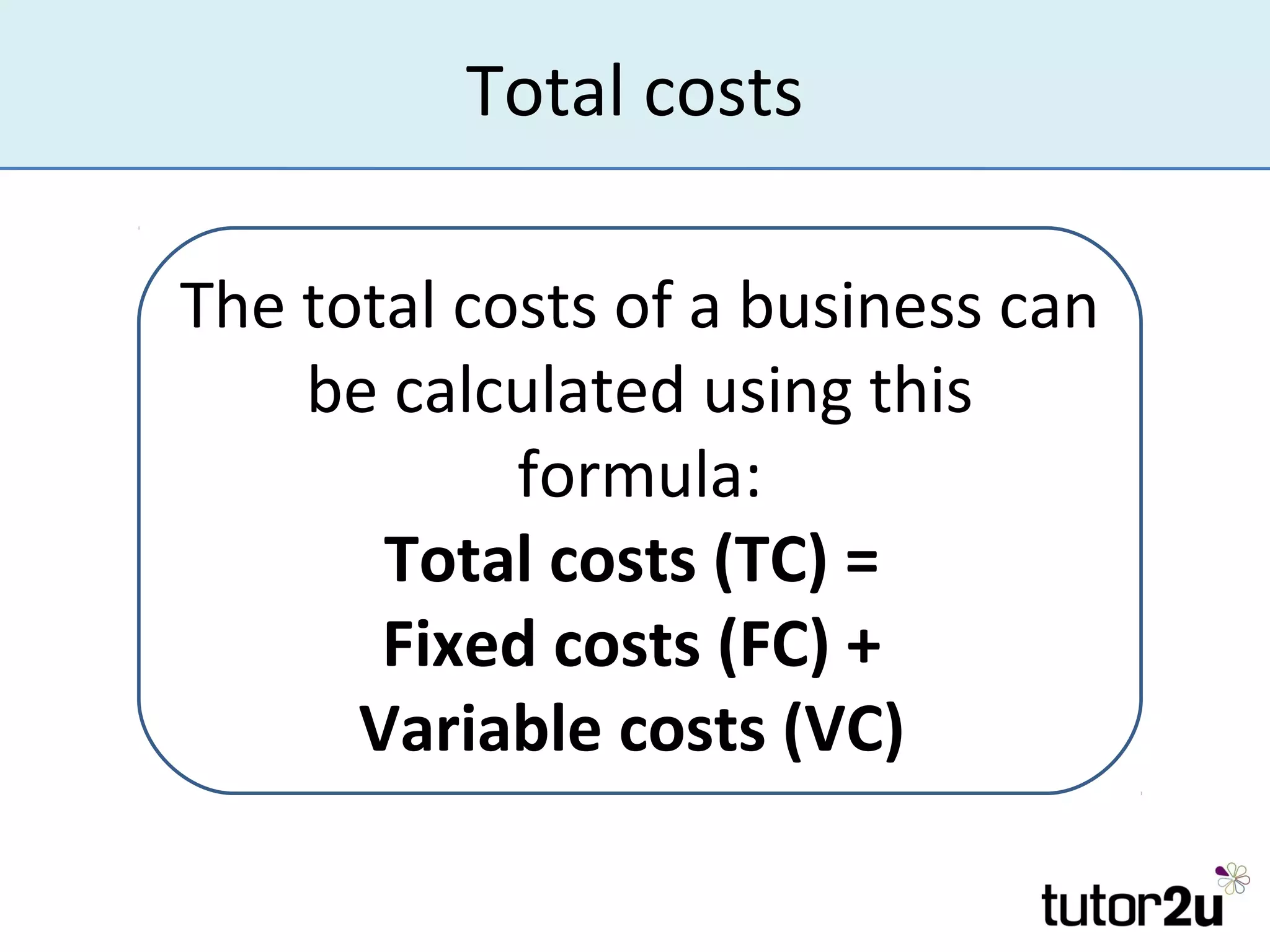
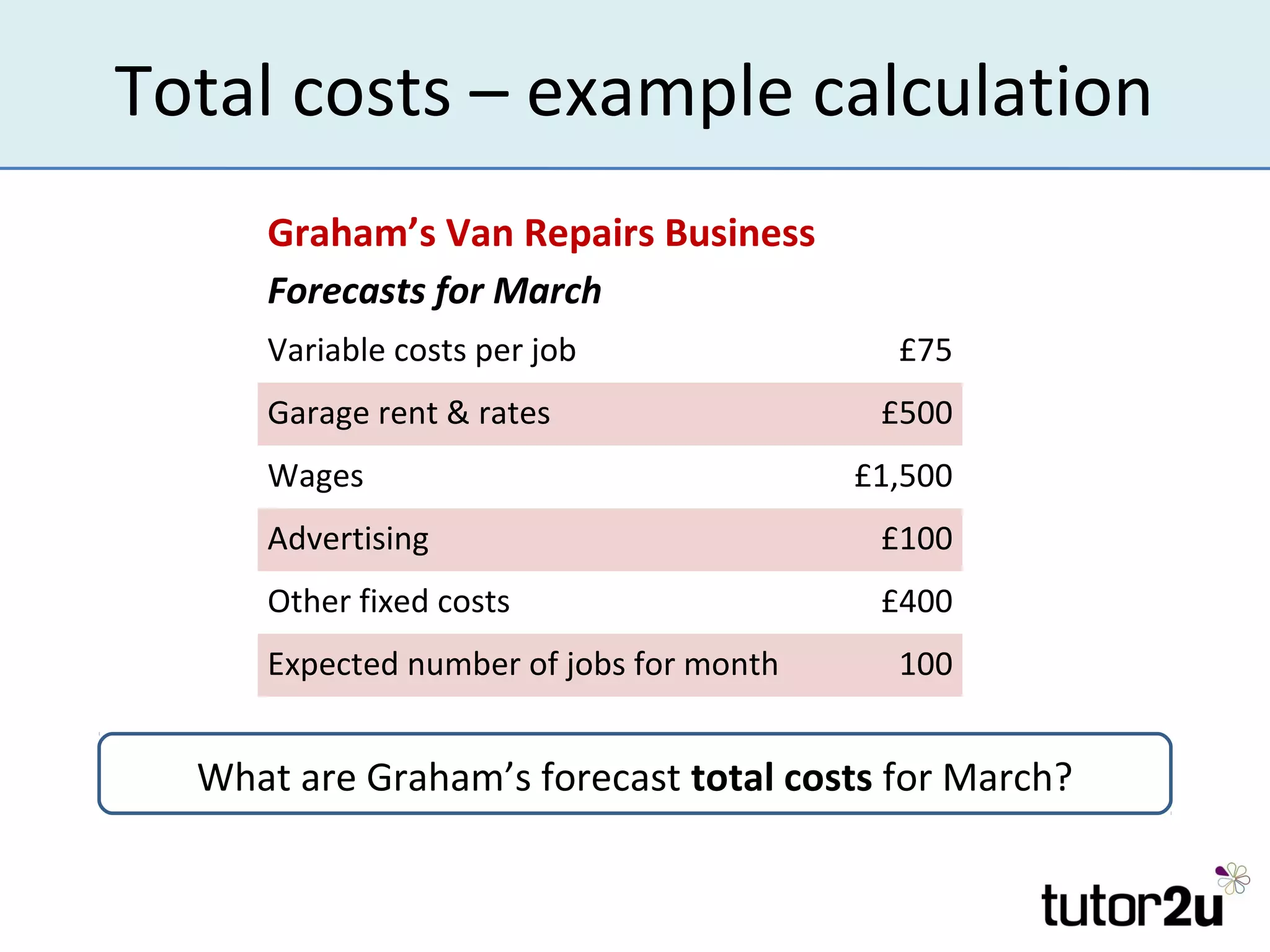
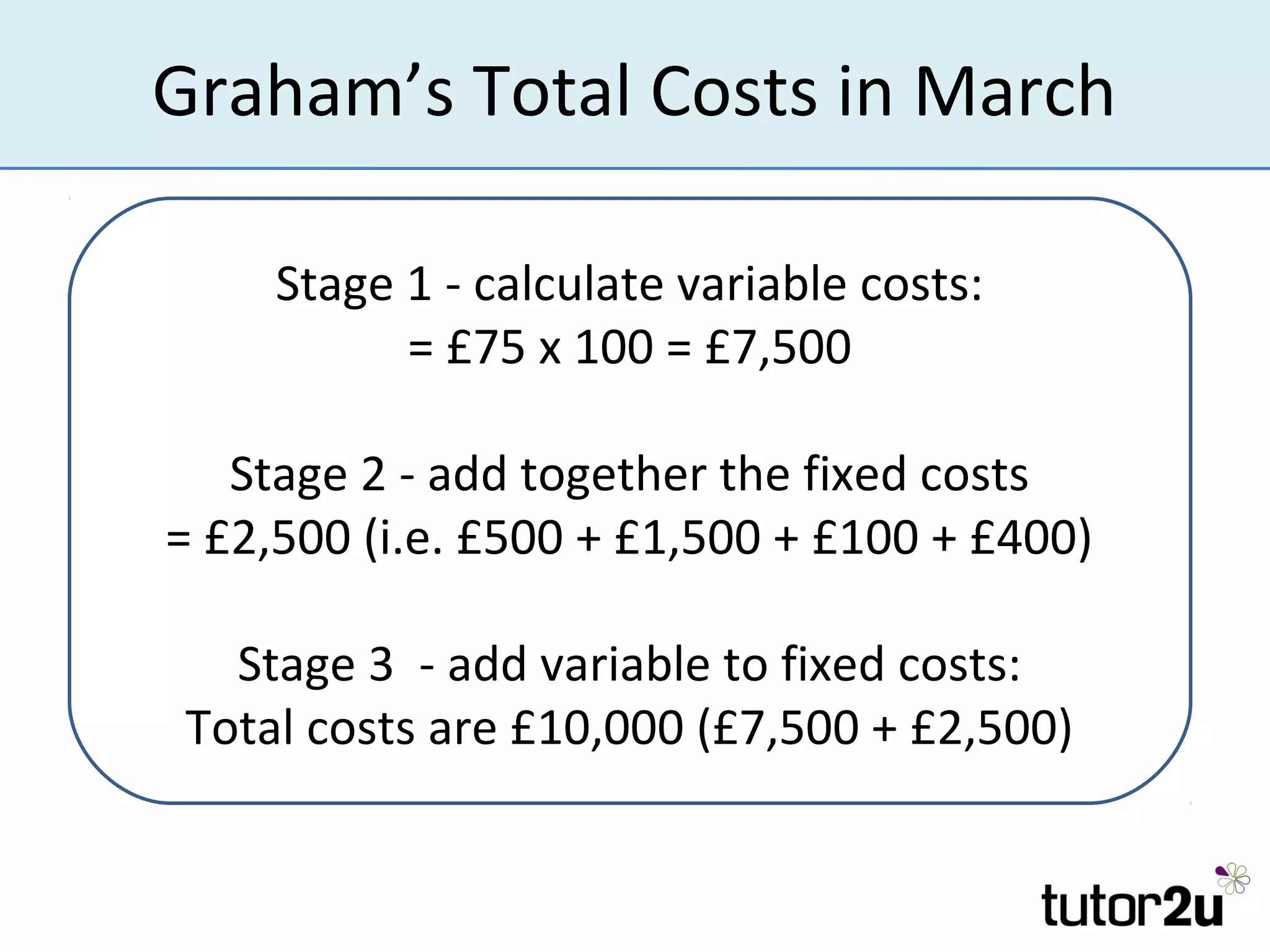
Costs are amounts that businesses incur to produce goods and services. There are variable costs that change with output and fixed costs that remain constant. Variable costs include raw materials and wages, while fixed costs include rent, salaries, and insurance. Total costs are the sum of fixed and variable costs. Understanding costs is important for entrepreneurs to manage profits, cash flow, and how costs may change with business decisions or activity levels. Accurately estimating all types of costs, which can be difficult, is crucial for business planning and forecasting.