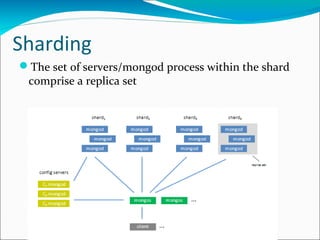
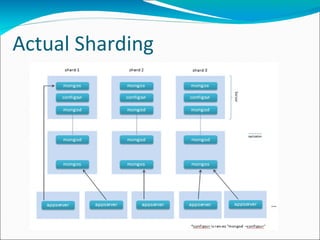
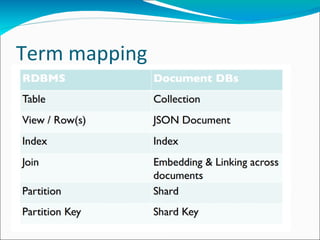
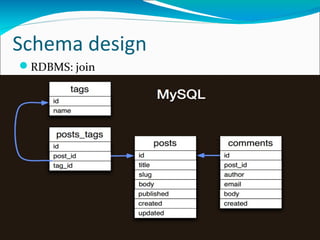
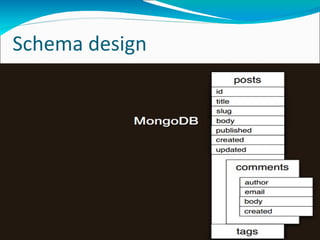
MongoDB is an open-source, document-oriented database designed for scalability and developer agility. It stores data in flexible JSON-like documents, rather than fixed schemas. MongoDB bridges the gap between traditional relational databases and key-value stores. Documents can easily be mapped to modern programming languages using BSON, a binary representation of JSON. Data is replicated across multiple servers for redundancy, automated failover, and read scaling. Sharding partitions data across machines for horizontal scaling. MapReduce provides a way to perform complex aggregations akin to SQL GROUP BY queries.






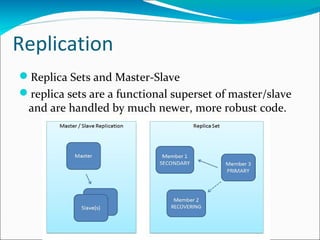


![Replica Sets experiment
bin/mongod --dbpath data/db --logpath
data/log/hengtian.log --logappend --rest --replSet
hengtian
rs.initiate({
_id : "hengtian",
members : [
{_id : 0, host : "lab3:27017"},
{_id : 1, host : "cms1:27017"},
{_id : 2, host : "cms2:27017"}
]
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtomongodb-140122001947-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-mongo-db-15-320.jpg)