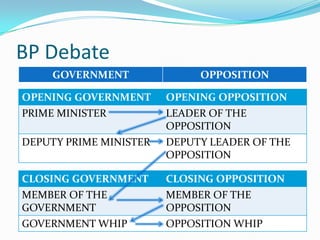
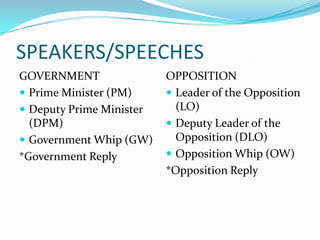
This document provides an overview of the benefits and process of debate. It discusses how debate can be academically beneficial, help prepare students for their careers, and aid in self-actualization. The document then gives examples of successful individuals who debated, including politicians and celebrities. It outlines the basic structure of a debate, including definitions, motions, types of debates, the two opposing sides, formats, and the roles and responsibilities of different speakers.