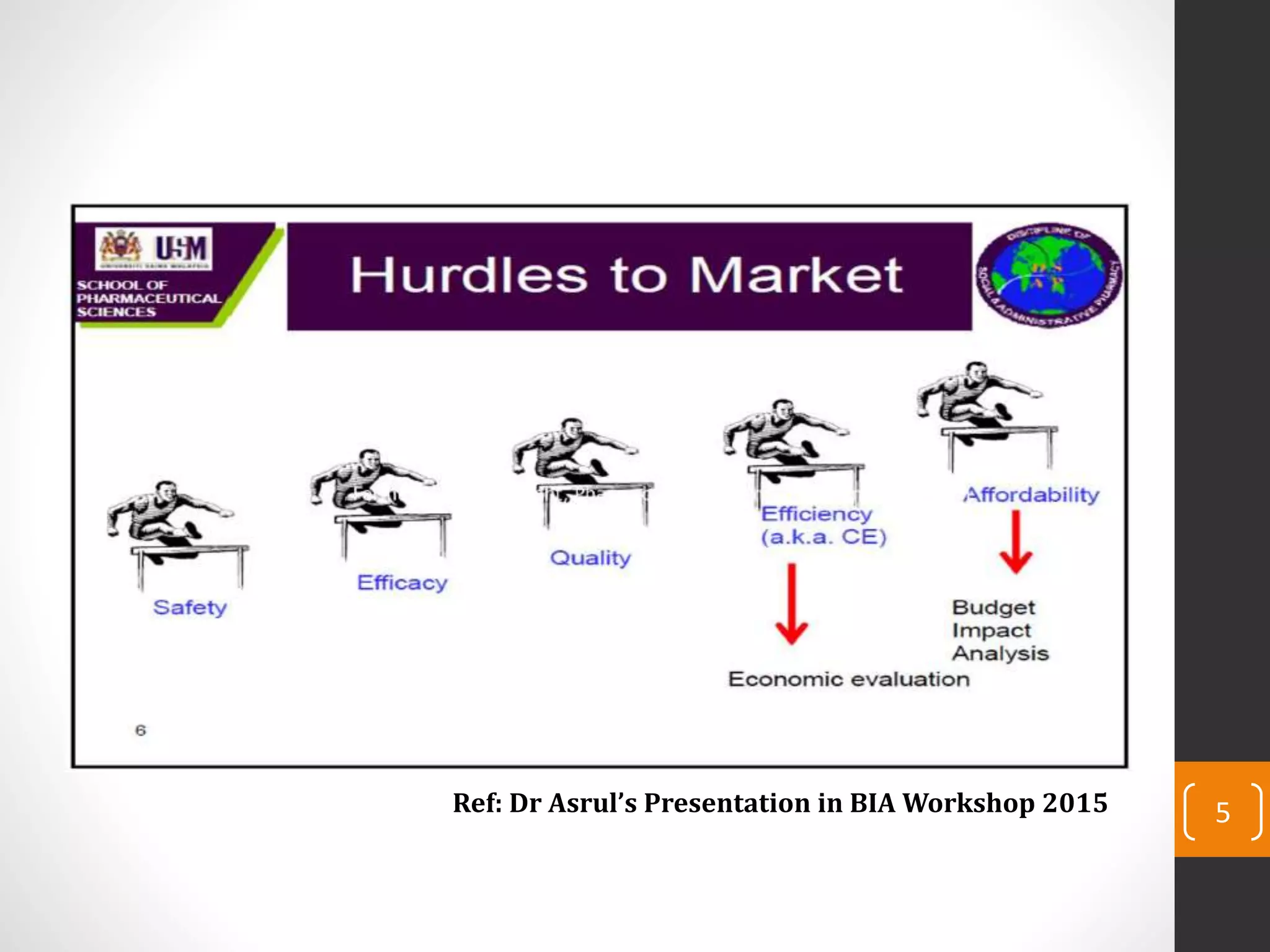
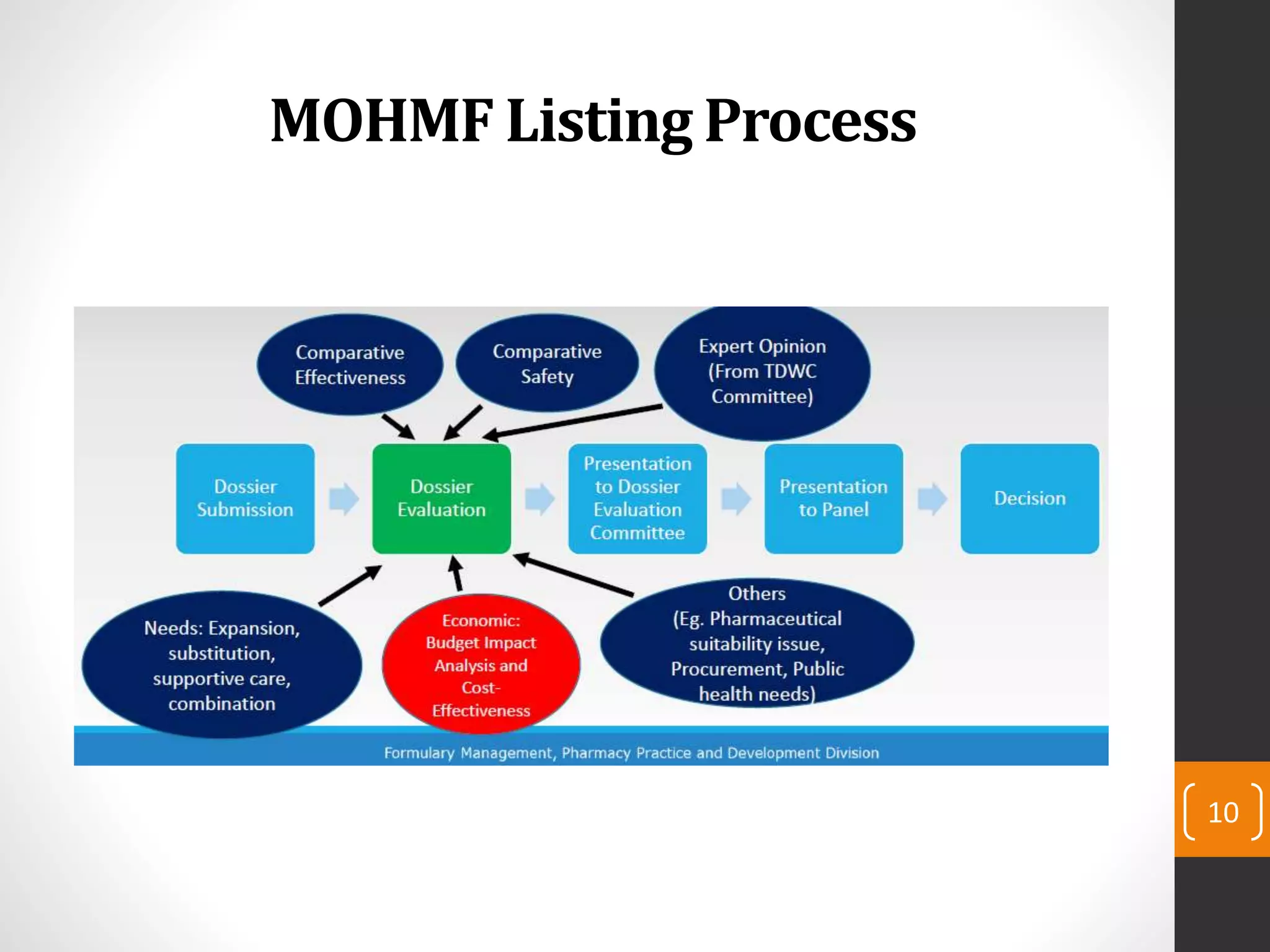
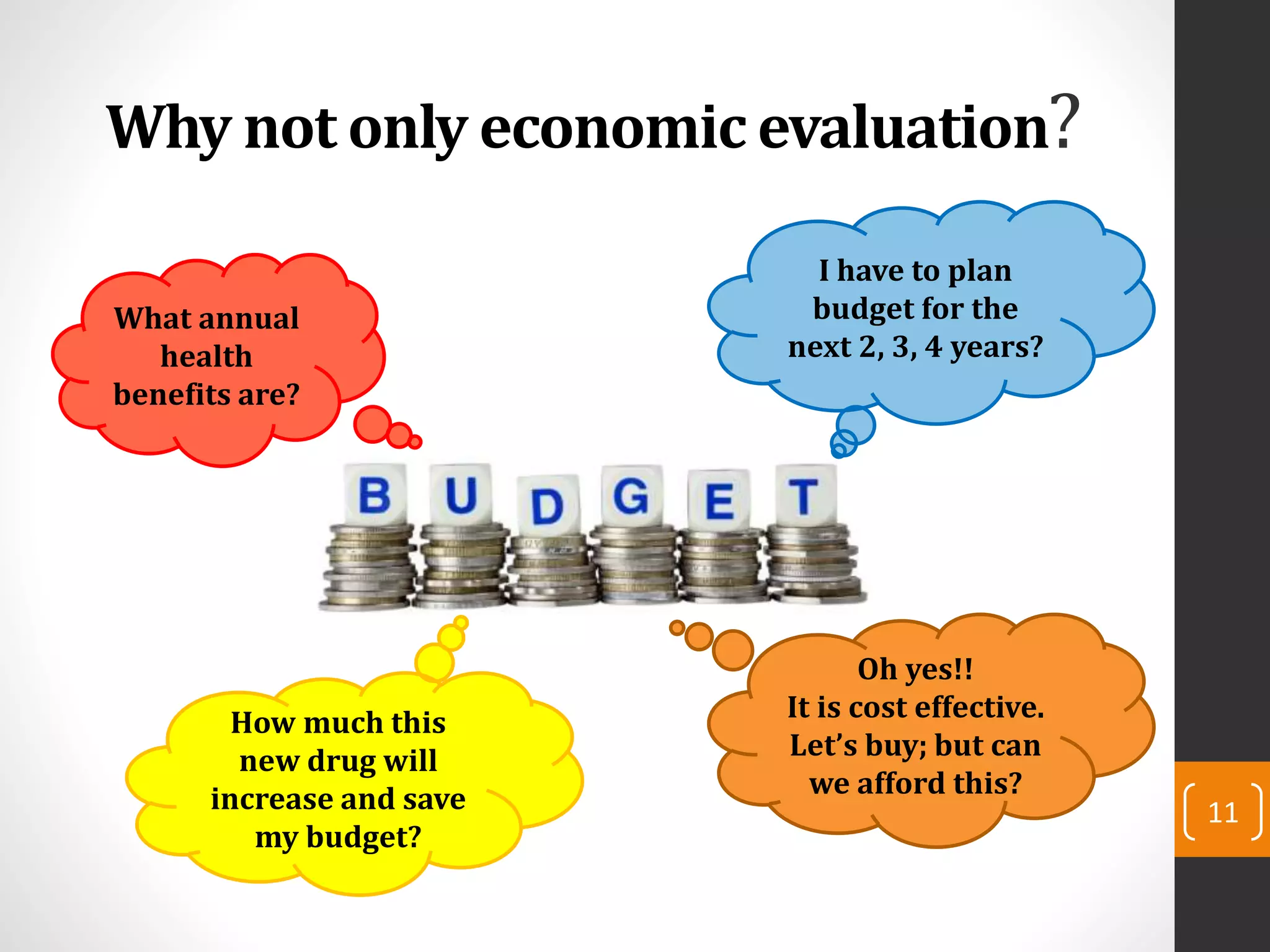
