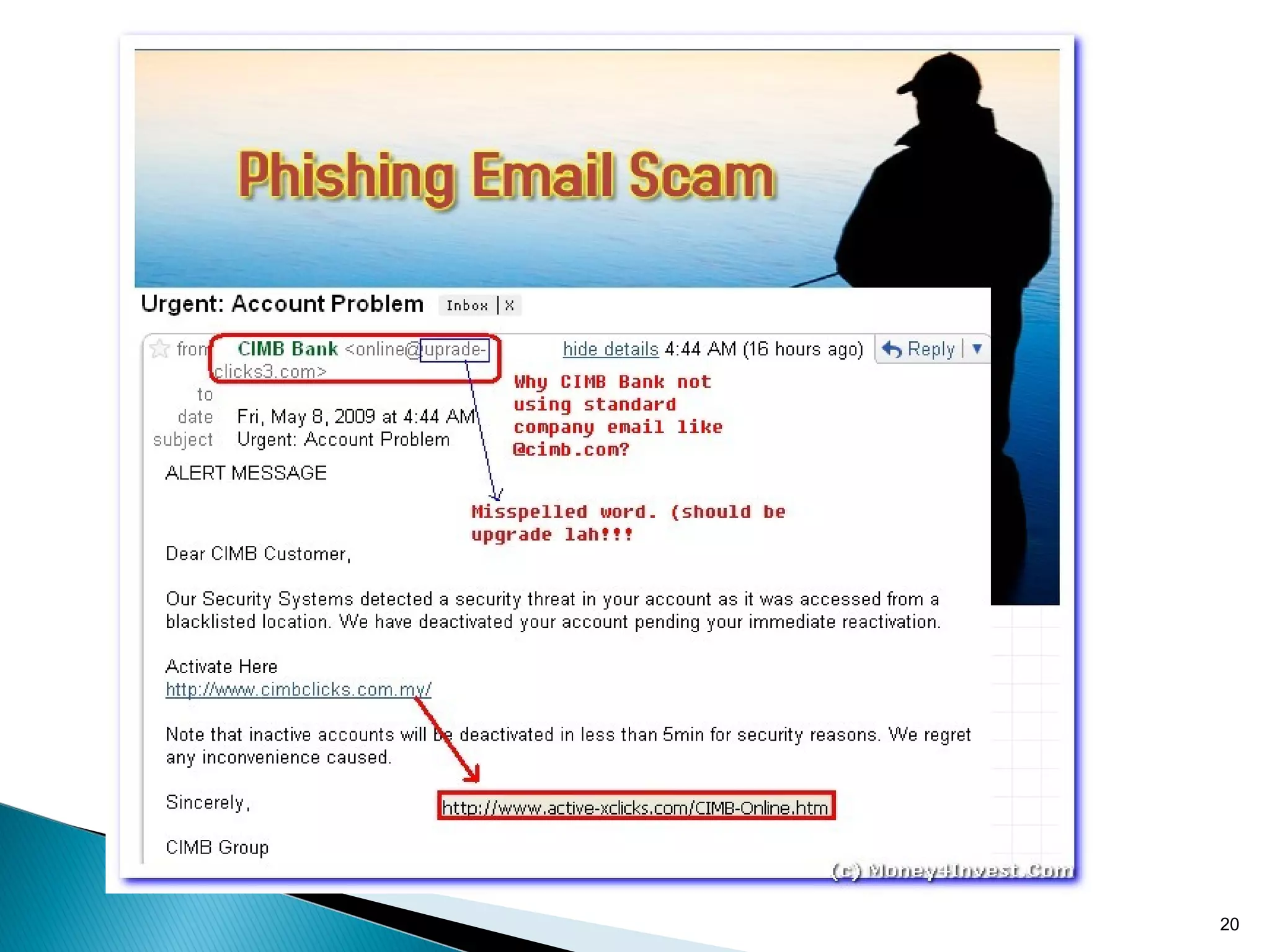
The seminar presented by Sayali Dayama aims to educate attendees about phishing scams, which are deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive personal information through fraudulent emails. It outlines the evolution of phishing tactics, including examples and statistics on the rise of phishing incidents, and emphasizes the need for vigilance and education to prevent falling victim to such attacks. Furthermore, it provides practical tips for recognizing and avoiding phishing scams, as well as a comparative analysis of security algorithms for detecting such threats.