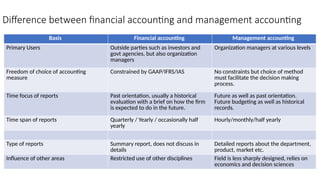
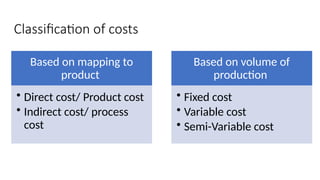
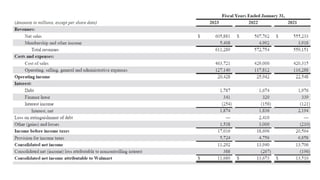
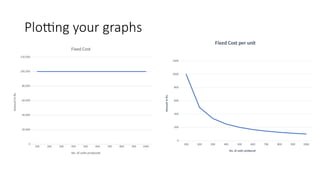
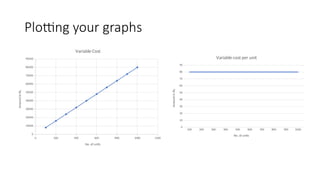
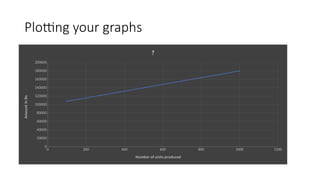
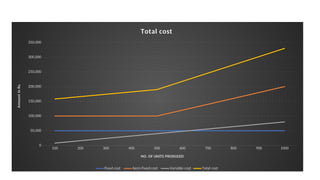
The document provides an introduction to management accounting, detailing its necessity, major functions, and differentiating it from financial accounting. It discusses various cost classifications, including direct, indirect, and period costs, as well as the significance of understanding fixed and variable costs in relation to production levels. The content emphasizes the role of cost drivers in determining expenses associated with manufacturing processes.