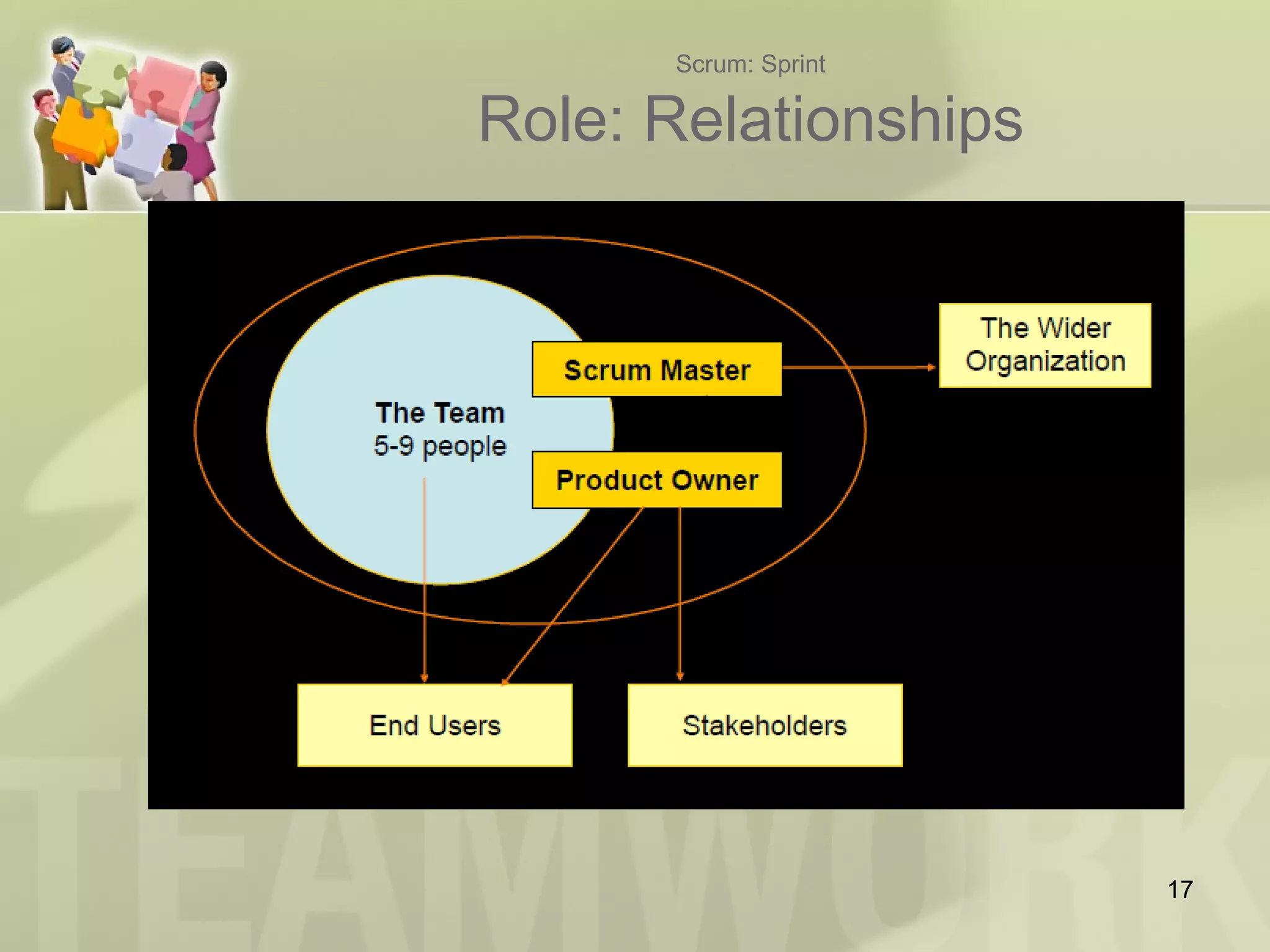
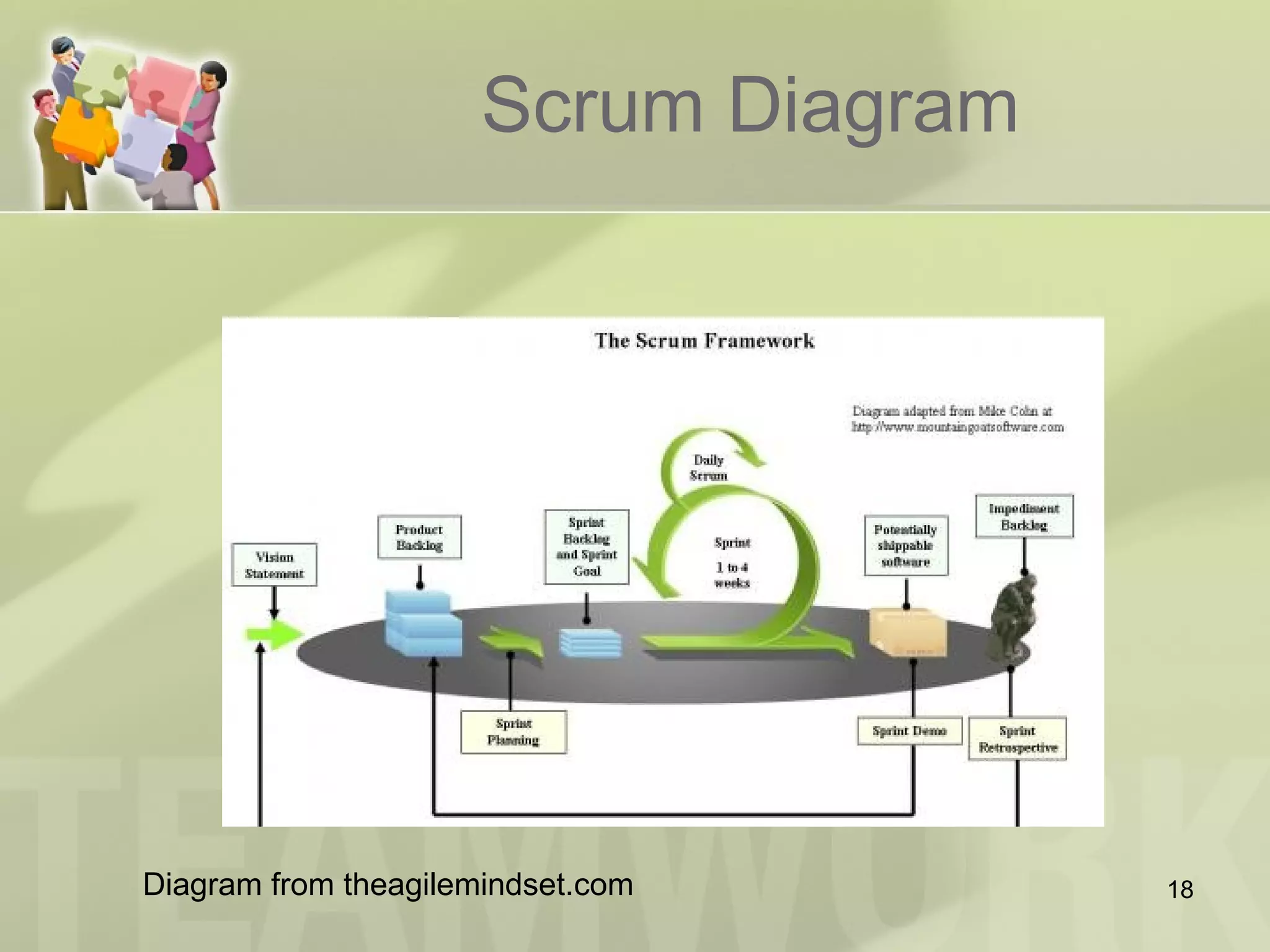
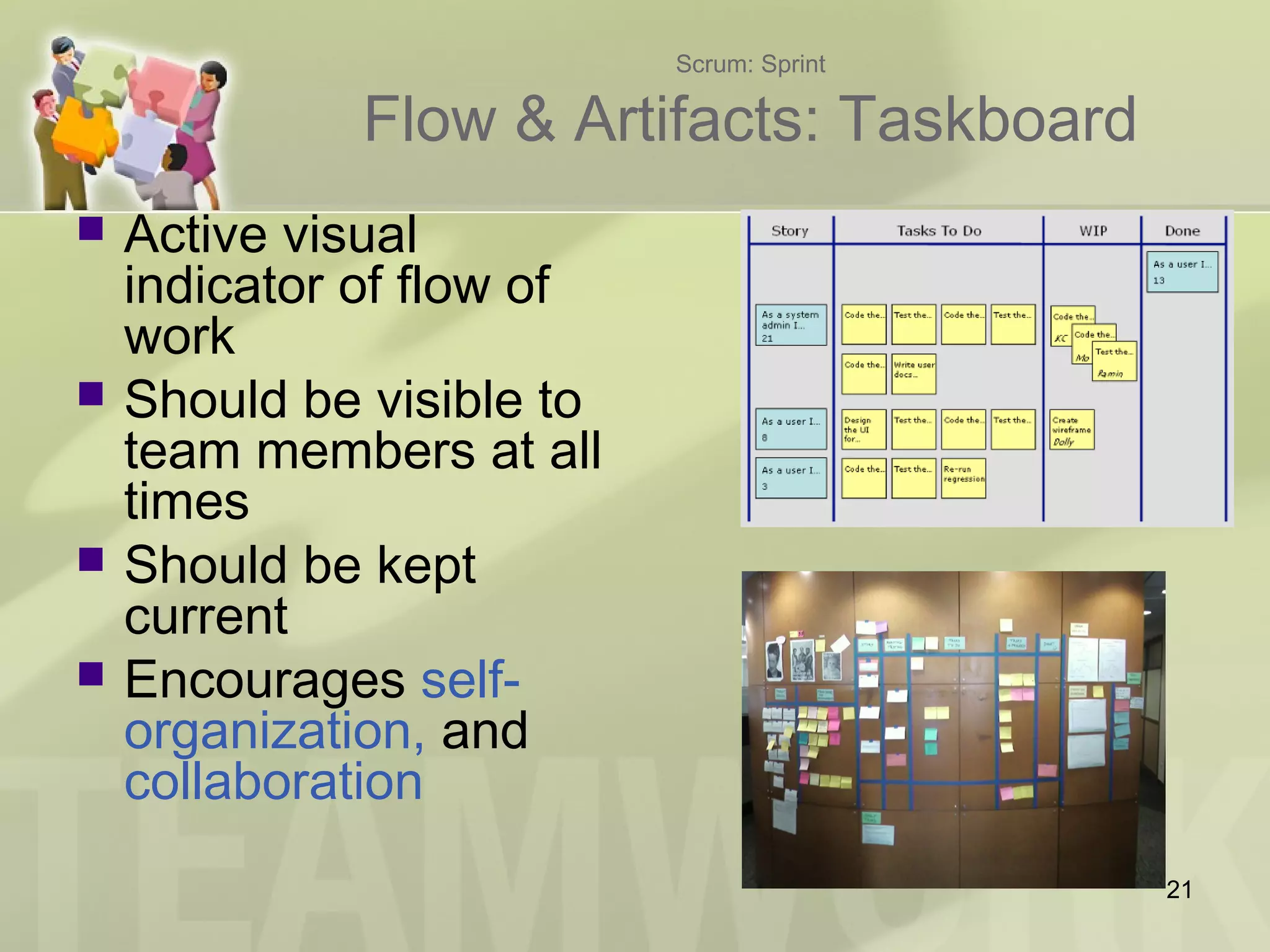
The document provides an introduction to Agile and Scrum, outlining core principles, the Scrum framework, and roles such as product owner and scrum master. It emphasizes the importance of collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement within teams to deliver quality software. Additionally, it addresses the benefits of Scrum for customers, leadership, and team members while encouraging experiential learning through practice.