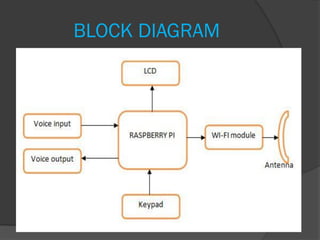
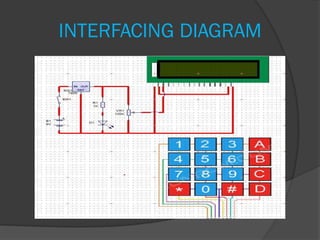
This document describes a project to develop a voice communication system over Wi-Fi networks using Raspberry Pi. The objectives were to create a Python application for full duplex voice calls between devices on the same Wi-Fi and build a mobile terminal with an LCD display and keypad. The system samples voice input, transmits over Wi-Fi, and supports future extensions. It was implemented using Raspberry Pi for processing and a Wi-Fi dongle for network access.















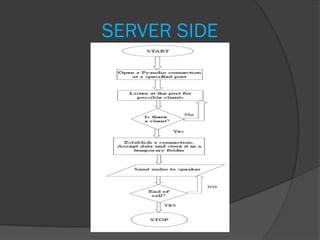
![SERVER SIDE
CHUNK = 1024
FORMAT = pyaudio.paInt16
CHANNELS = 1
RATE = 44100
RECORD_SECONDS = 10
WIDTH = 2
frames = []
HOST = '' # Symbolic name meaning
all available interfaces
PORT = 50010 # Arbitrary non-privileged
port](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/441f6c40-8bcb-41d5-bcd7-58a21dd7b661-160203164139/85/Intra-Institutional-Communication-System-21-320.jpg)


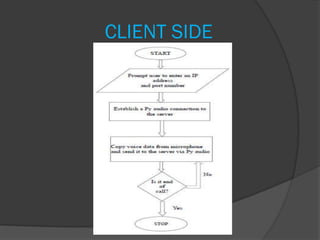

![s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect((HOST, PORT))
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(format=FORMAT,
channels=CHANNELS,
rate=RATE,
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
print("*recording")
frames = []
for i in range(0, int(RATE/CHUNK*RECORD_SECONDS)):
data = stream.read(CHUNK)
frames.append(data)
s.sendall(data)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/441f6c40-8bcb-41d5-bcd7-58a21dd7b661-160203164139/85/Intra-Institutional-Communication-System-26-320.jpg)







