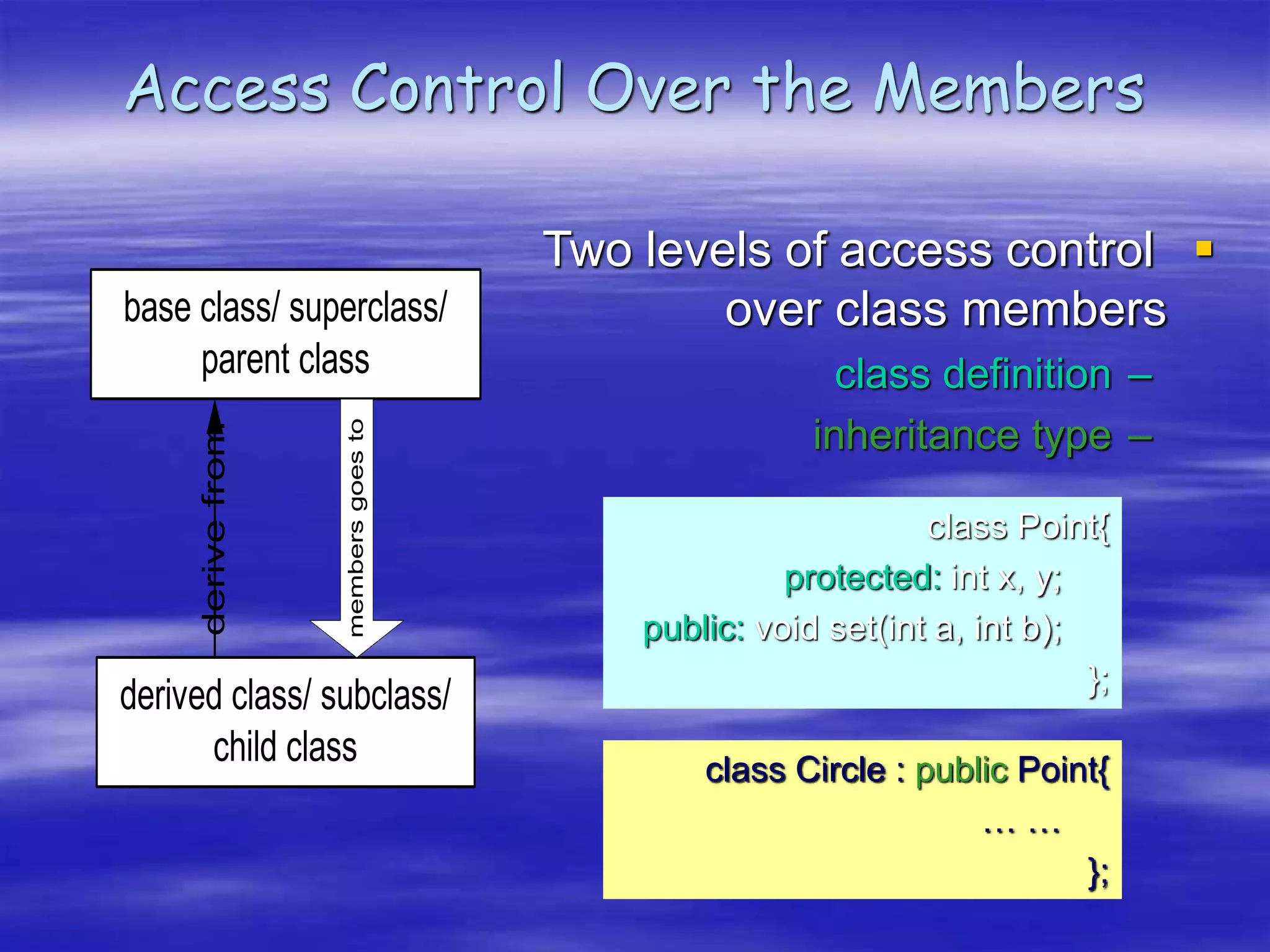
Object Oriented Programming involves modeling real-world entities as objects that encapsulate both data and behavior. Classes define these objects by grouping the data (attributes) and functions (methods) that operate on that data. In C++, classes use access specifiers like public and private to control whether data and methods can be accessed from outside the class or only within the class. Methods are defined either inside or outside the class using the scope resolution operator. Objects are instantiated from classes and their methods and data can be accessed using dot or arrow operators.






























































![Example:
Class person
{
char name[30];
float age;
public:
person(char *s,float a)
{
strcpy(name,s);
age=a;
}
person& greater(person &x)
{
if(x.age>=age)
return x;
else
return *this;
}
void display (void)
{
cout<<name<<age;
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti1-230731070518-1bb9f9e5/75/UNIT-I-1-ppt-85-2048.jpg)