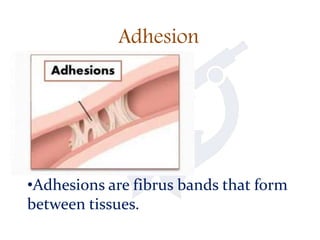
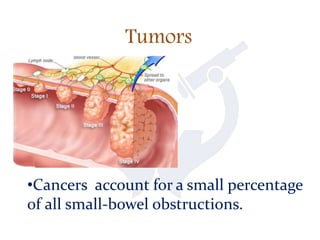
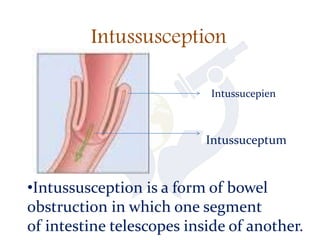
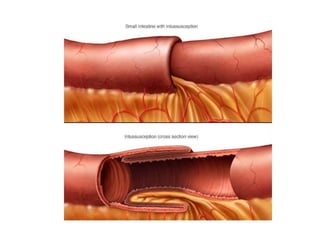
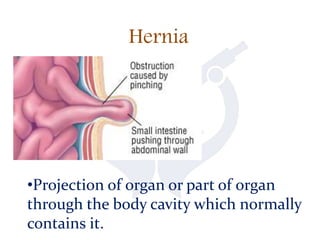
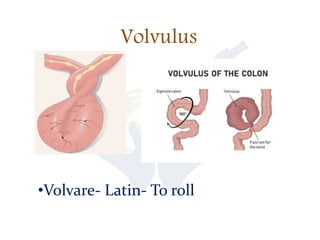
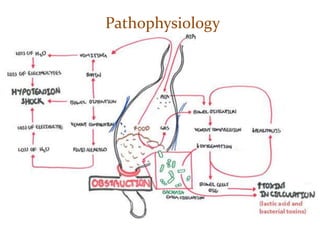
This document discusses intestinal obstruction, which is a blockage of the intestine that impairs or arrests the passage of contents. There are two main types - small bowel and large bowel obstruction. Obstructions can be partial or complete. Mechanical obstructions are caused by factors like adhesions, tumors, intussusception, hernias or volvulus twisting of the intestine. Pseudo-obstructions involve obstruction without a demonstrable blockage. Risk factors include birth defects, pregnancy, adhesions or middle age. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and distension. Without treatment, complications like ischemia, perforation or sepsis can occur.