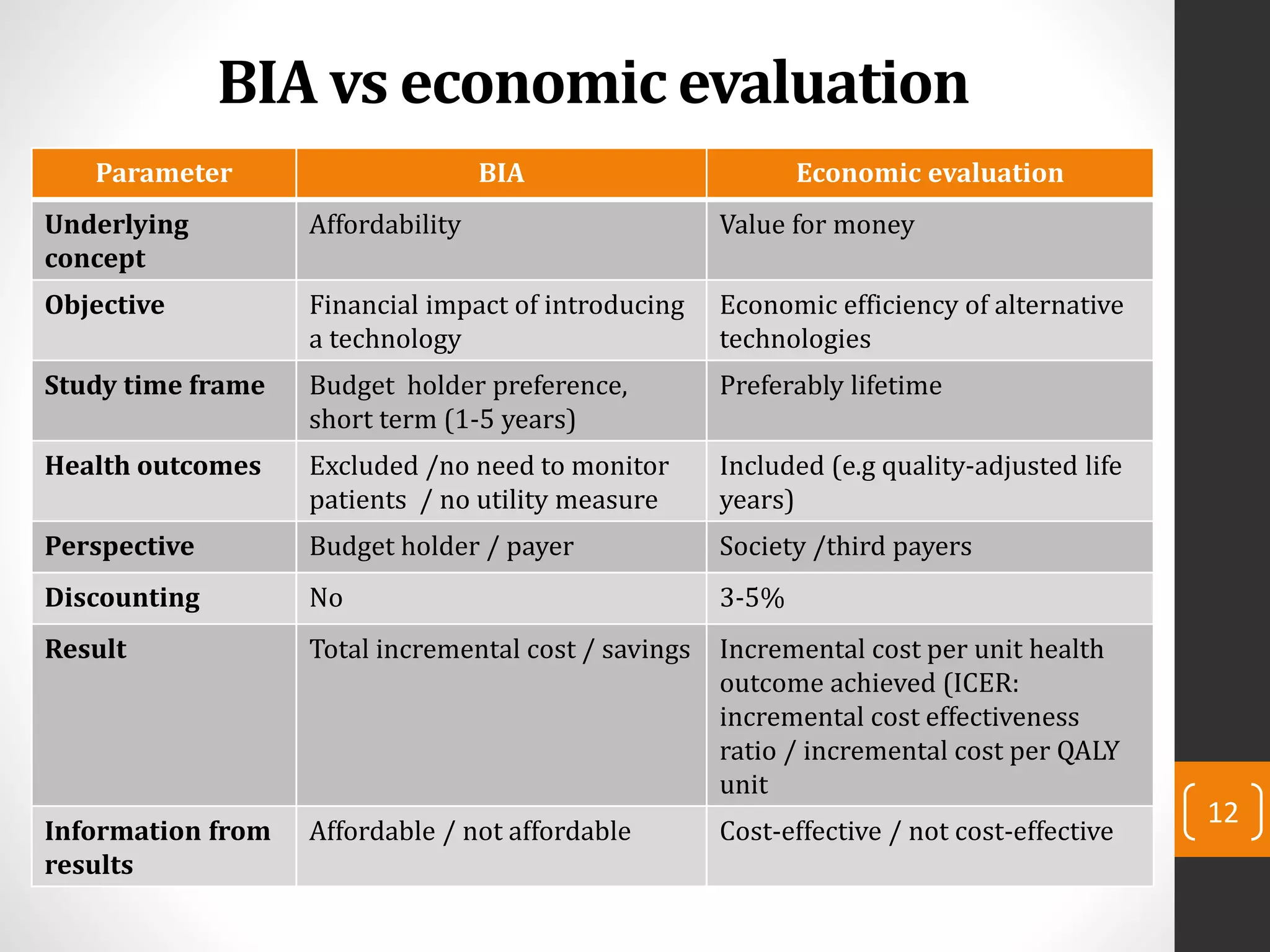
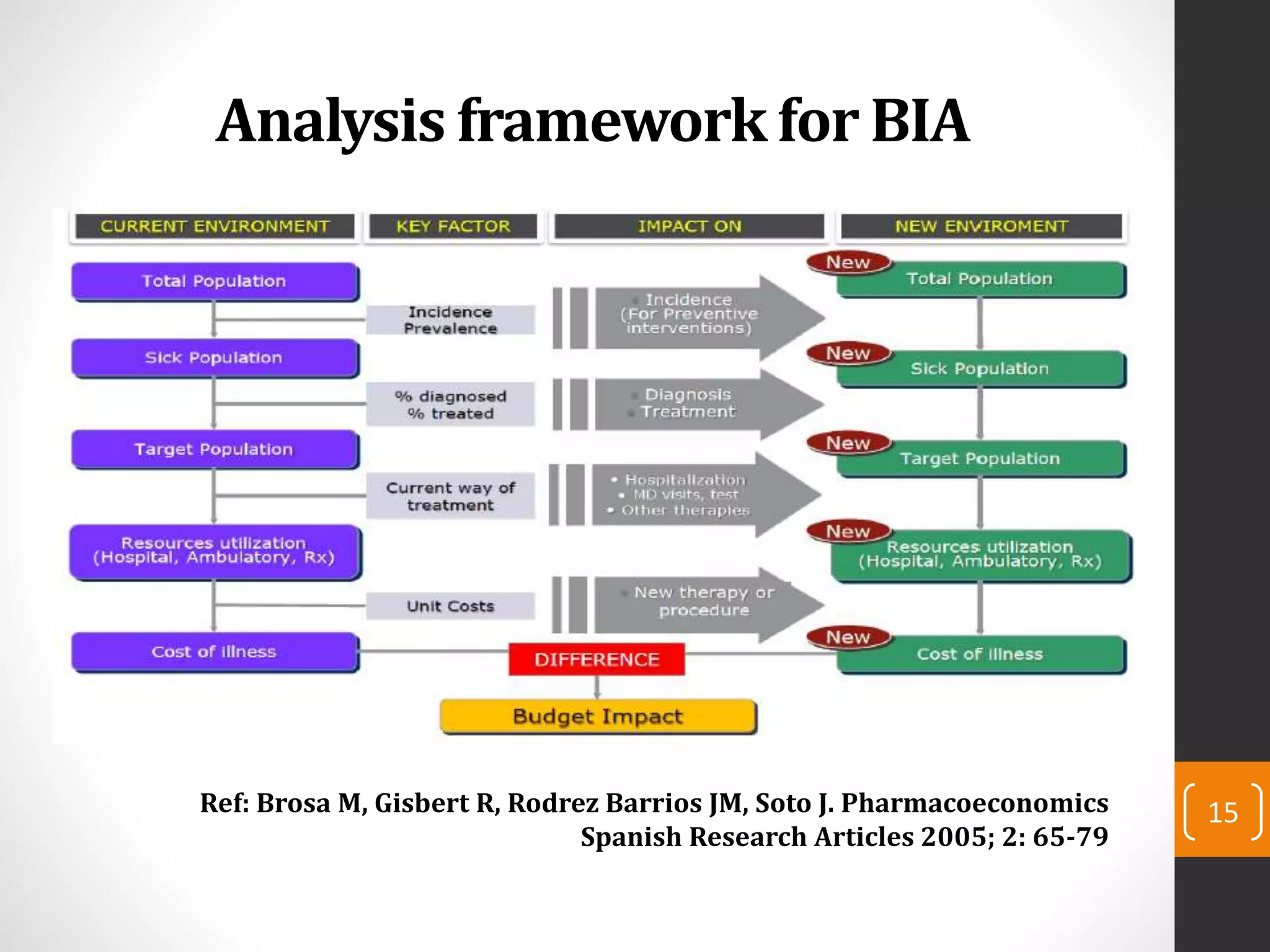
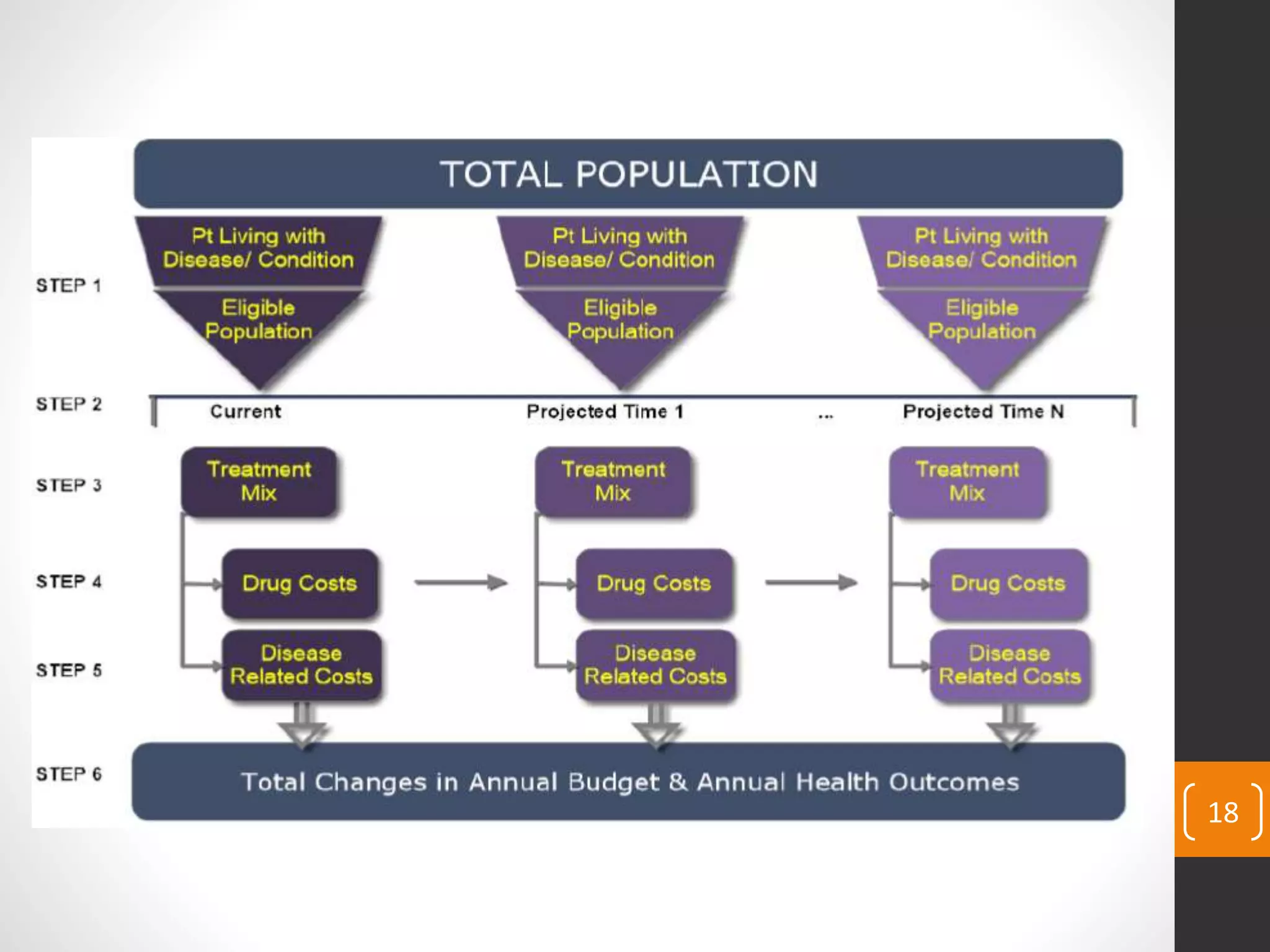
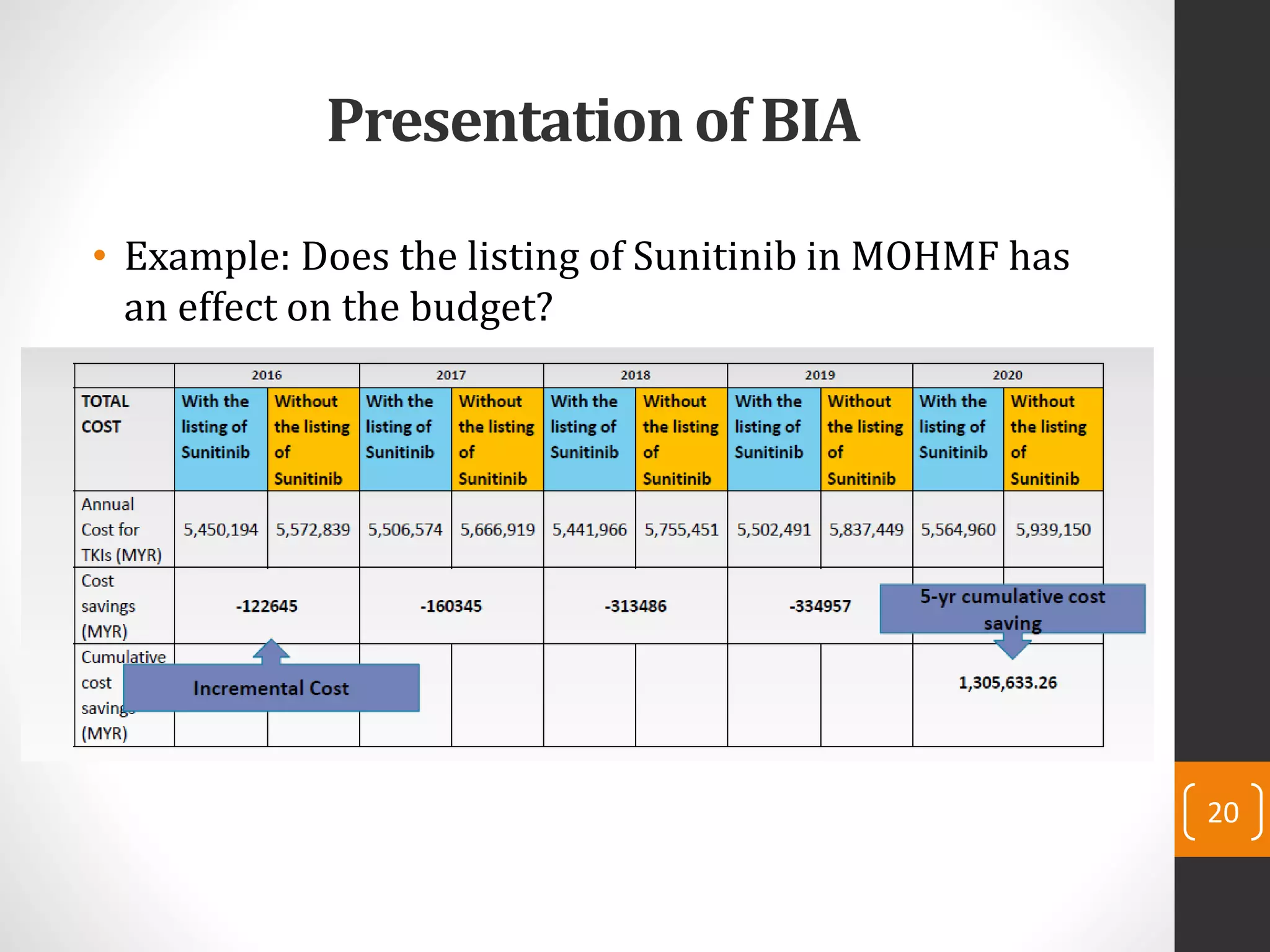
