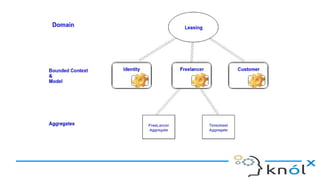
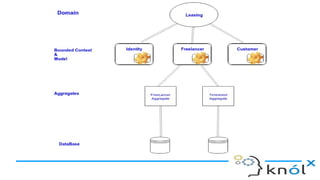
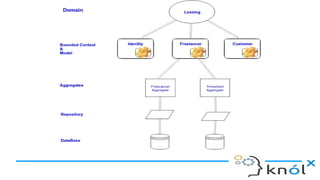
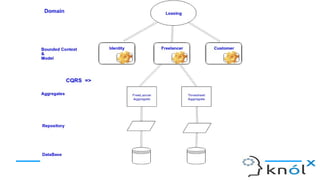
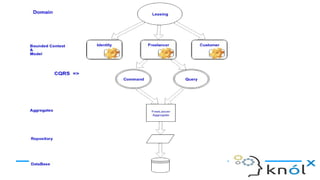
The document outlines key concepts of Domain-Driven Design (DDD), a methodology for developing software that aligns closely with business requirements, focusing on core domains and their identification. It details various components such as models, bounded contexts, aggregates, domain events, and the separation of command and query responsibilities (CQRS). Additionally, it introduces best practices for implementing domain-specific languages (DSL) and emphasizes the use of a ubiquitous language for improved communication in software projects.