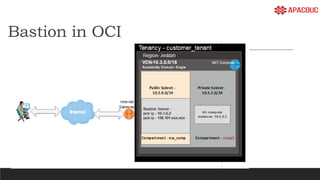
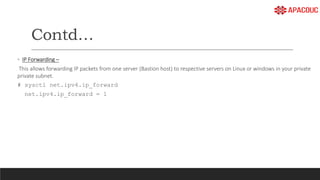
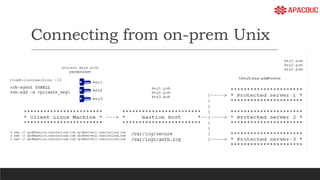
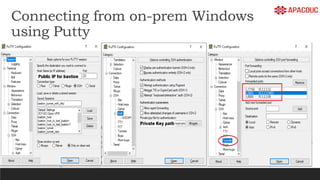
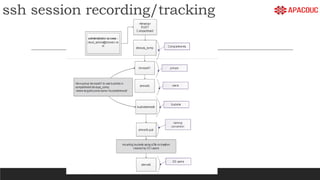
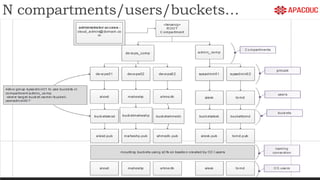
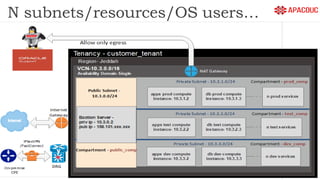
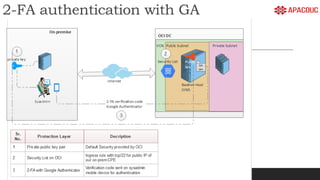
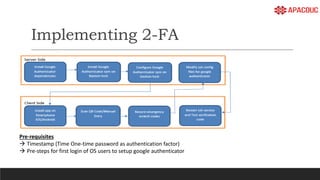
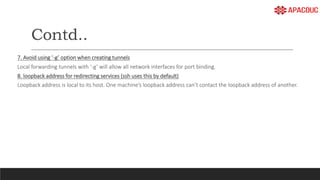
The document introduces bastion hosts in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, explaining their role in providing secure access control between public and private subnets. It outlines configuration methods, best practices for securing bastion hosts, and compares them with alternatives like OpenVPN. Key concepts including SSH tunneling, port forwarding, and strategies for user and log management are also discussed.