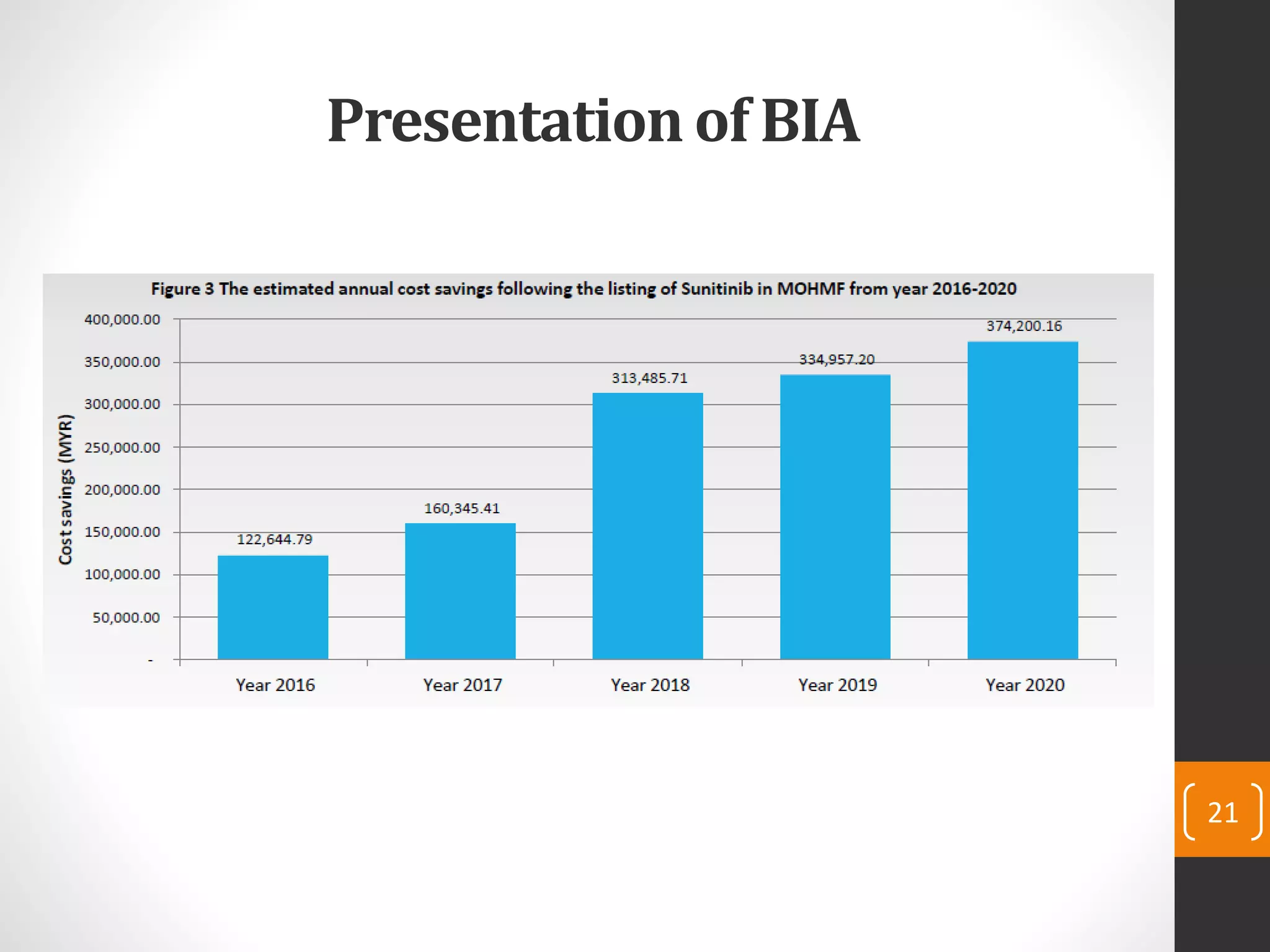
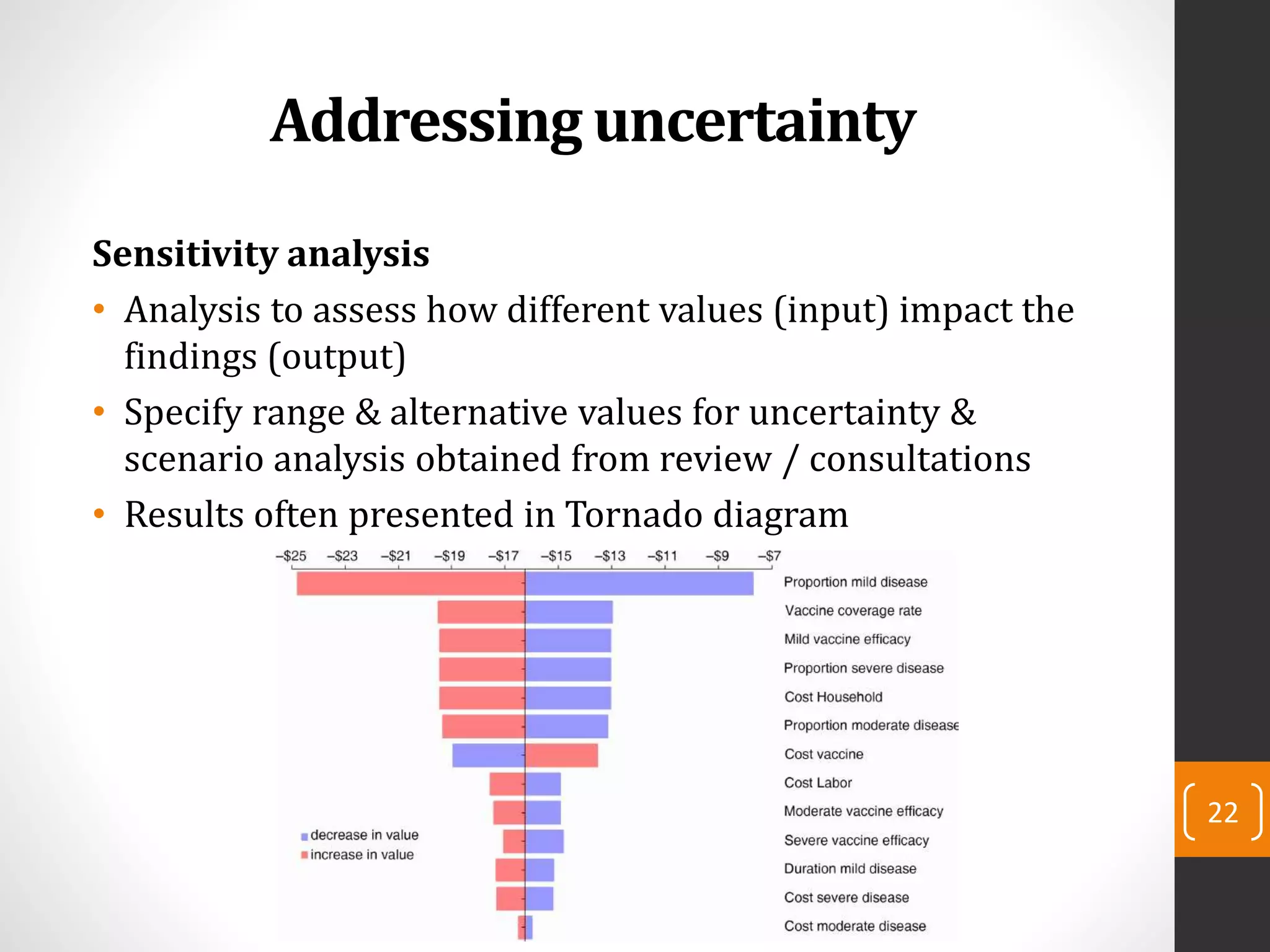
This document provides an introduction to budget impact analysis (BIA). It discusses that BIA is an economic assessment that estimates the financial consequences of adopting a new healthcare intervention. It notes that BIA is an essential part of comprehensive economic assessments along with cost-effectiveness analysis. The document outlines the key components of a BIA, including estimating the eligible patient population, time horizon, current and future treatment costs, and changes in disease-related costs. It also discusses presenting the changes in annual healthcare budget impact. The document compares BIA and economic evaluation, and provides considerations for BIA such as substitution, combination, and expansion effects of new interventions.