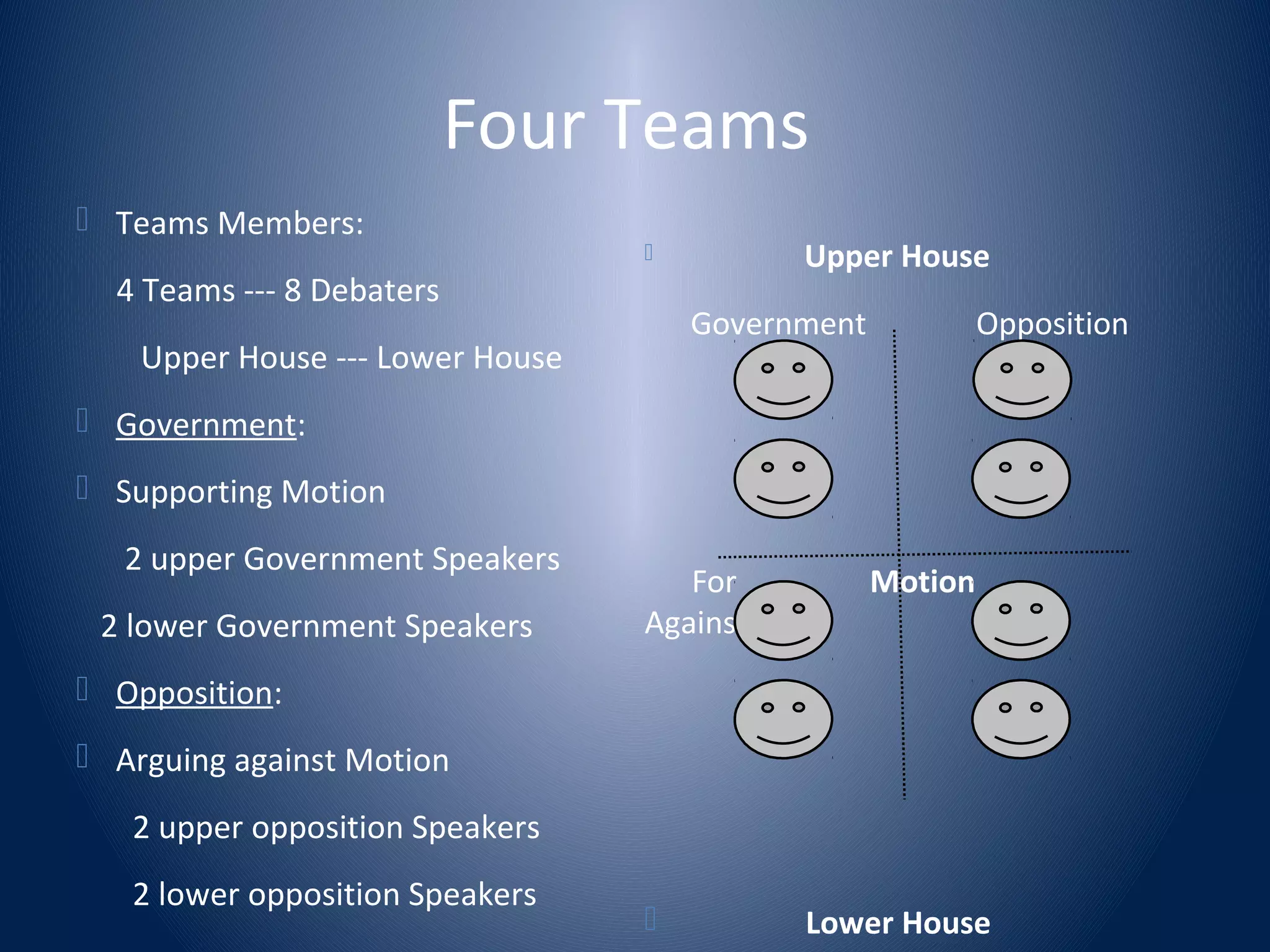
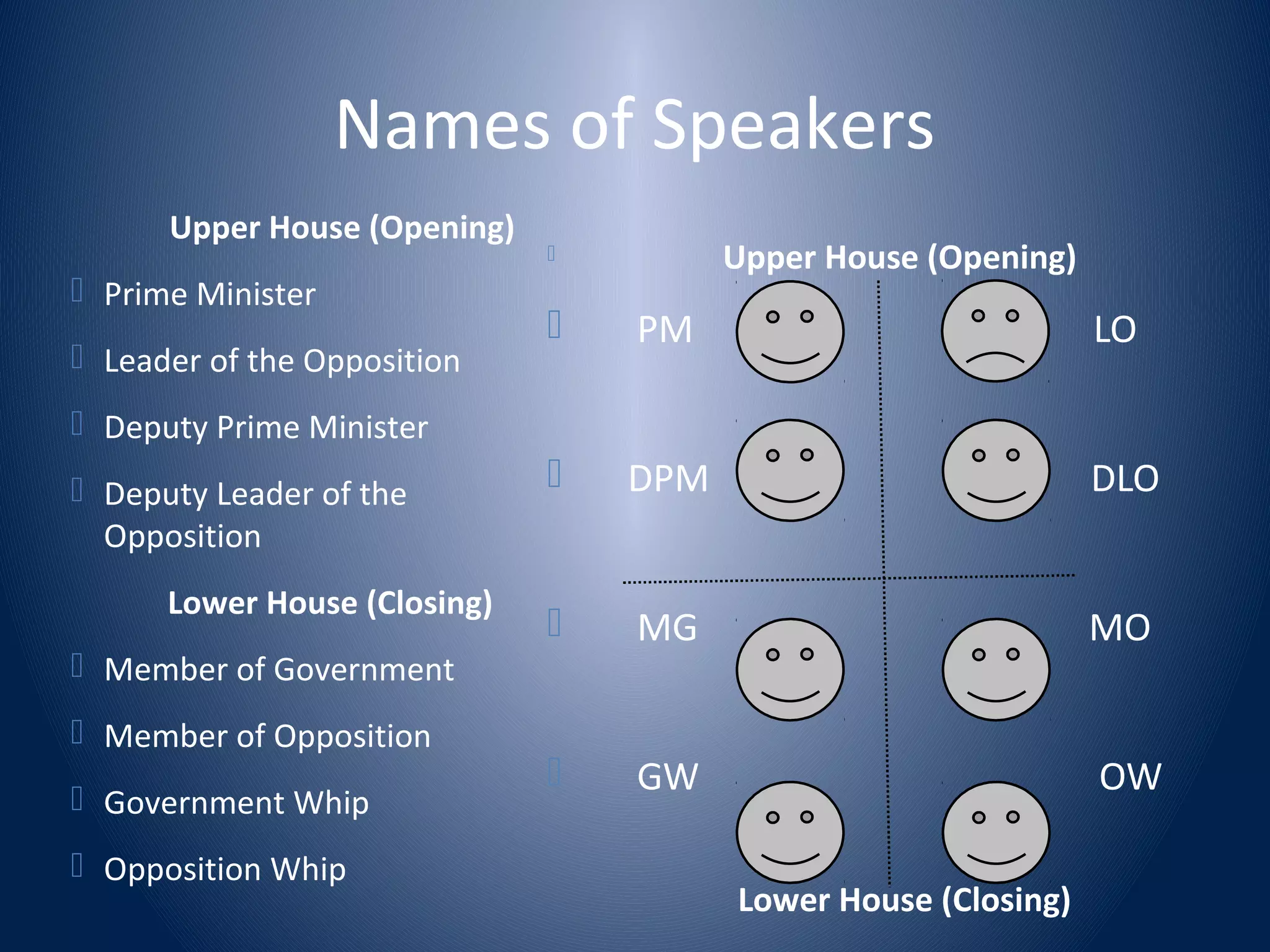
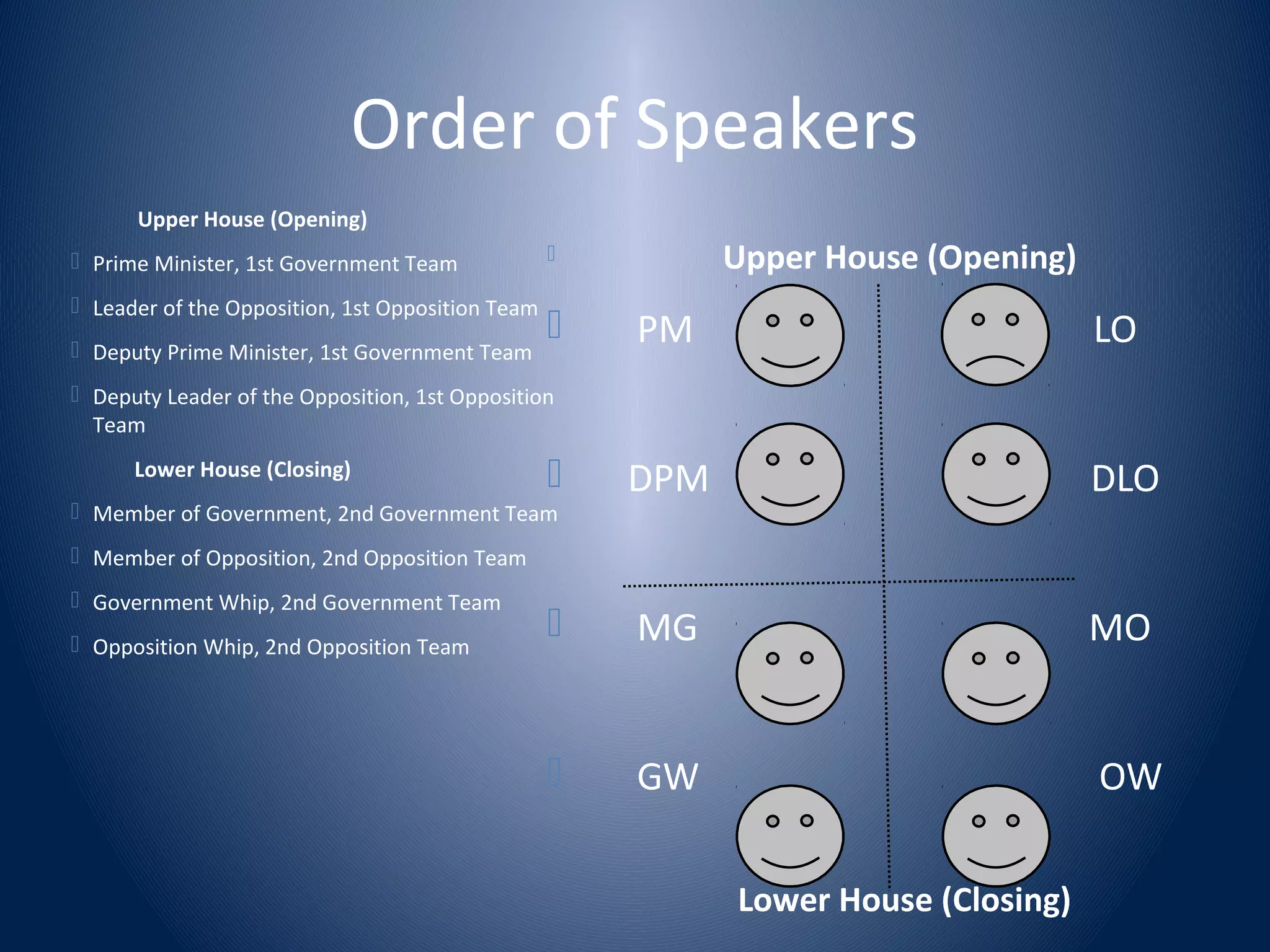
This document provides an introduction to the format of British parliamentary debate. It outlines the key components of a parliamentary debate, including the motions or topics that are debated, the order and roles of the eight speakers (prime minister, leader of opposition, etc.), and how debates are evaluated. The main points covered are: (1) Debates involve four teams of two debaters each who are assigned to support or oppose a motion. (2) Speakers present arguments in a set order, with specific roles like defining the motion or rebutting opponents. (3) Points of information can be offered to other speakers. (4) Debates are evaluated based on the strength of arguments rather than speaking ability.