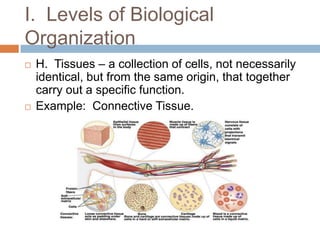
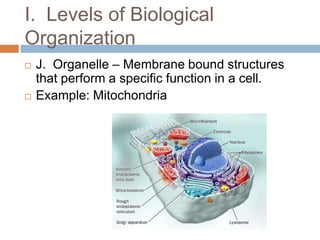
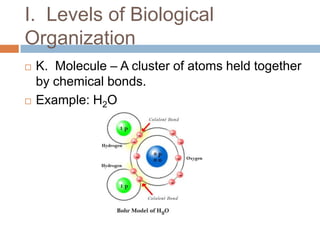
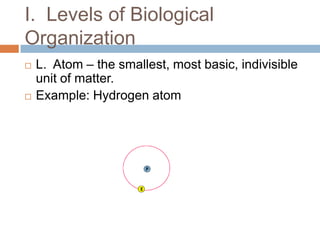
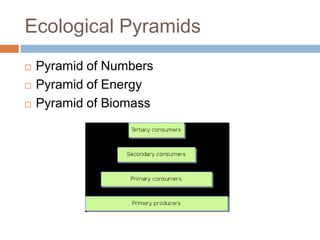
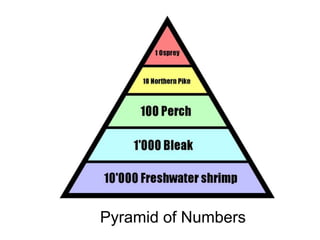
The document introduces the levels of biological organization from the broadest to the most specific. It discusses the biosphere, ecosystems, communities, populations, organisms, organ systems, organs, tissues, cells, organelles, molecules, and atoms. It also briefly introduces ecological pyramids including pyramids of numbers, energy, and biomass. Examples are provided for each level of organization.